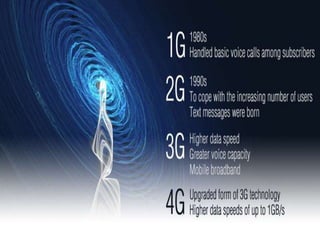
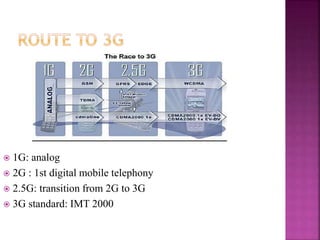
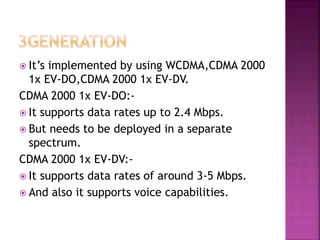
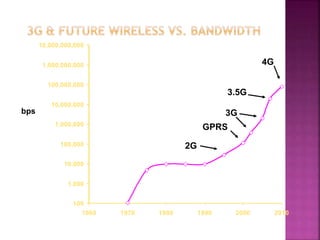
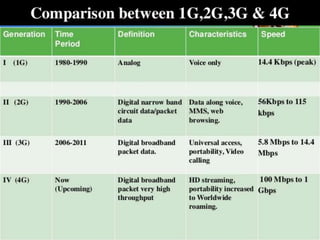
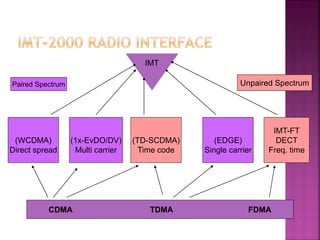
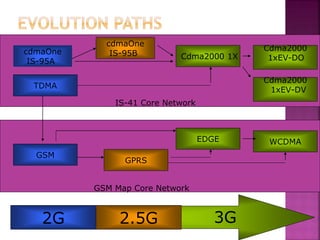
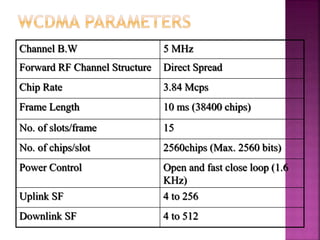
3G technologies provide improved digital voice and higher bandwidth data services over 2G. The key 3G standards are WCDMA, CDMA2000, and TD-SCDMA. WCDMA addresses issues like handover and power control. 4G will offer even higher data rates and bandwidth below 5GHz, along with lower costs per bit than 3G.