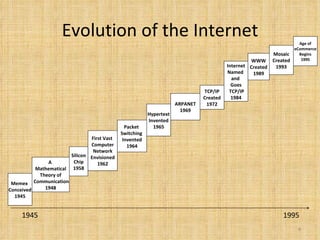
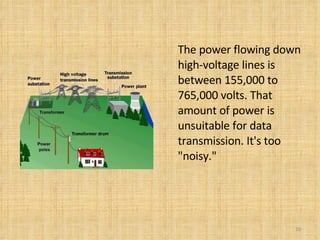
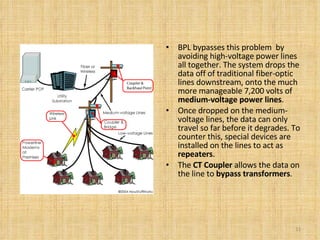
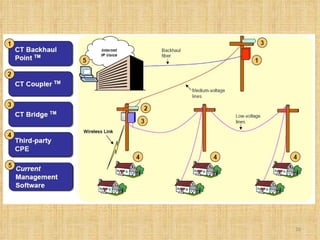
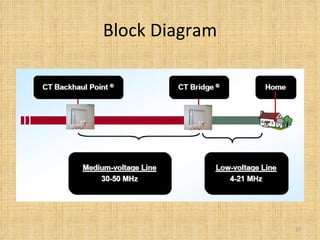
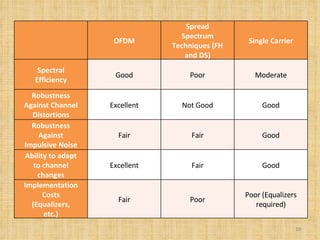
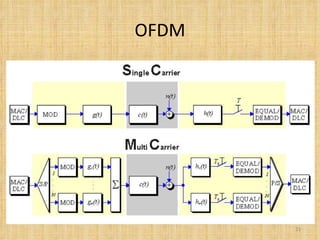
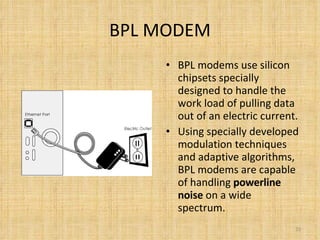
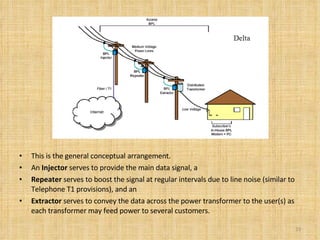
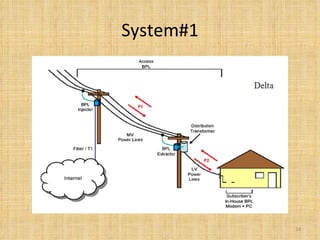
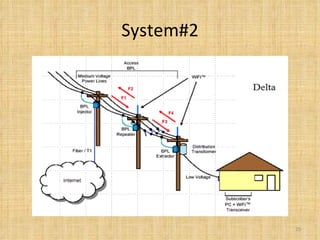
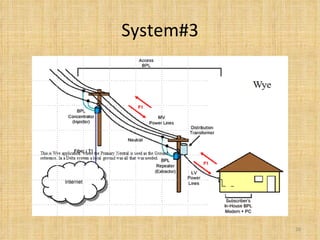
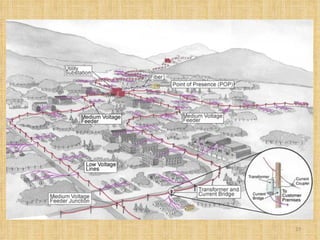
Broadband Over Power Lines (BPL) allows internet data to be transmitted over existing power lines, providing broadband access without requiring phone, cable, or satellite connections. BPL works by modulating radio waves with internet data signals and transmitting them onto medium-voltage power lines using technologies like OFDM to overcome noise. Special devices called injectors, repeaters, and extractors are used to introduce the signals, boost them at intervals, and deliver them to users through power transformers.