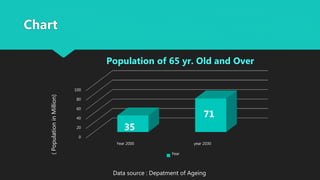
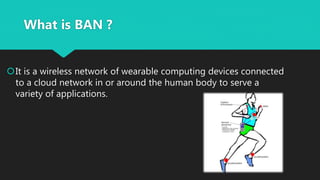
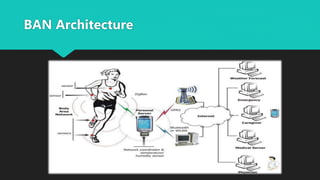
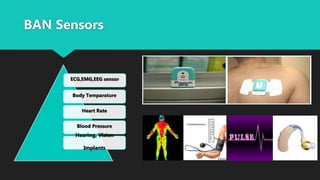
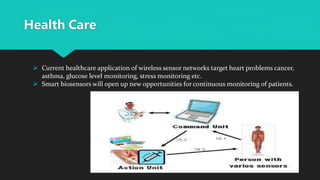
A Body Area Network (BAN) is a wireless network of wearable devices designed for health monitoring and data communication close to or within the human body. As the population ages, the demand for BAN technology, which includes various sensors for monitoring health metrics, is increasing to facilitate proactive healthcare. The IEEE 802.15.6 standard aims to ensure low-power, reliable communication in these networks, addressing security and interoperability challenges while promising to enhance patient care and reduce healthcare costs.