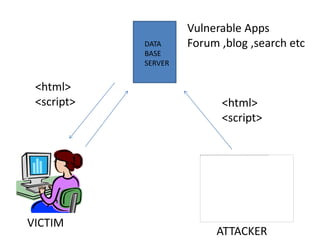
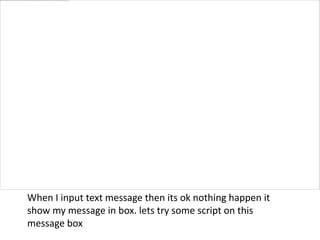
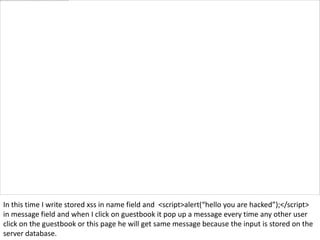
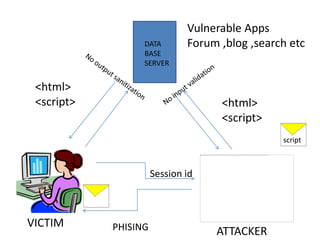
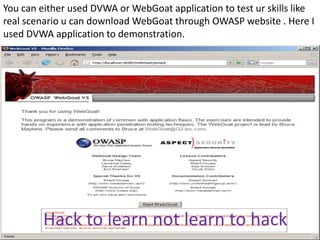
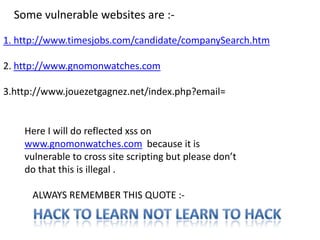
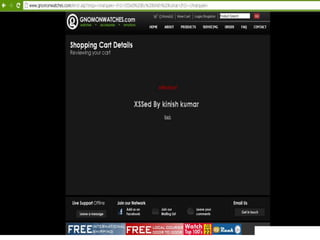
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) is a type of vulnerability that allows attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users. There are three main types: persistent XSS saves the attack script on the server; reflected XSS executes a script based on user-supplied input; and DOM-based XSS occurs when active browser content processes untrusted user input. Attackers use XSS to steal session cookies or other private information that can be used to impersonate users.