This document discusses the nature and characteristics of language. It defines language as a symbol system that is uniquely human, arbitrary yet structured, and acquired through social learning rather than instinct. The key points made are:
1) Language is a system of symbols that allows for the communication of ideas, emotions, culture and identity between humans.
2) It is characterized by properties such as displacement, infinite complexity, open-endedness, discreteness, and structural complexity that distinguish it from animal communication systems.
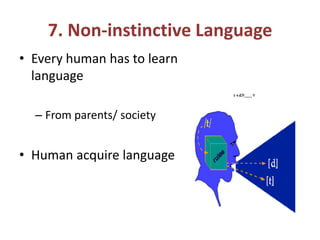
3) Language is acquired socially rather than instinctively, and every human must learn the language of their community.