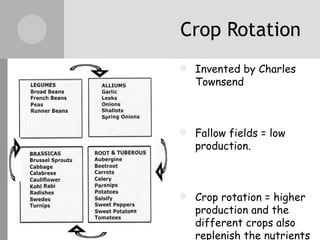
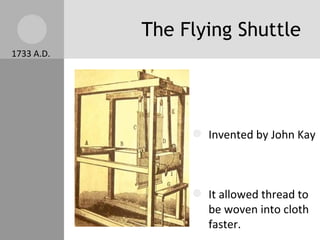
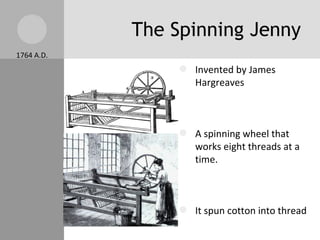
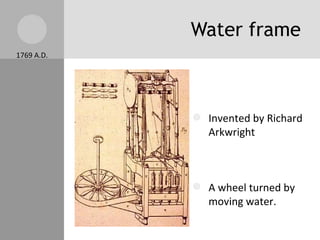
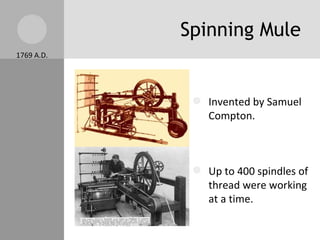
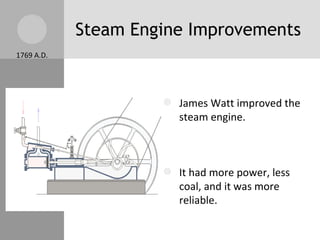
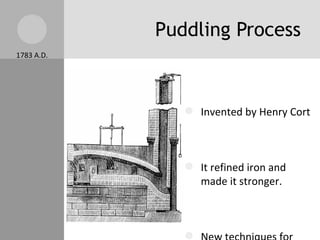
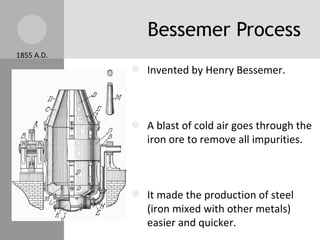
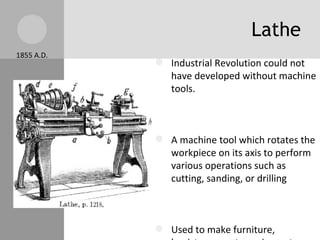
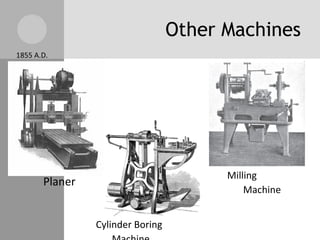
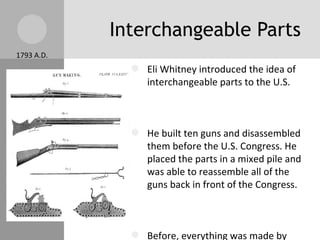
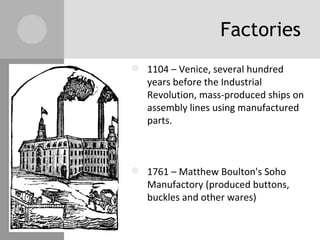
The document discusses key inventions and developments during the Industrial Revolution, including the seed drill, crop rotation, cotton gin, steam engine, railroads, and factories. These innovations increased agricultural and textile production, powered new machines, and transformed transportation. The Industrial Revolution drew people into cities for factory work and led to rapid urbanization, but also poor living and working conditions for many.