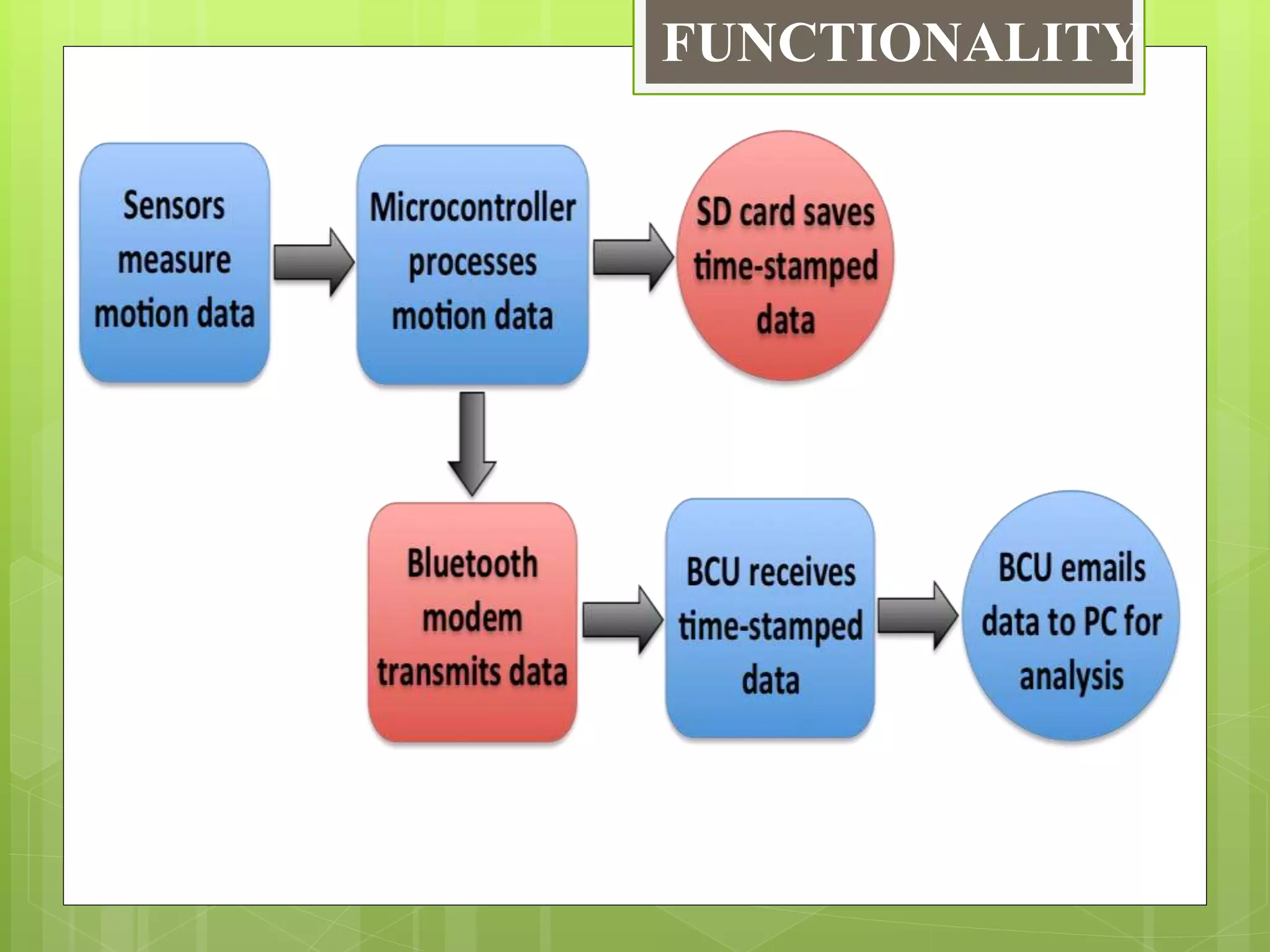
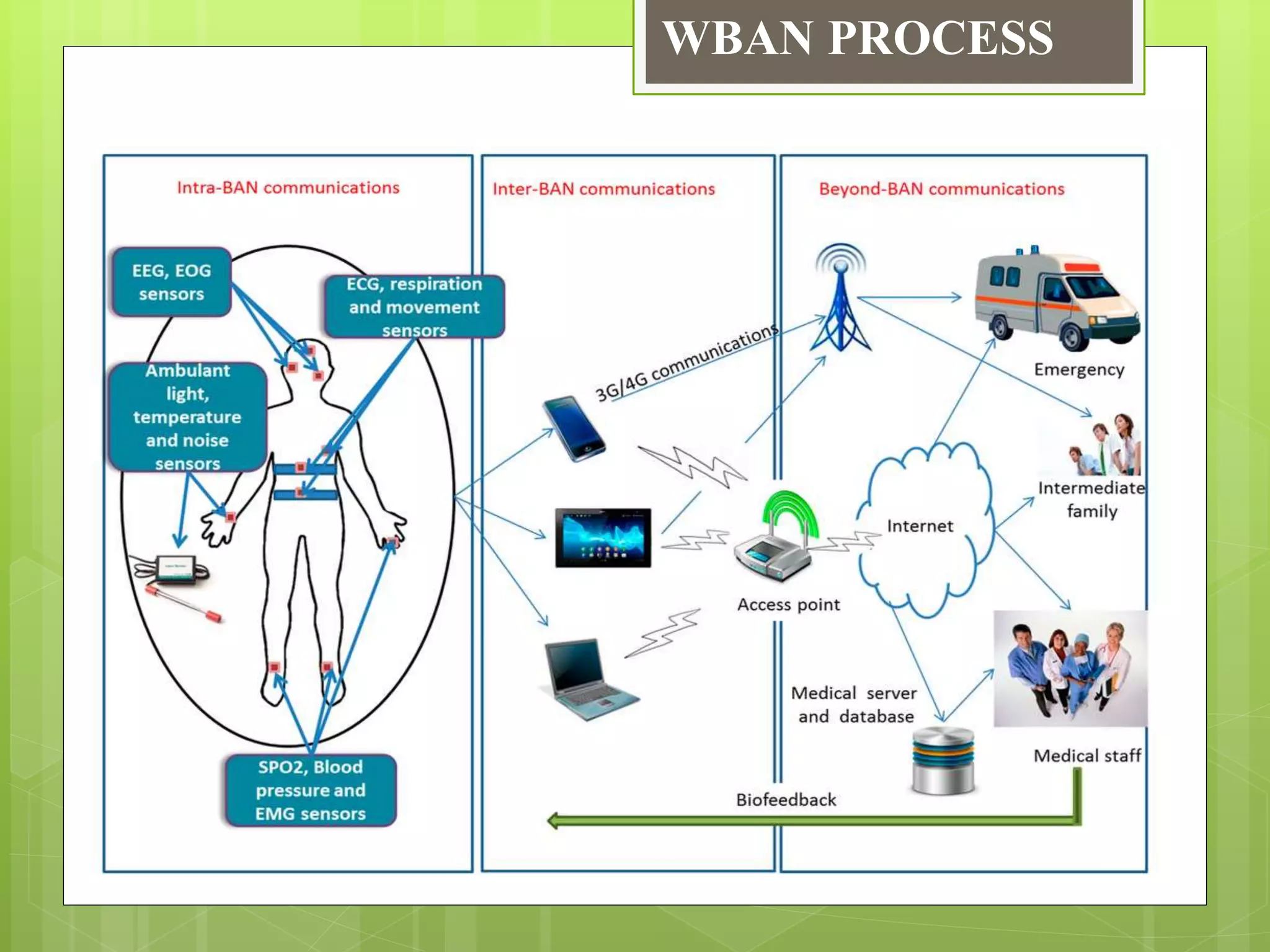
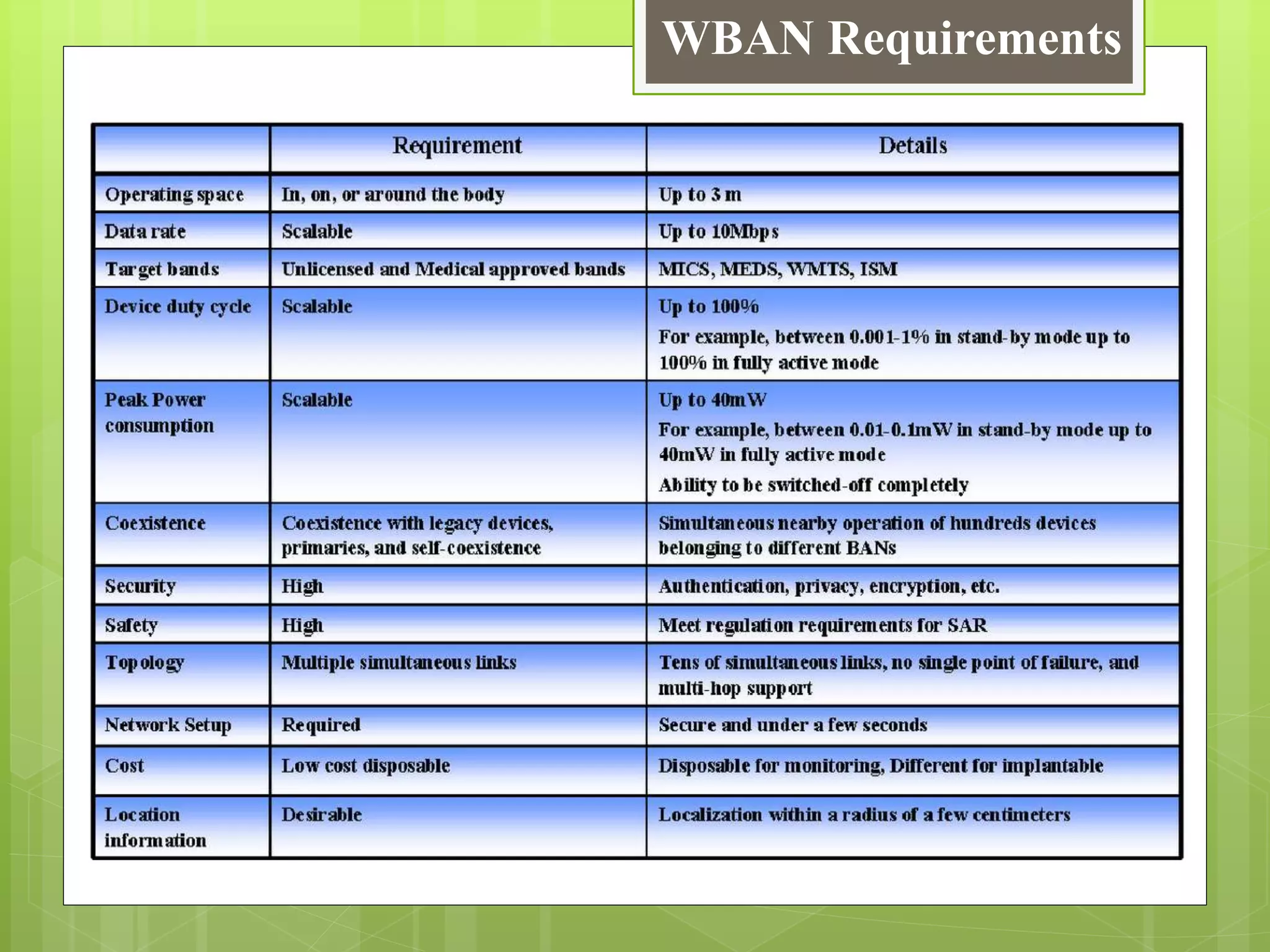
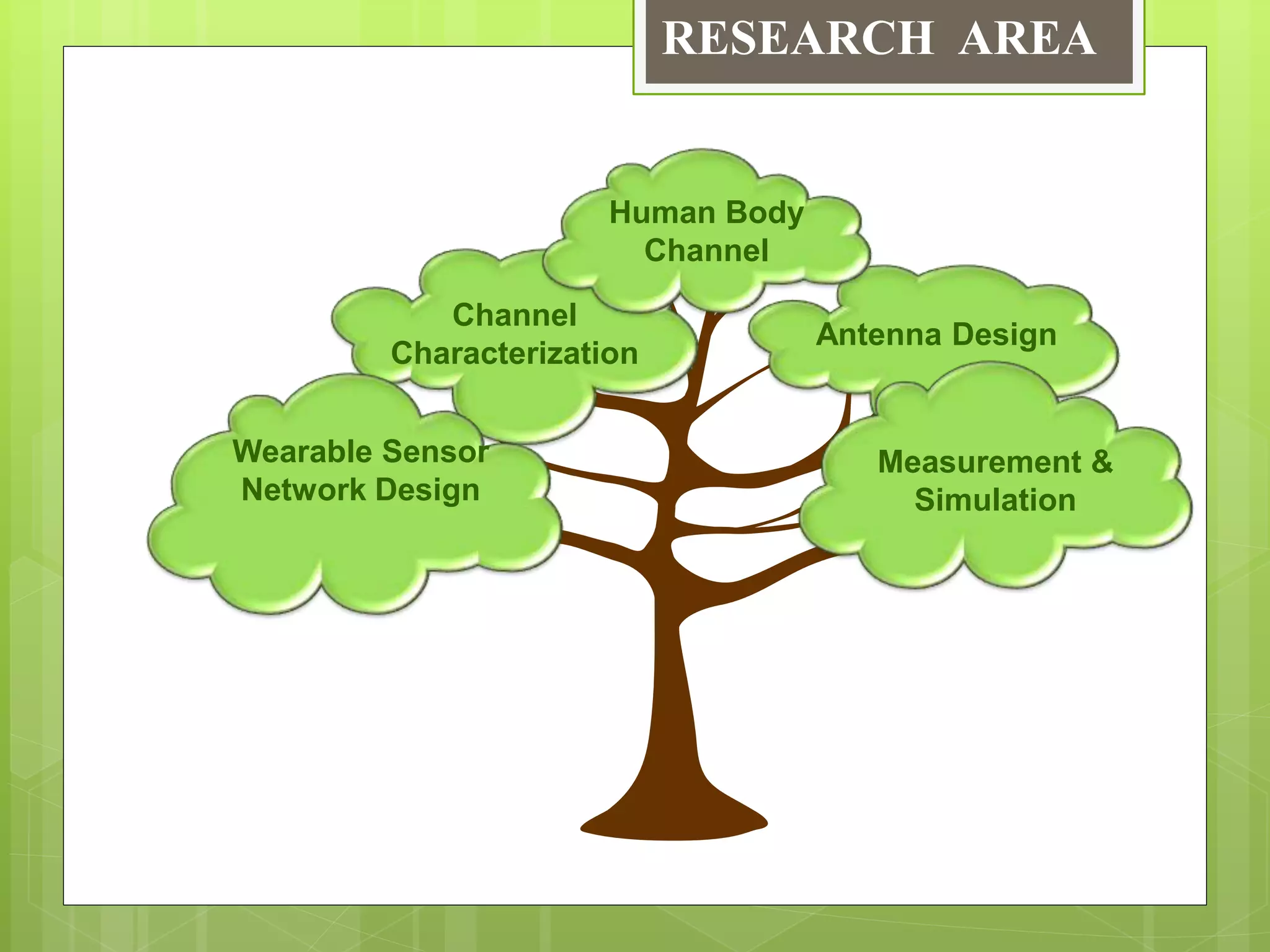
This document provides an overview of wireless body area networks (WBANs). It defines WBANs as low-power wireless networks designed for use on or around the human body to monitor vital signs. The document outlines the key components of a WBAN including body sensor units that measure parameters, a body control unit that receives and saves data, and a 3-tier architecture involving sensors, personal devices, and medical servers. Challenges, applications, research areas and the future scope of WBANs are also discussed.