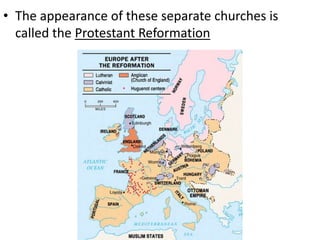
This document summarizes the major religious challenges and reforms in Europe between 1400-1600. It describes how the Avignon Papacy weakened the universal authority of the Catholic Church. It also discusses the Great Western Schism, Black Plague, and new ideas spread during the Renaissance that challenged Church leaders. The Protestant Reformation began as an attempt to reform abuses in the Catholic Church led by figures like Martin Luther and John Calvin, resulting in new Protestant churches. The Council of Trent was convened to answer Protestant disputes and reform the Catholic Church.