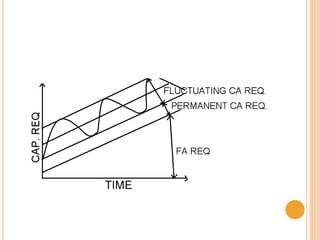
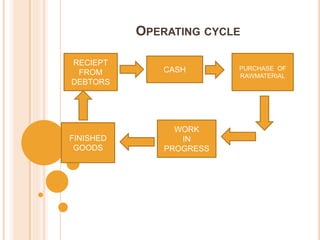
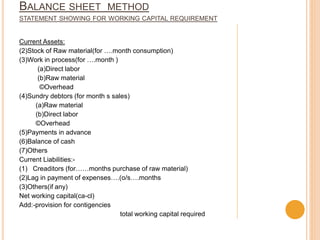
This document discusses working capital management and provides definitions and concepts related to working capital. It defines working capital as the amount of cash used to run day-to-day business operations. There are two concepts of working capital: gross working capital, which refers to total current assets, and net working capital, which is current assets minus current liabilities. Current assets that are considered include cash, debtors, inventory, and more. Current liabilities include bills payable, creditors, loans, and other short-term obligations. The document also discusses the importance of working capital, types of working capital, factors that influence working capital needs, and methods for estimating working capital requirements including the operating cycle method and balance sheet method.