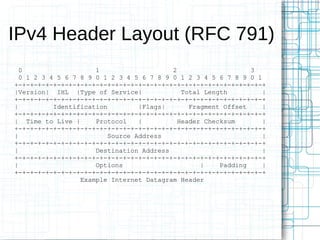
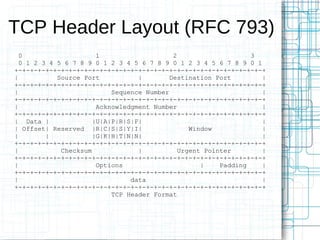
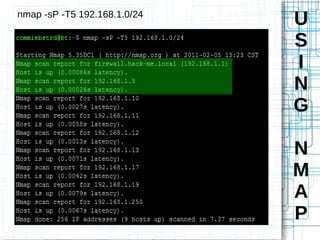
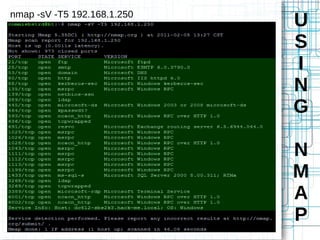
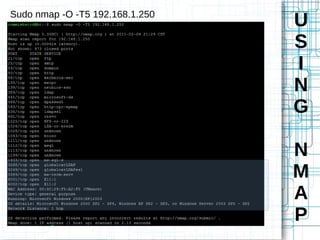
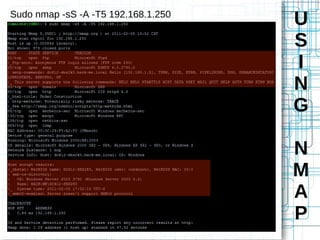
Nmap is an open source tool that scans networks to identify devices, services, and operating systems. It works by crafting custom IP packets with different flags using raw sockets to elicit responses that provide information not otherwise available. Nmap can perform various types of scans, identify hosts and services, detect firewalls and IDS, and determine operating systems through detailed analysis of responses. It provides flexible output options and techniques for advanced scanning, packet alteration, and timing control.


![Scan Types
-sS – TCP SYN
-sT – TCP Connect
-sA – TCP ACK
-sW – TCP Window
-sM – TCP Maimon
-sU – UDP Scan
-sN – TCP Null (No Flags)
-sF – TCP FIN (Just FIN Flag)
-sX – TCP Xmas (All Flags)
-sY – SCTP INIT
-sZ – SCTP COOKIE-ECHO
-sO – IP protocol scan
-b <FTP relay host> - FTP bounce scan
--scanflags <flags> - Customize TCP flags
-sI <zombie host[:probeport]> - Idle scan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scanningwithnmap-120706105950-phpapp01/85/Scanning-with-nmap-6-320.jpg)
![Output Options
Output Types
-oN <file> – Normal
-oX <file> – XML
-oS <file> – s|<rIpt kIddi3
-oG <file> - Grepable
-oA <file> - 3 Major Formats
Output Options
-v: Increase verbosity level (use twice or more for greater effect)
-d[level]: Set or increase debugging level (Up to 9 is meaningful)
--reason: Display the reason a port is in a particular state
--open: Only show open (or possibly open) ports
--packet-trace: Show all packets sent and received
--iflist: Print host interfaces and routes (for debugging)
--log-errors: Log errors/warnings to the normal-format output file
--append-output: Append to rather than clobber specified output files
--resume <filename>: Resume an aborted scan
--stylesheet <path/URL>: XSL stylesheet to transform XML output to HTML
--webxml: Reference stylesheet from Nmap.Org for more portable XML
--no-stylesheet: Prevent associating of XSL stylesheet w/XML output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scanningwithnmap-120706105950-phpapp01/85/Scanning-with-nmap-7-320.jpg)

![Packet Alteration D
-f – Fragment packets (-f = 8 bytes -f -f = 16 bytes)
--mtu – Set maximum MTU size (Do not use with -f)
E
-D <decoy1>[, <decoy2>] - Include decoys in scan F
-S <IP> - Spoof source IP
-g <portnumber> - Specify source port
E
--data-length <number> - Append an amount of data A
--ip-options - Specify IP layer options
--ttl – Set time to live
T
--randomize-hosts – Allow nmap to select random targets I
--spoof-mac – Specify a mac address, vendor or random
--badsum – Force an invalid checksum
N
G
Timing Commands
--scan-delay <time> - Sets a minimum wait between probes
--max-scan-delay <time> - Sets max delay between probes I
--min-rate --max-rate – Sets min and max packet per sec
-T <0-5> - Set generic scan speeds
D
S](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scanningwithnmap-120706105950-phpapp01/85/Scanning-with-nmap-13-320.jpg)
