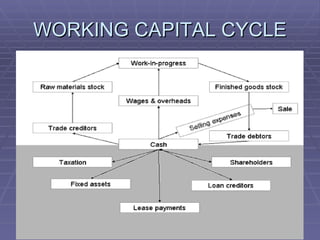
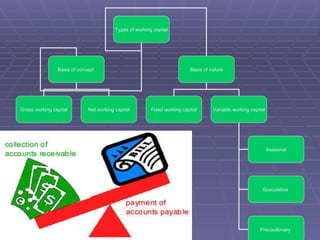
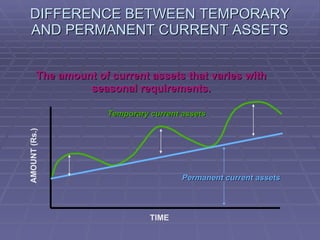
Working capital refers to the capital required to finance short-term operating expenses such as raw materials, wages, and other day-to-day expenses. It is needed to purchase inventory, pay employees, and cover other daily costs. Determining the appropriate level of working capital requires considering factors like the nature of the business, size, production processes, cash needs, and seasonality. There are various methods for estimating working capital, and having the right amount provides benefits like maintaining goodwill and securing favorable loan terms, while too little or too much can lead to inefficiency.