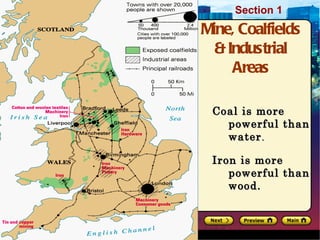
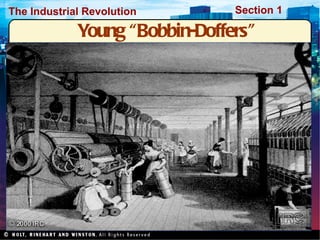
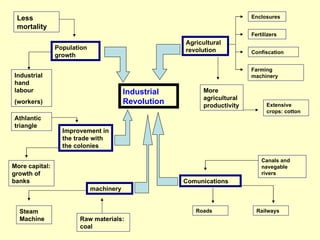
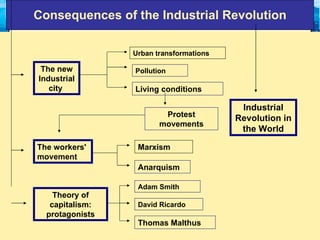
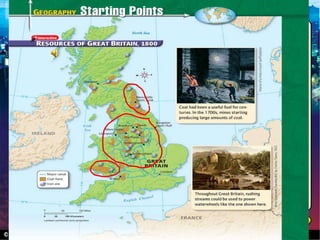
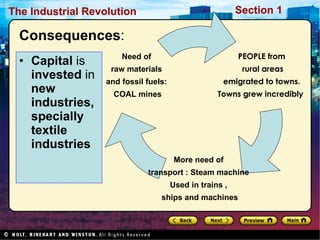
The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain in the late 18th century due to several factors. Agricultural advances led to population growth and a surplus of rural workers who moved to cities to work in factories. Britain had essential elements for economic success like capital, land, labor, and access to raw materials from its colonies. The development of steam power, new machinery, and factories revolutionized production and allowed industries like textiles to grow rapidly. The Industrial Revolution then spread beyond Britain to other parts of Europe and North America in the early 19th century.










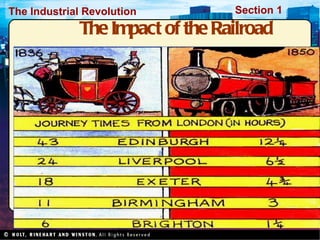
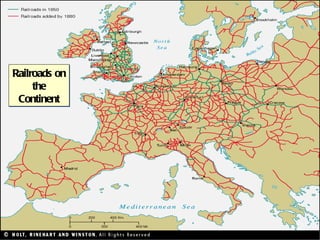



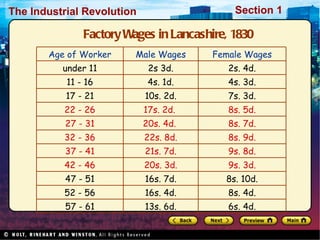

![Factory Production Concentrates production in one place [raw materials, labor and machinery]. Located near sources of power Requires a lot of capital investment [factory, machines, etc.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/industrialrevolution-111031040211-phpapp01/85/Industrial-revolution-20-320.jpg)