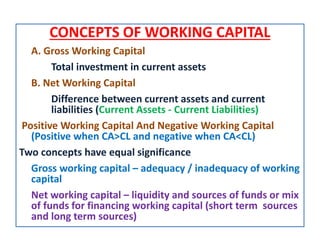
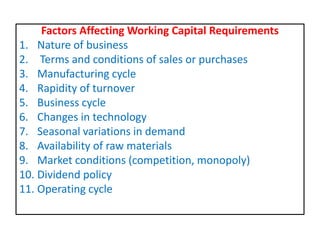
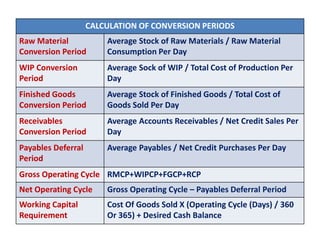
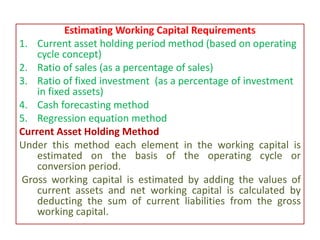
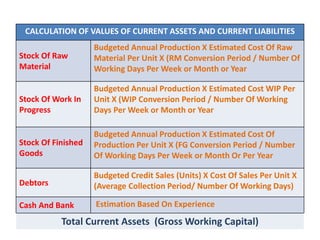
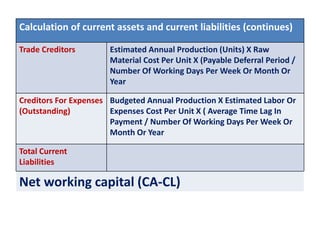
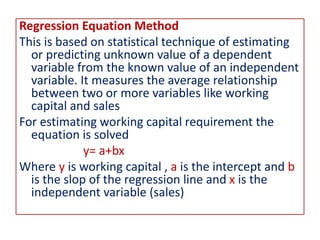
This document discusses concepts and management of working capital. It defines key terms like gross working capital, net working capital, fixed working capital and variable working capital. It also outlines factors that affect working capital requirements and methods for estimating working capital needs like the operating cycle method and regression equation method. The document concludes by discussing policies for financing current assets through long term, short term and spontaneous sources.