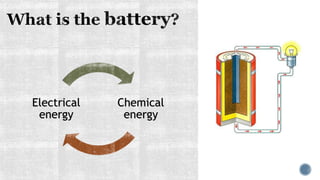
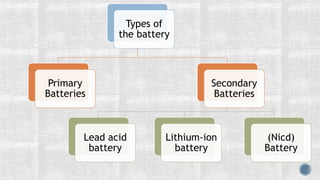
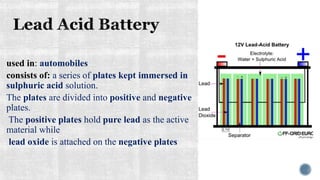
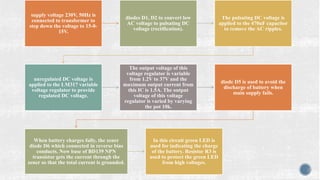
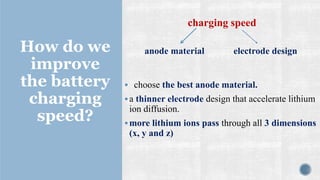
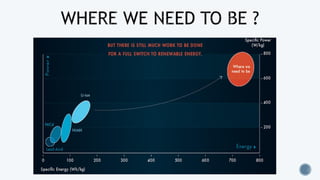
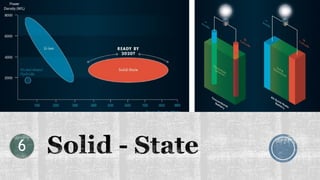
The document discusses various types of batteries, including lead-acid and lithium-ion, their characteristics, weight, and technical specifications. It also covers the principles of battery operation, charging methods, and future advancements in battery technology. Additionally, it provides insights into how to improve battery charging speed and includes references for further reading.
















![[1] Buchari, A. Maimulyanti, and Y. A. Winarko, “Preparation and potentiometric performance
of micro Ag/AgCl reference electrode,” Asahi Garasu Zaidan Josei Kenkyu Seika Hokoku, no.
December, p. 06 02 07/1-06 02 07/33, 2006.
[2] “Tesla Inc And The Future Of Battery Technology [INFOGRAPHIC],” 2017. [Online].
Available: https://www.valuewalk.com/2017/02/tesla-inc-future-battery-tech/. [Accessed: 08-
Mar-2019].
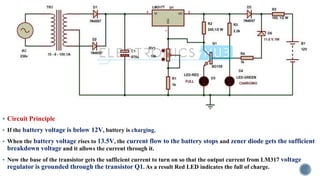
[3] “Automatic 12v Portable Battery Charger Circuit using LM317,” 2016. [Online]. Available:
https://www.electronicshub.org/automatic-battery-charger-circuit/. [Accessed: 08-Mar-2019].
[4] Adam Jacobson, “How batteries work,” TED-ED, 2015. [Online]. Available:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9OVtk6G2TnQ. [Accessed: 08-Mar-2019].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/battery-190308211350/85/Battery-25-320.jpg)
