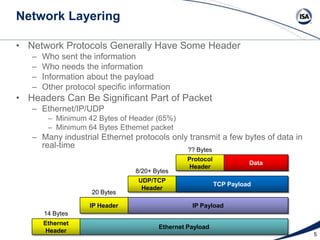
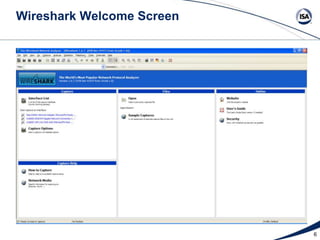
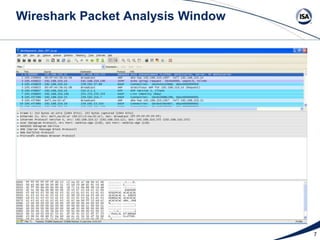
This document discusses the network packet analysis tool Wireshark. It begins with an introduction to Jim Gilsinn and his background in cybersecurity and industrial control systems. It then provides an overview of Wireshark, describing it as an open-source, multi-platform network protocol analyzer that allows users to capture, interactively browse, and decode network traffic. Key features of Wireshark like its large protocol support and graphical interface are highlighted. The document concludes by discussing advanced analysis features, developing custom protocol decoders, and providing resources for more information on Wireshark.