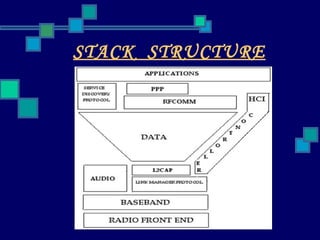
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances using short-wavelength UHF radio waves in the industrial, scientific and medical radio bands. It was created in 1994 by Ericsson to replace cables connecting devices like mobile phones, laptops, printers, and other electronic devices. Bluetooth allows for wireless connections between various devices to share information and transmit data wirelessly over short distances of around 10 meters. It uses a radio technology called frequency-hopping spread spectrum to handle interference and improve communication quality.