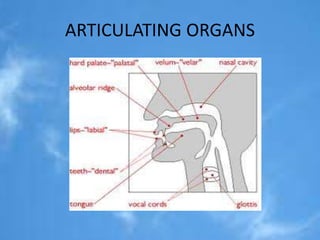
This document provides a classification and description of consonants in English. It begins by defining consonants as sounds produced with an egressive air flow accompanied by obstruction or friction in the articulators. It then lists and describes the 24 consonant sounds in English. Consonants can be classified based on their air stream mechanism, glottal state, position of the soft palate, point of articulation, and manner of articulation. Each English consonant is then individually described based on these phonetic characteristics.