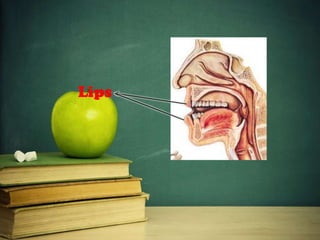
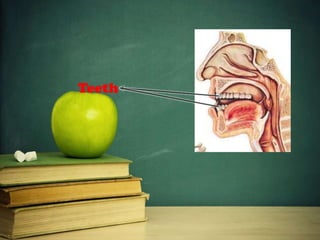
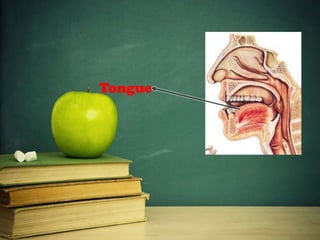
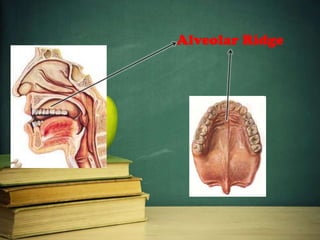
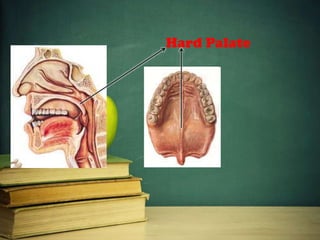
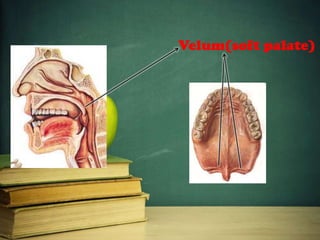
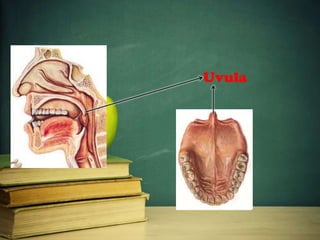
This document provides an overview of phonetics and its subfields. It defines phonetics as the study of sounds and their production in language. The three main subfields are articulatory phonetics, which studies speech production using the organs of speech; acoustic phonetics, which deals with the acoustic aspects of sounds; and auditory phonetics, which concerns the hearing of speech sounds. It then provides details on the organs of speech involved in sound production, such as the lips, teeth, tongue, alveolar ridge, hard palate, velum, uvula, and glottis.