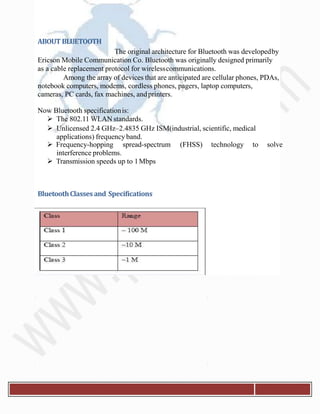
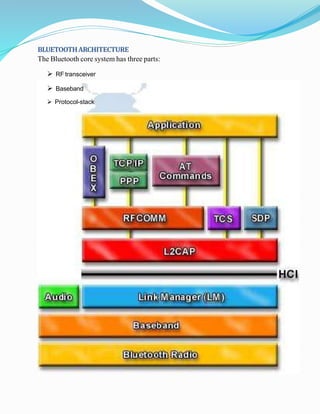
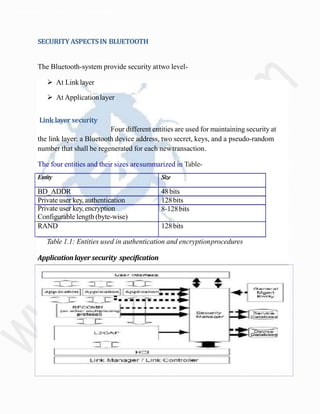
The document provides an overview of Bluetooth technology, its architecture, and security aspects, highlighting specific vulnerabilities to wireless networks. It describes various types of Bluetooth networks and the methods used for attacks, including tools and techniques such as bluejacking and bluesnarfing. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of user awareness and education in managing Bluetooth security risks, as user actions often facilitate unauthorized access.