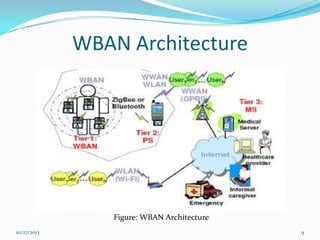
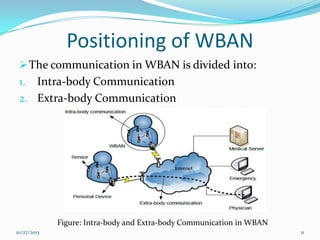
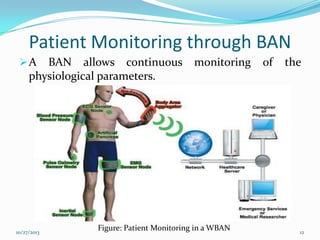
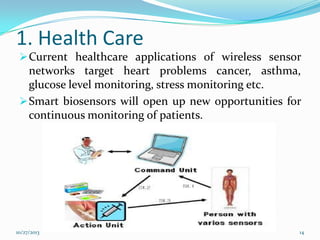
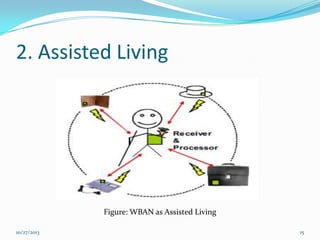
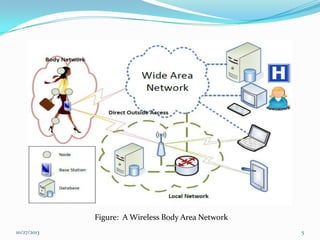
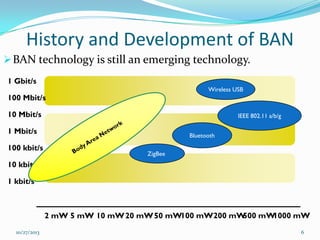
The document discusses Wireless Body Area Networks (WBANs). It defines WBANs and outlines their history and development. The key aspects covered include WBAN architecture, applications for healthcare, assisted living and entertainment, challenges and future scope. WBANs have the potential to revolutionize healthcare through continuous patient monitoring and early disease detection using small wearable sensors.





![Contd…
Implementation module cost
Should be comparable to Bluetooth module
Effective sleep mode(s)
Operates in global, license-exempt band
Peer to peer communication, point to multi-point
Omni-directional antennas: small, flexible
Future proof [for 5 years?]
Upgradeable, saleable, backwards compatibility
10/27/2013
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ban-131027064831-phpapp01/85/Body-Area-Network-8-320.jpg)