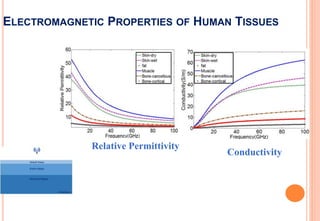
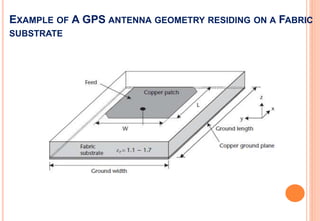
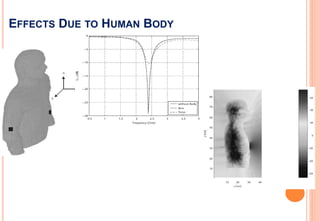
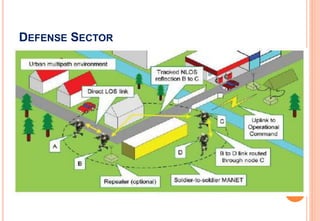
This document discusses wireless body area networks (WBANs) and some of the key considerations for their design and implementation. WBANs allow for communication between devices worn on or implanted in the human body. Key application areas include healthcare, fitness/sports, defense, and entertainment. Moving communications to higher millimeter wave frequencies offers advantages like increased data rates and security, but introduces challenges from atmospheric absorption and varying channel characteristics based on the human body. Ongoing research seeks to better characterize the on-body communication channel and develop optimized antennas and sensor network designs for WBANs.





![4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
2014 2015 2016 2017 2018
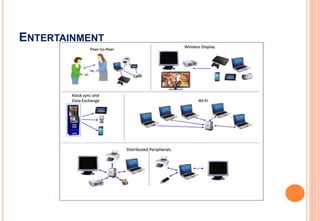
Consumer applications
Health-care applications
Industrial applications
Other applications
Projected growth of revenue for wearable systems in different applications from 2014 to 2018
(Recreated from [1])
PROJECTED GROWTH IN WEARABLE INDUSTRY
“Wearable Electronics and Technology Market by Applications-2020”. [Online]. Available: http://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/wearable-
electronics-market-983.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ulabwbanupdated-150805144545-lva1-app6891/85/Wireless-Body-Area-Networks-8-320.jpg)




![MOVING TO V-BAND FREQUENCIES FOR ON-BODY
COMMUNICATIONS
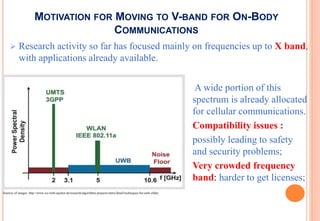
One possible solution would be to move to higher frequency bands : FCC has
opened an unlicensed frequency band around 60GHz and many countries are
using it.
Given the smaller wavelength and the higher free space attenuations at such
frequencies, it is easier to confine the signal around the human body.
Country
Frequency Band
[GHz]
USA 57.05-64
Canada 57-64
Europe 57-64
Japan 59-66
Australia 59.4-62
Korea 57-64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ulabwbanupdated-150805144545-lva1-app6891/85/Wireless-Body-Area-Networks-14-320.jpg)