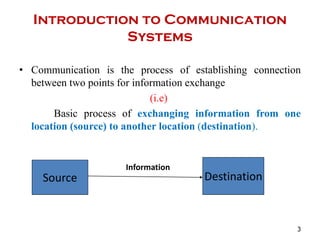
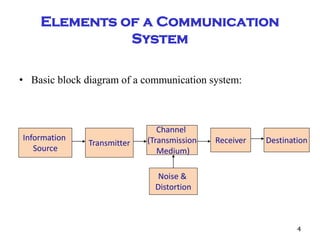
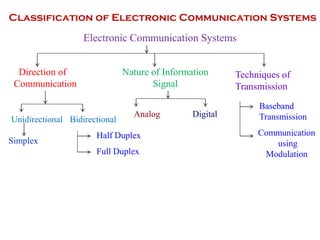
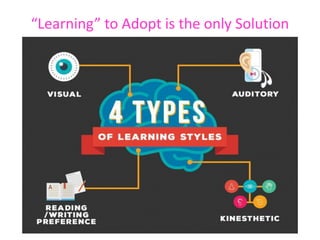
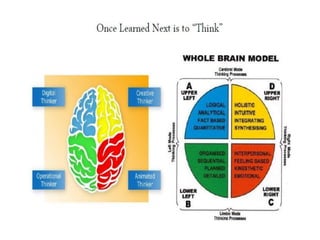
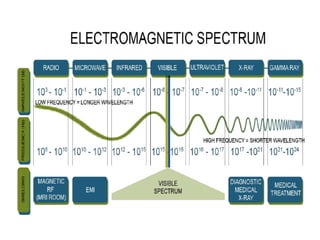
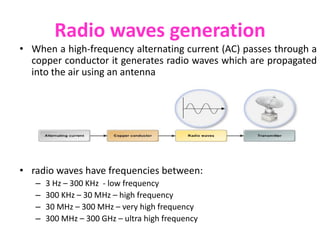
The document discusses cognitive radios and wireless communication. It begins with defining communication as the exchange of information between two points. It then outlines the basic elements of a communication system including an information source, transmitter, channel, noise/distortion, and receiver. Wireless communication provides mobility but is influenced by obstructions and interference. The radio spectrum is divided into licensed and unlicensed frequencies, with the licensed spectrum exclusively for designated users and the unlicensed spectrum freely accessible by any user within certain rules. Cognitive radios can "learn" to adopt to different frequencies to avoid interference and optimize communication in the radio environment.