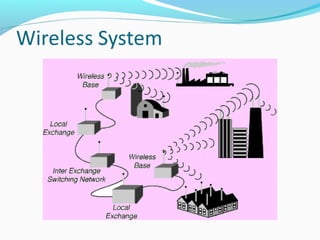
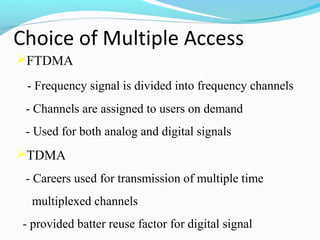
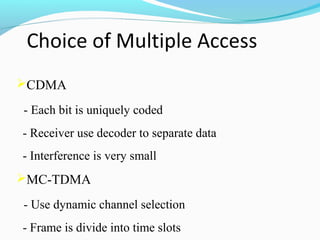
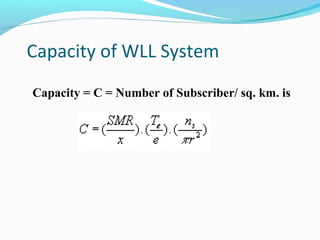
This document defines and compares wireless local loop (WLL) networks to mobile systems. WLL uses wireless links to connect subscribers to local exchanges instead of copper cables, shortening construction periods and reducing costs. It is designed to serve subscribers at home or work with high voice quality and traffic support, unlike mobile systems meant for those on the move. The efficiency of WLL depends on factors like channel payload, signaling overhead, modulation, cell radius, and interference reduction techniques. Future technologies discussed include smart antennas, turbo codes, and multi-user detection to improve WLL network capacity.