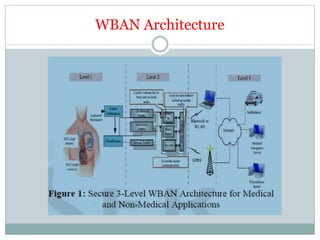
This document summarizes a review paper on Wireless Body Area Networks (WBANs) by Fentahun Yersie. It discusses that WBANs consist of small intelligent devices attached to or implanted in the body that wirelessly communicate health and physiological data. It describes the two main types of devices as sensors that measure parameters like heartbeat and temperature, and actuators that take actions based on sensor data. The document outlines the typical three-level architecture of WBANs and common applications like remote health monitoring. It also discusses the key requirements for WBAN MAC protocols including reducing energy consumption through efficient handling of collision, overhearing, idle listening while supporting communication across multiple frequency bands.





![Cont...
WBAN MAC should support simultaneous operation on inbody is called
Medical Implant Communications Service (MICS) and on-body
frequency bands/channels [Industrial, Scientific and Medical (ISM) or
Ultra Wide Band (UWB)] at the same time. It means, that should
support Multiple Physical layers (Multi-PHYs) communication.
The important factors are scalability and adaptability to changes in the
network, throughput, bandwidth utilization and delay. The position of
the human body network topology, the node density and the position of
the human body should be handled rapidly and successfully. MAC
protocol for a WBAN should consider the electrical properties of the
human body and the diverse traffic nature of in-body and on-body
nodes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bahirdarinstituteoftechnology-170425043423/85/Wireless-body-are-network-9-320.jpg)


