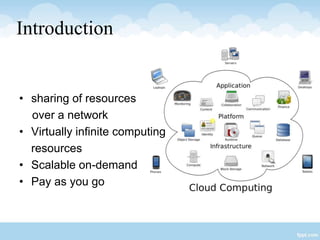
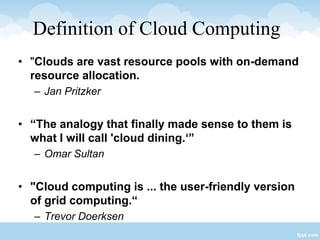
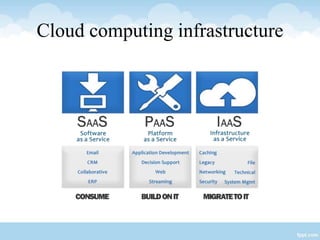
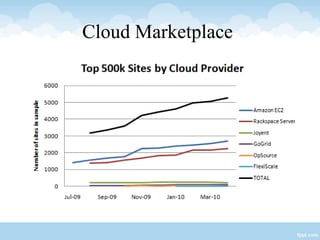
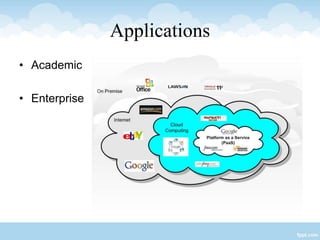
This presentation provides an overview of cloud computing, including definitions, models of cloud services (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS), advantages like scalability and cost savings, and disadvantages like lack of control. It defines cloud computing as sharing virtualized computing resources over a network on-demand, with users paying only for what they use. The major cloud service models - SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS - are explained in terms of the infrastructure and services provided to users at each level.