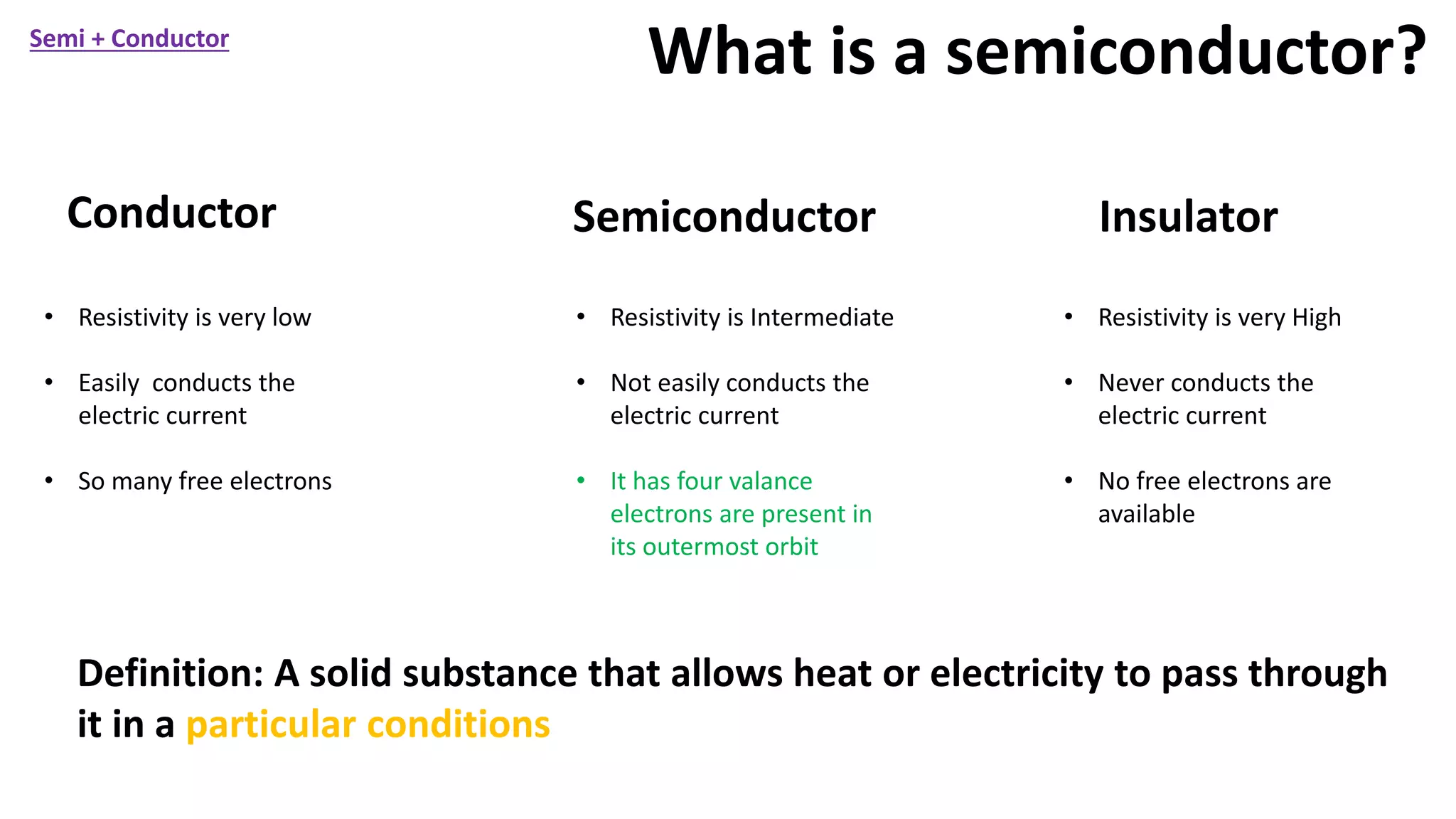
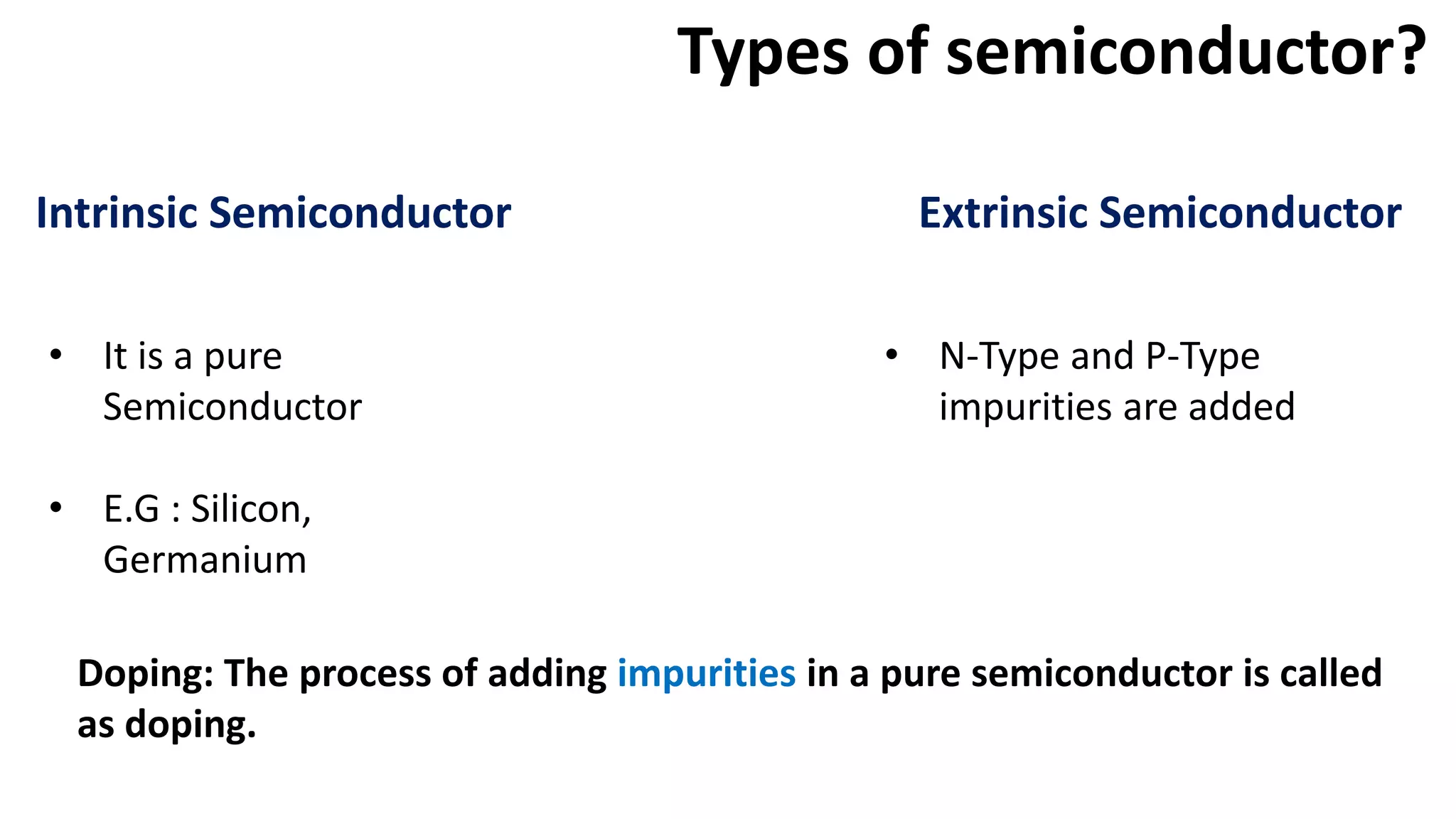
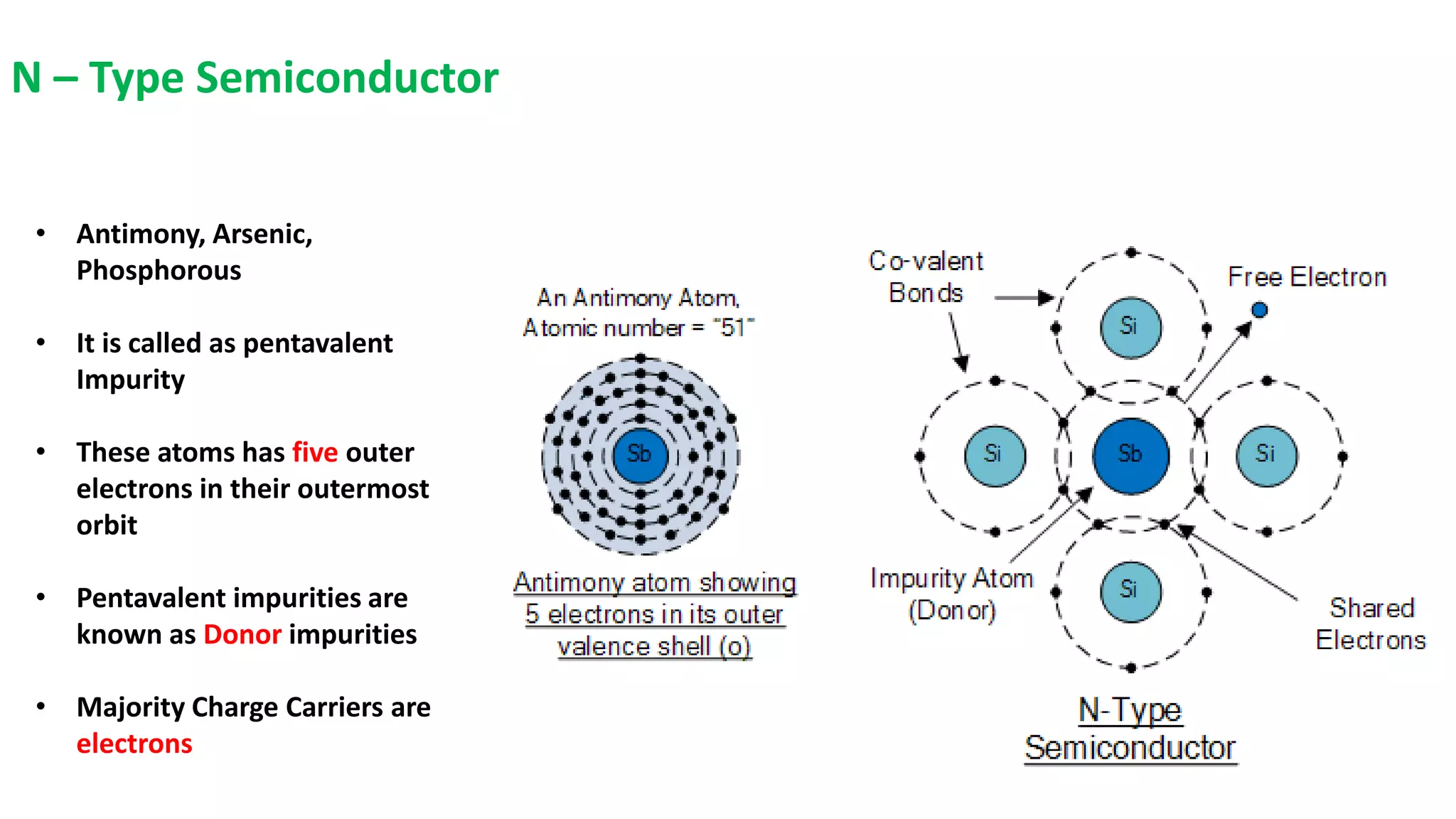
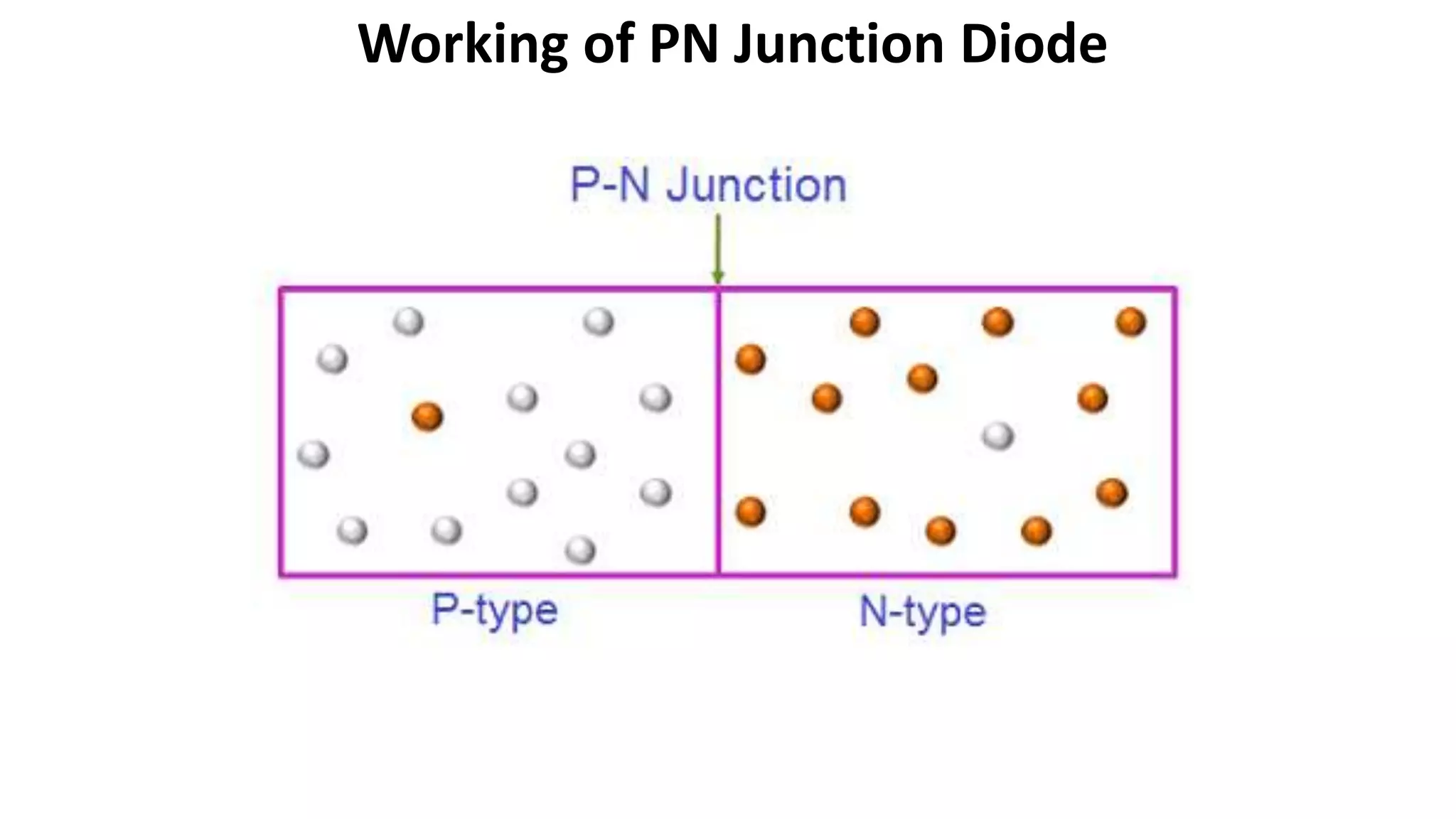
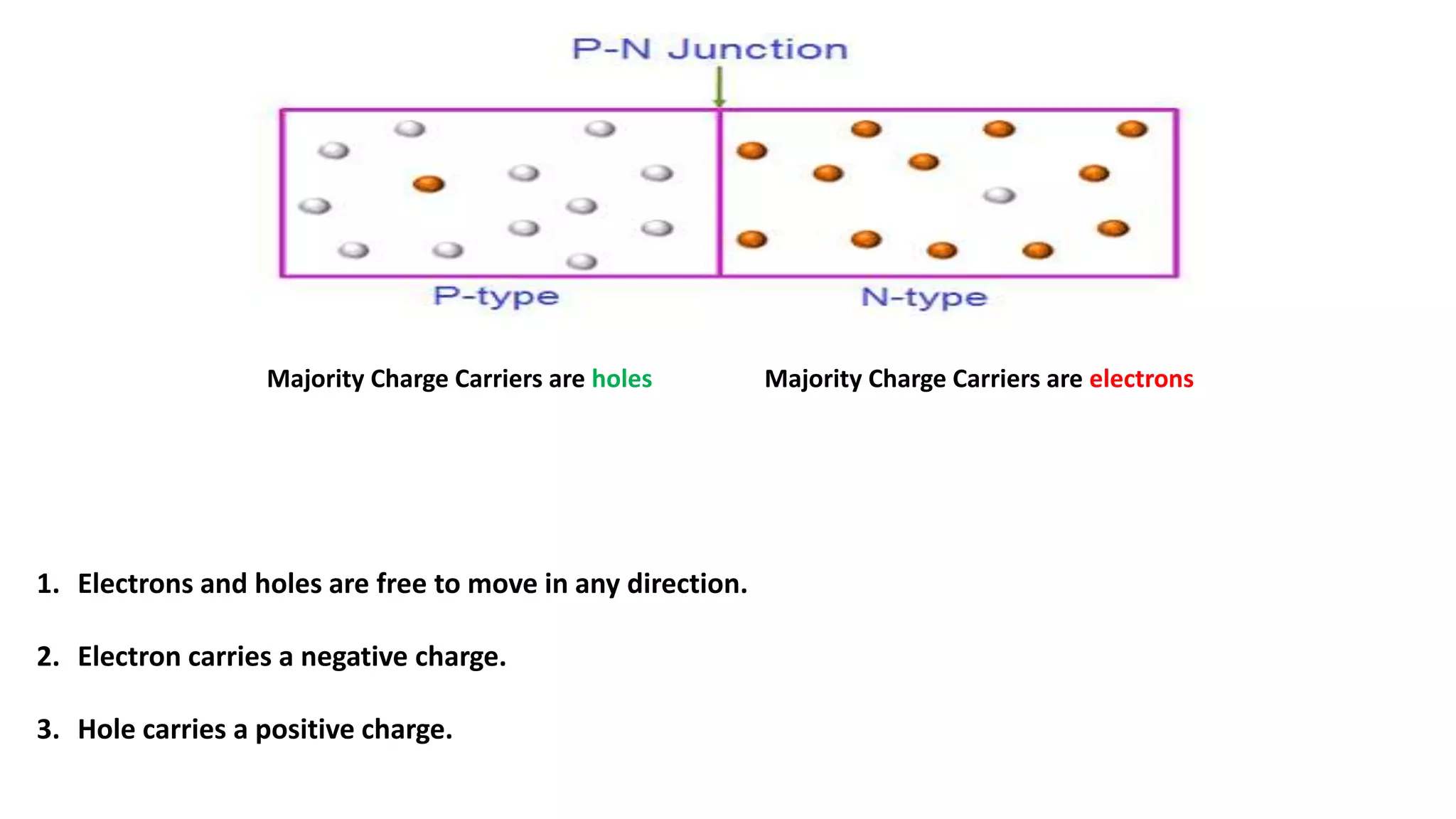
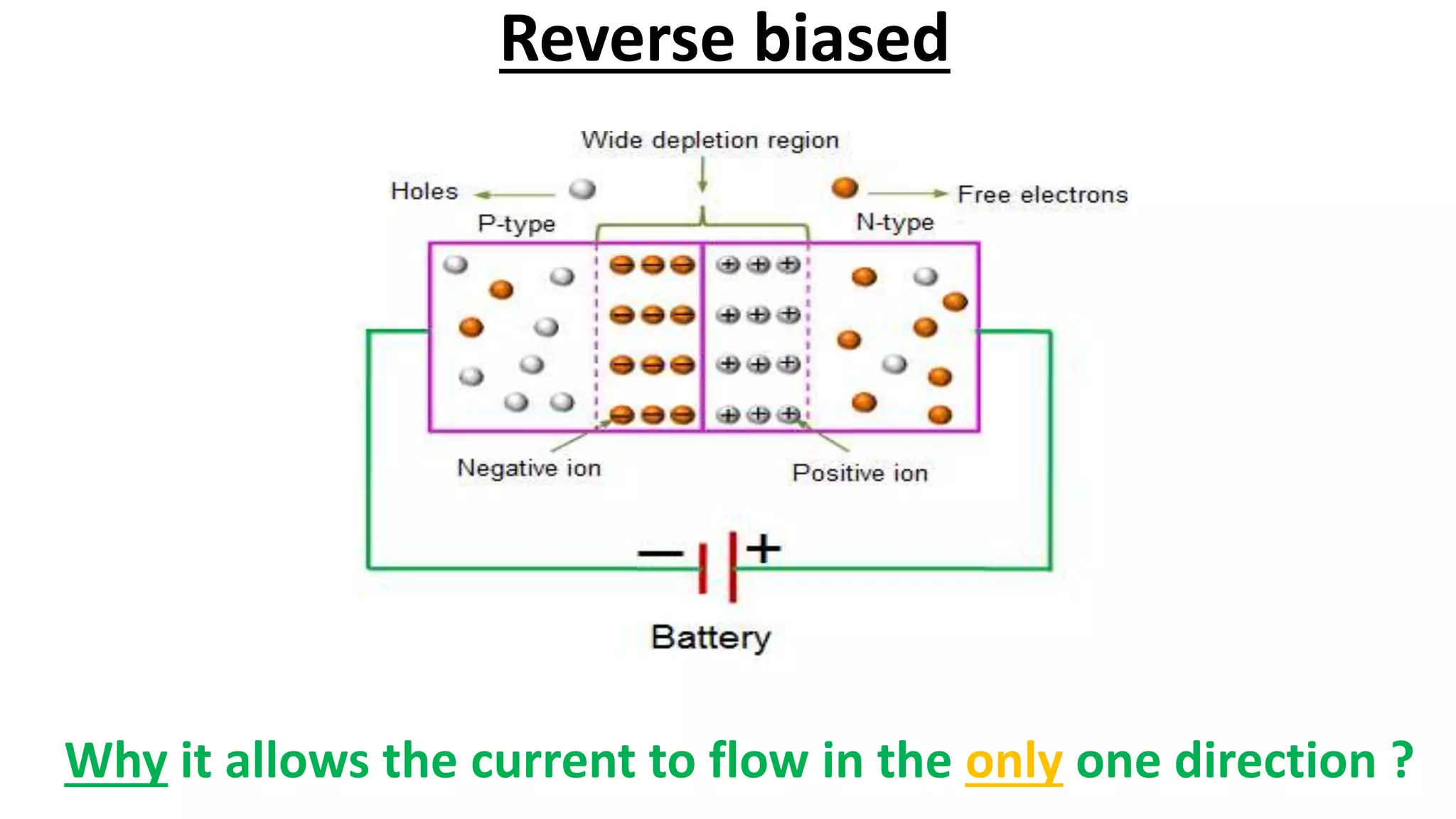
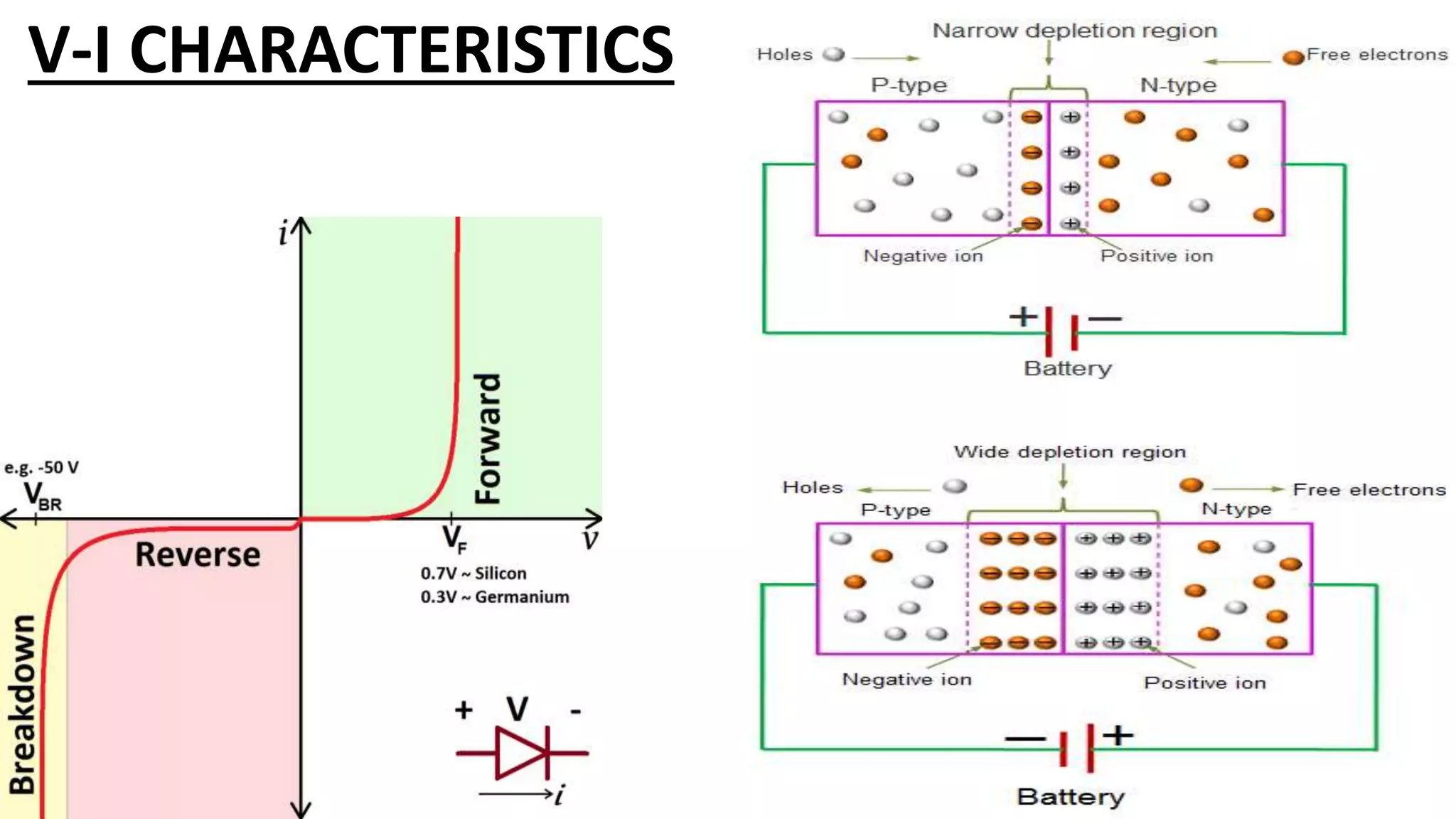
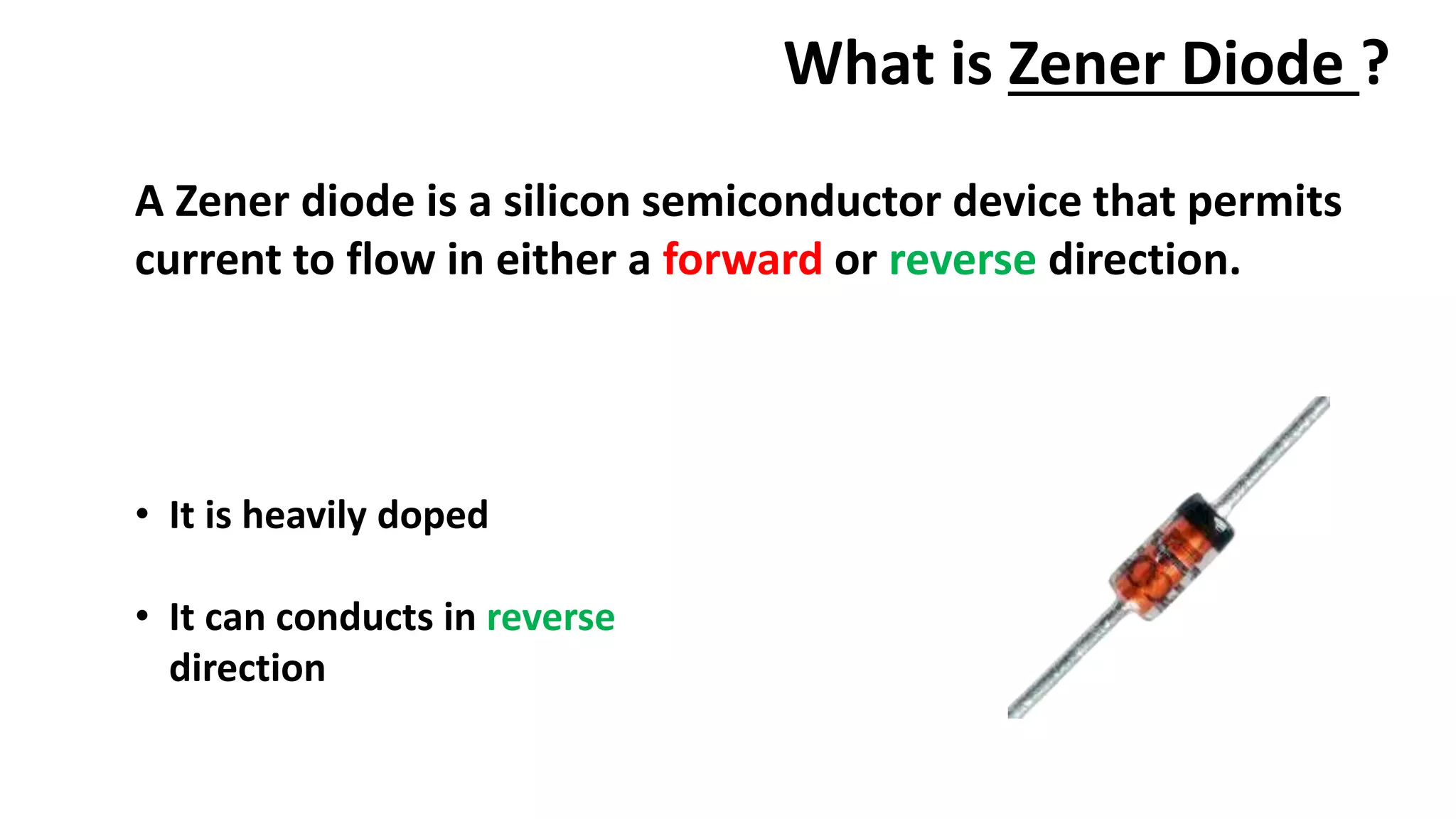
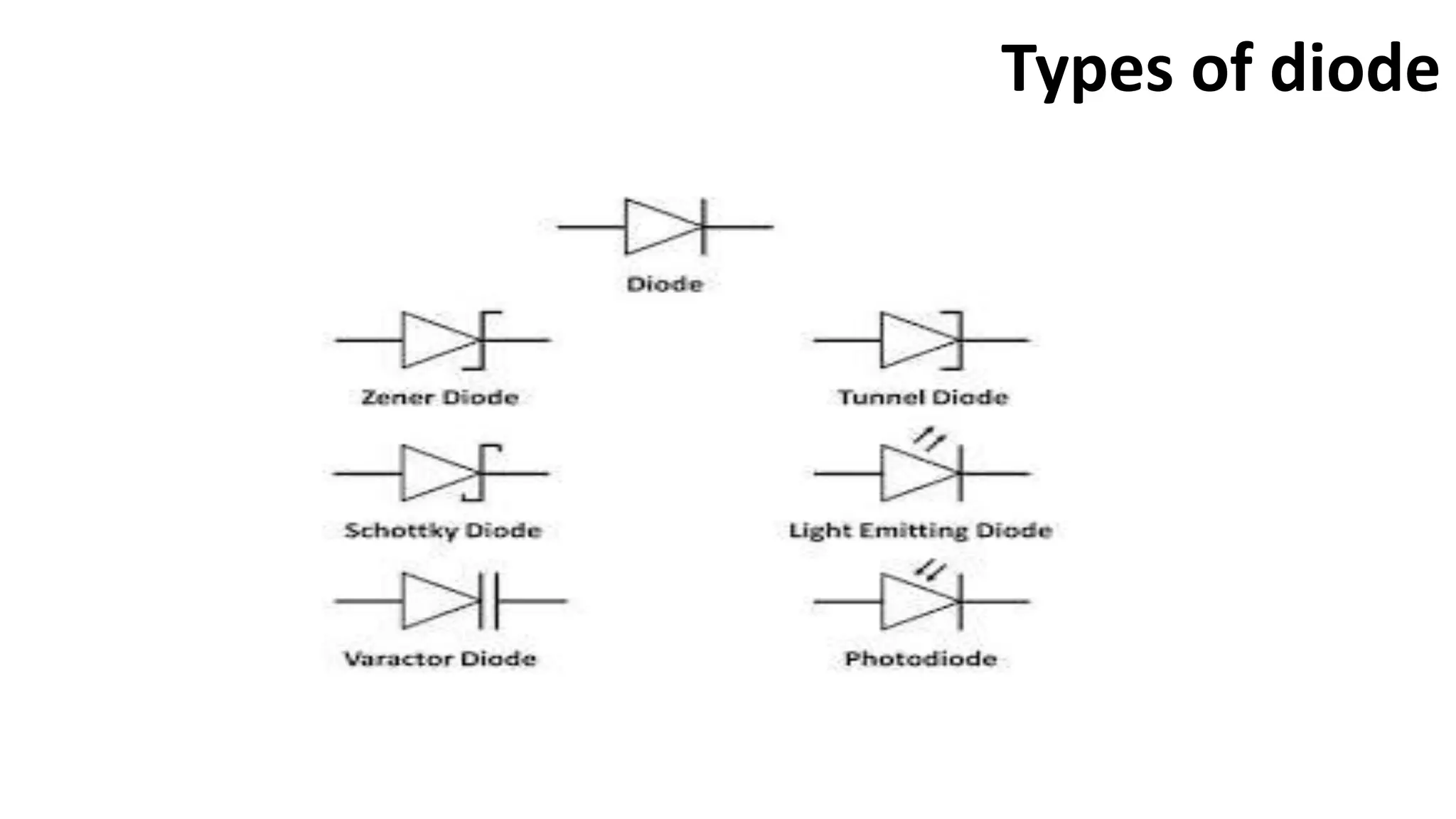
Nikhil Raut from RCOEM Nagpur is presenting about diodes. A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor component that allows current to flow in only one direction. It works by taking advantage of the properties of intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors like silicon and germanium, which are materials that have electrical conductivity between that of conductors and insulators. When a P-type and N-type semiconductor are joined, it forms a PN junction that only allows current to flow from P to N under forward bias, and blocks it under reverse bias. Different types of diodes include Zener diodes, tunnel diodes, LEDs, and Schottky diodes.