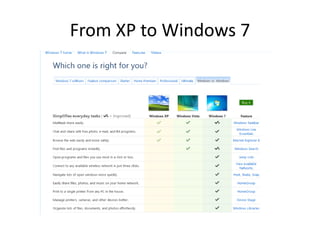
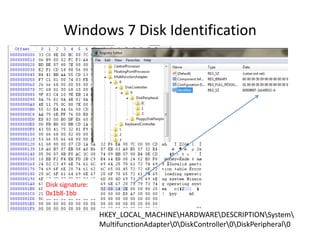
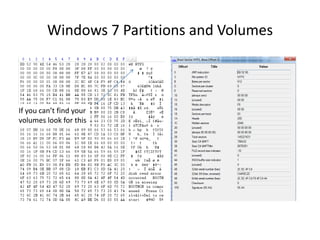
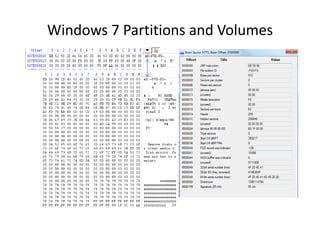
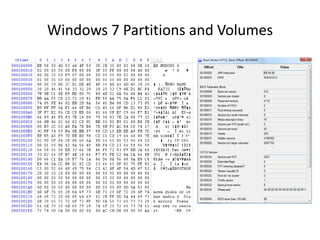
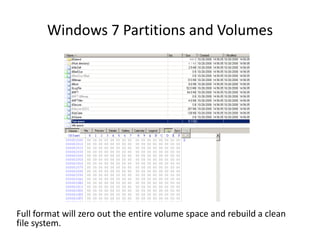
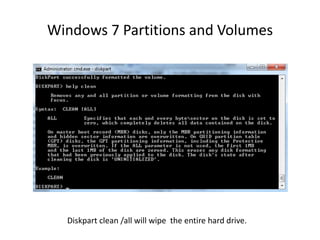
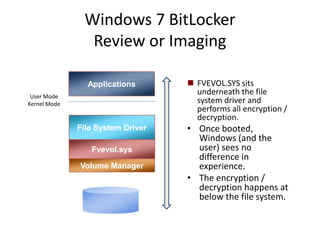
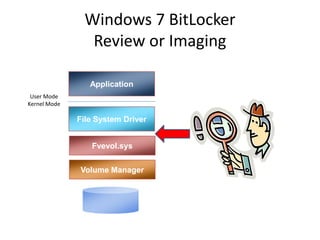
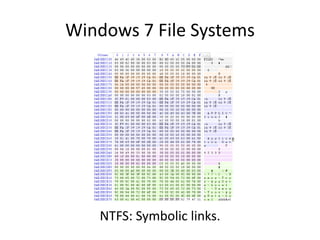
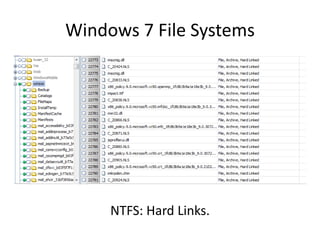
Windows 7 introduces several changes from previous versions of Windows that are relevant to digital forensics. These include updated formats for BitLocker encryption that may not be readable by older forensic tools, new artifacts in the search index, prefetch and jump list files, and changes to how volume shadow copies store differential backups of file systems. Windows 7 also expands the use of virtualization for things like the registry and user folders, creating additional locations that must be examined during an investigation.









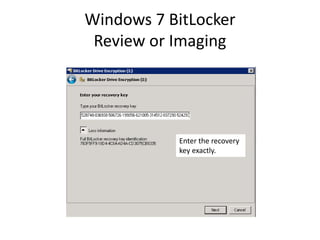
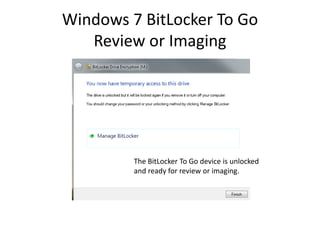
![Windows 7 BitLocker
Review or Imaging
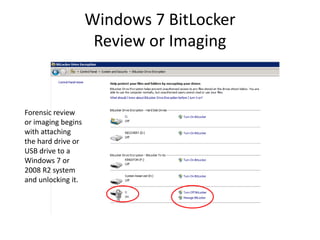
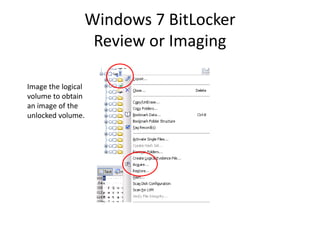
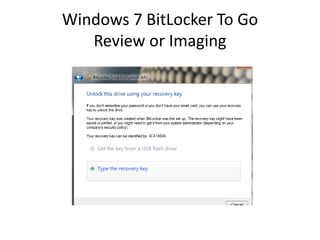
To unlock a BitLockered volume, first get the Recovery
Password ID: manage-bde –protectors –get [volume].
The Recovery Password ID can be used to recover the
Recovery Password from the AD.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7forensics-overview-r3-110606165431-phpapp02/85/Windows-7-forensics-overview-r3-22-320.jpg)

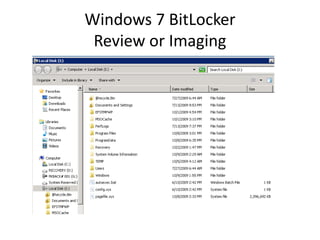
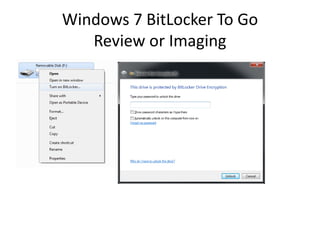
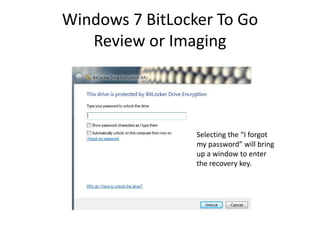
![Windows 7 BitLocker
Review or Imaging
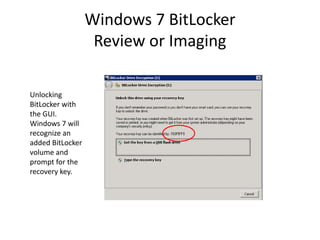
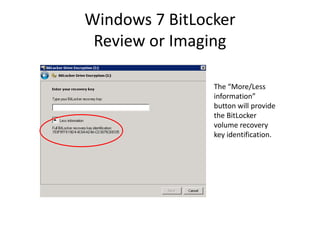
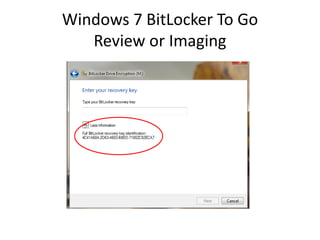
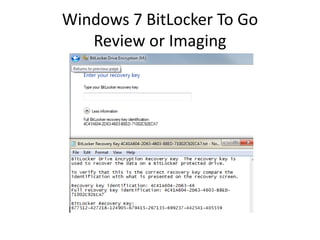
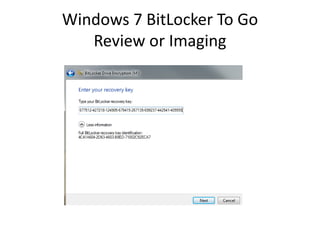
Unlock the BitLocker volume:
Manage-bde.exe –unlock [volume] –rp [recovery password].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7forensics-overview-r3-110606165431-phpapp02/85/Windows-7-forensics-overview-r3-25-320.jpg)


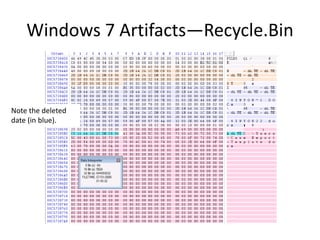
![Windows 7 Artifacts—Recycle.Bin
• [Volume]:$Recycle.Bin.
• $Recycle.Bin is visible in Explorer (view hidden files).
• Per user store in a subfolder named with account SID.
• When a file is moved to the Recycle Bin, it becomes two files.
• $I and $R files.
• $I file—original name and path, as well as the deleted date.
• $R file—original file data stream and other attributes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7forensics-overview-r3-110606165431-phpapp02/85/Windows-7-forensics-overview-r3-47-320.jpg)


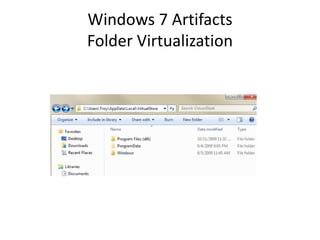
![Windows 7 Artifacts
Folder Virtualization
– Part of User Access Control—Standard user cannot
write to certain protected folders.
• C:Windows
• C:Program Files
• C:Program Data
– To allow standard user to function, any writes to
protected folders are “virtualized” and written to
C:Users[user]AppDataLocalVirtualStore](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7forensics-overview-r3-110606165431-phpapp02/85/Windows-7-forensics-overview-r3-52-320.jpg)
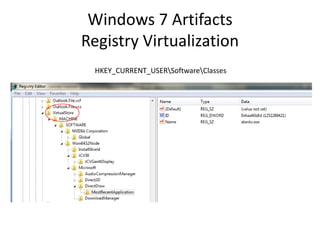

![Windows 7 Artifacts
Registry Virtualization
• Location of the registry hive file for the
VirtualStore
– Is NOT the user’s NTUSER.DAT
– It is stored in the user’s UsrClass.dat
Users[user]AppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsUsrClass.dat
• Investigation of Vista through 2008 R2 requires
the investigator to examine at least two account
specific registry hive files for each user account.
– NTUSER.DAT
– UsrClass.dat](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7forensics-overview-r3-110606165431-phpapp02/85/Windows-7-forensics-overview-r3-55-320.jpg)

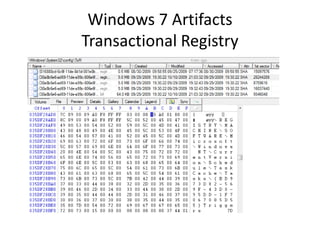
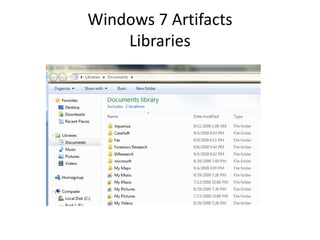
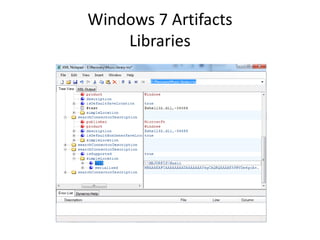
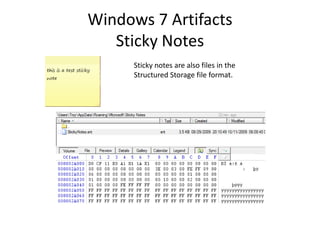
![Windows 7 Artifacts
Libraries
Users[account]AppDataRoamingMicrosoftWindowsLibraries.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7forensics-overview-r3-110606165431-phpapp02/85/Windows-7-forensics-overview-r3-60-320.jpg)



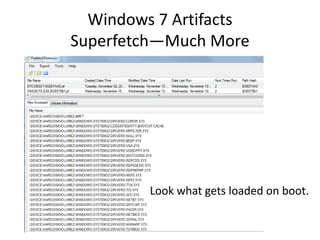
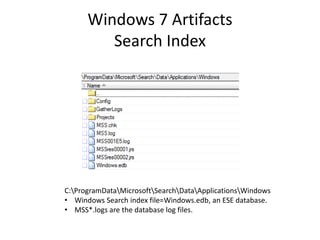
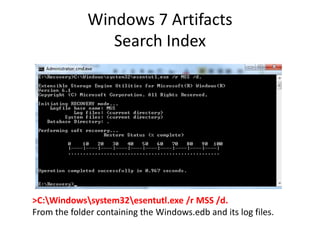
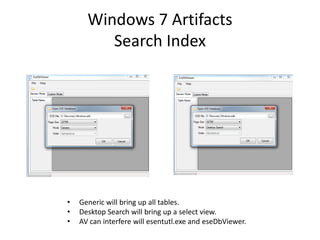
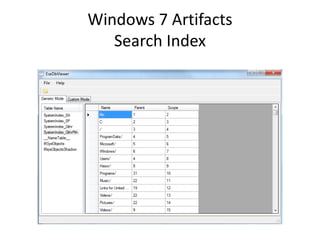
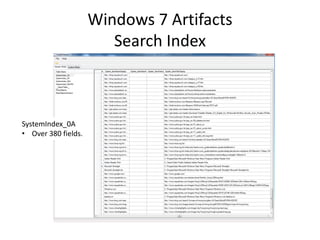
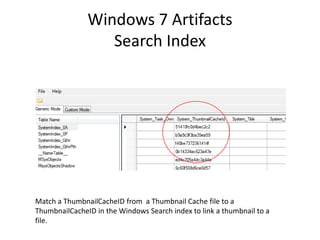




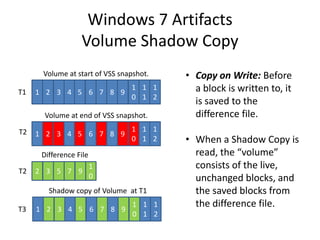

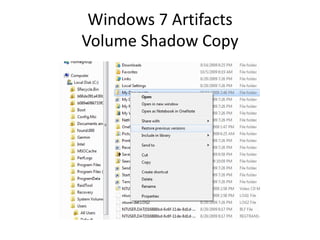
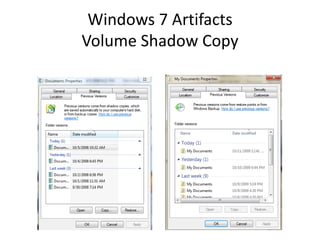
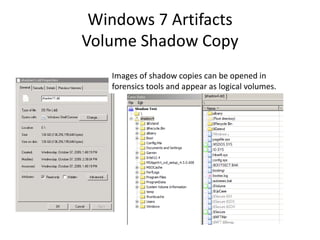
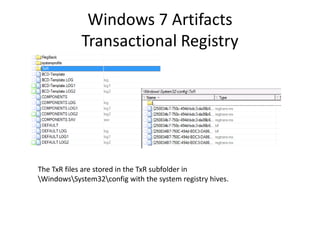
![Windows 7 Artifacts
Volume Shadow Copy
vssadmin list shadows /for=[volume]:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7forensics-overview-r3-110606165431-phpapp02/85/Windows-7-forensics-overview-r3-87-320.jpg)



![Windows 7 Artifacts
Volume Shadow Copy
>psexec [computername] vssadmin list shadows /for=C:
>psexec [computername] net share testshadow=.HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy20
PsExec v1.94 - Execute processes remotely
. . .
testshadow was shared successfully.
net exited on [computername] with error code 0.
>robocopy /S /R:1 /W:1 /LOG:D:VSStestcopylog.txt [computername] testshadow D:vssTest
Log File : D:VSStestcopylog.txt
. . .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7forensics-overview-r3-110606165431-phpapp02/85/Windows-7-forensics-overview-r3-91-320.jpg)