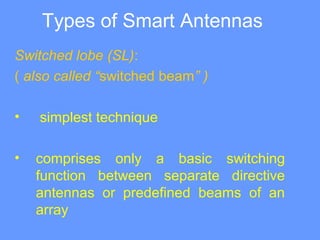
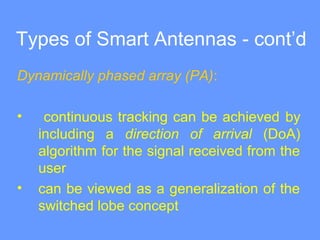
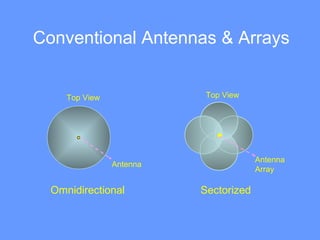
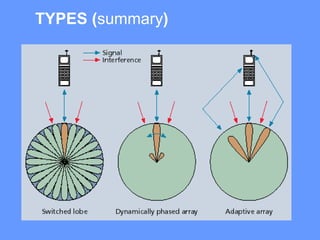
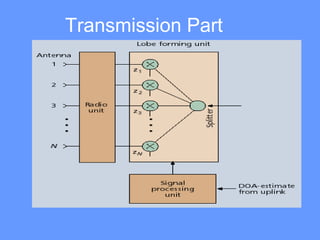
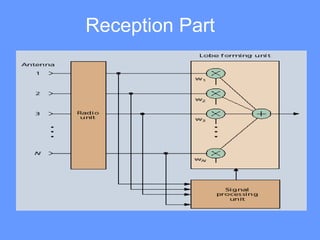
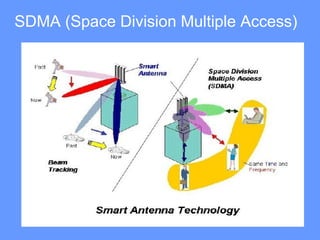
Smart antenna arrays use digital signal processing to transmit and receive signals in an adaptive, spatially sensitive manner. They have applications in cellular networks, radar, satellite systems, and electronic warfare for counteracting jamming. Key benefits include higher capacity, coverage, bit rates, link quality and spectral efficiency. Smart antennas contain radiating elements, a combining network, and a control unit to maximize gain towards desired signals and minimize it for interferers. Two main types are switched beam antennas, which switch between predefined beams, and dynamically phased arrays, which continuously track signals using direction of arrival algorithms. Smart antennas allow for space division multiple access by separating multiple users on the same channel based on angle. They provide improved interference rejection compared to conventional or