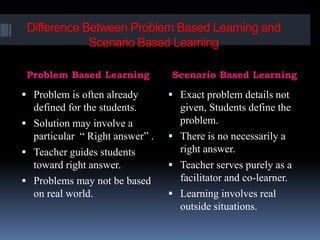
Scenario-based learning (SBL) engages students in interactive scenarios that enhance active learning through problem-solving and critical thinking in real-world contexts. It is effective for simulating real-world practice and is best utilized for tasks requiring decision-making in complex situations. The role of the teacher shifts to a facilitator, guiding students to learn through their decisions and experiences rather than providing direct instruction.