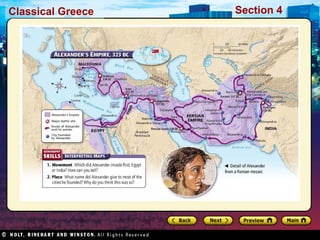
Alexander the Great conquered a vast empire and spread Greek culture throughout Egypt and Asia. After his death, his empire broke apart as his generals fought for power, dividing it among themselves. This created the Hellenistic world, where Greek culture blended with local traditions. Society changed as women gained more rights and monarchy replaced democracy. The exchange of ideas led to advances in philosophy, science, technology, art and literature. Hellenistic scholars made discoveries in geometry, astronomy, mechanics and anatomy.