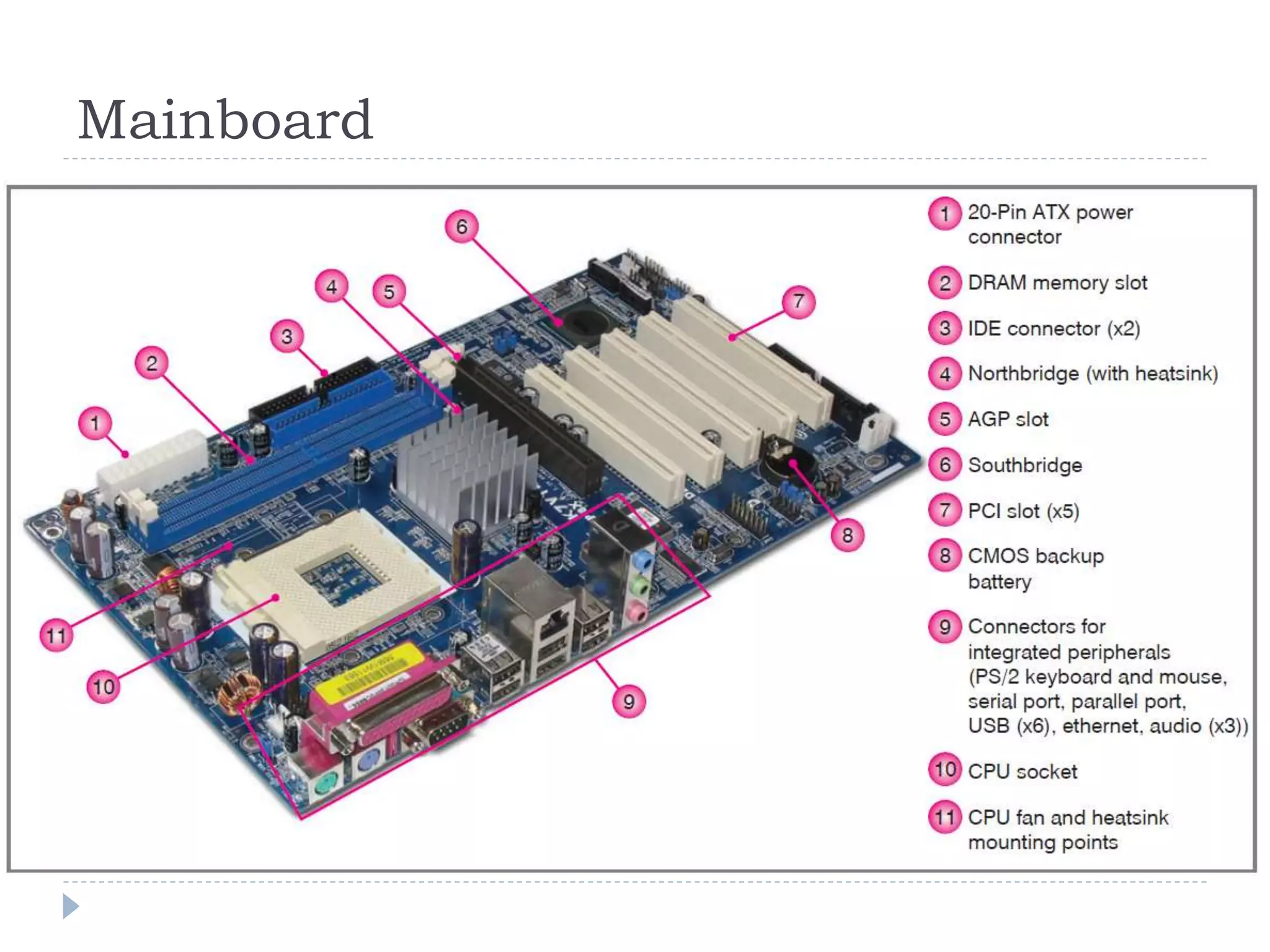
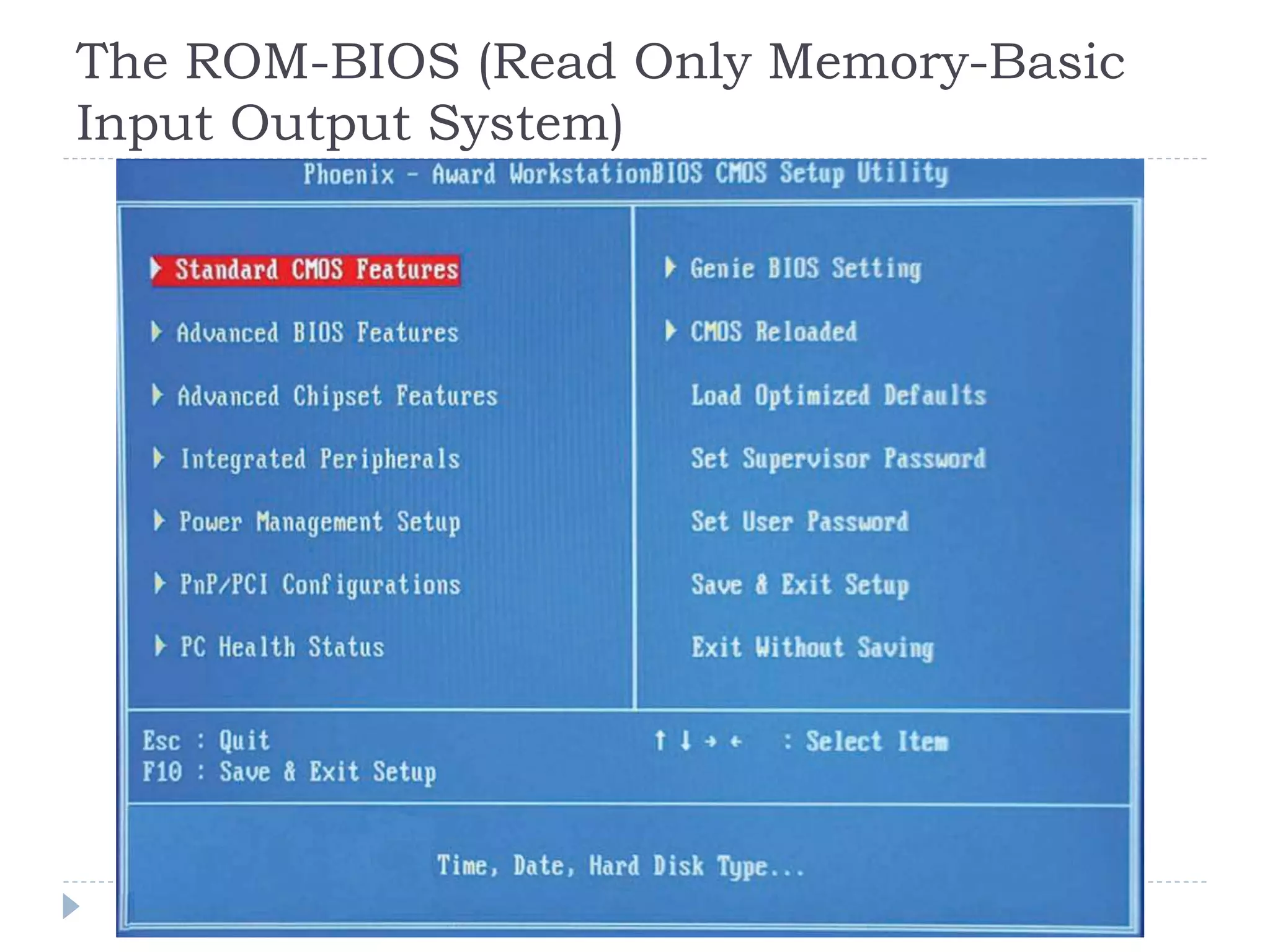
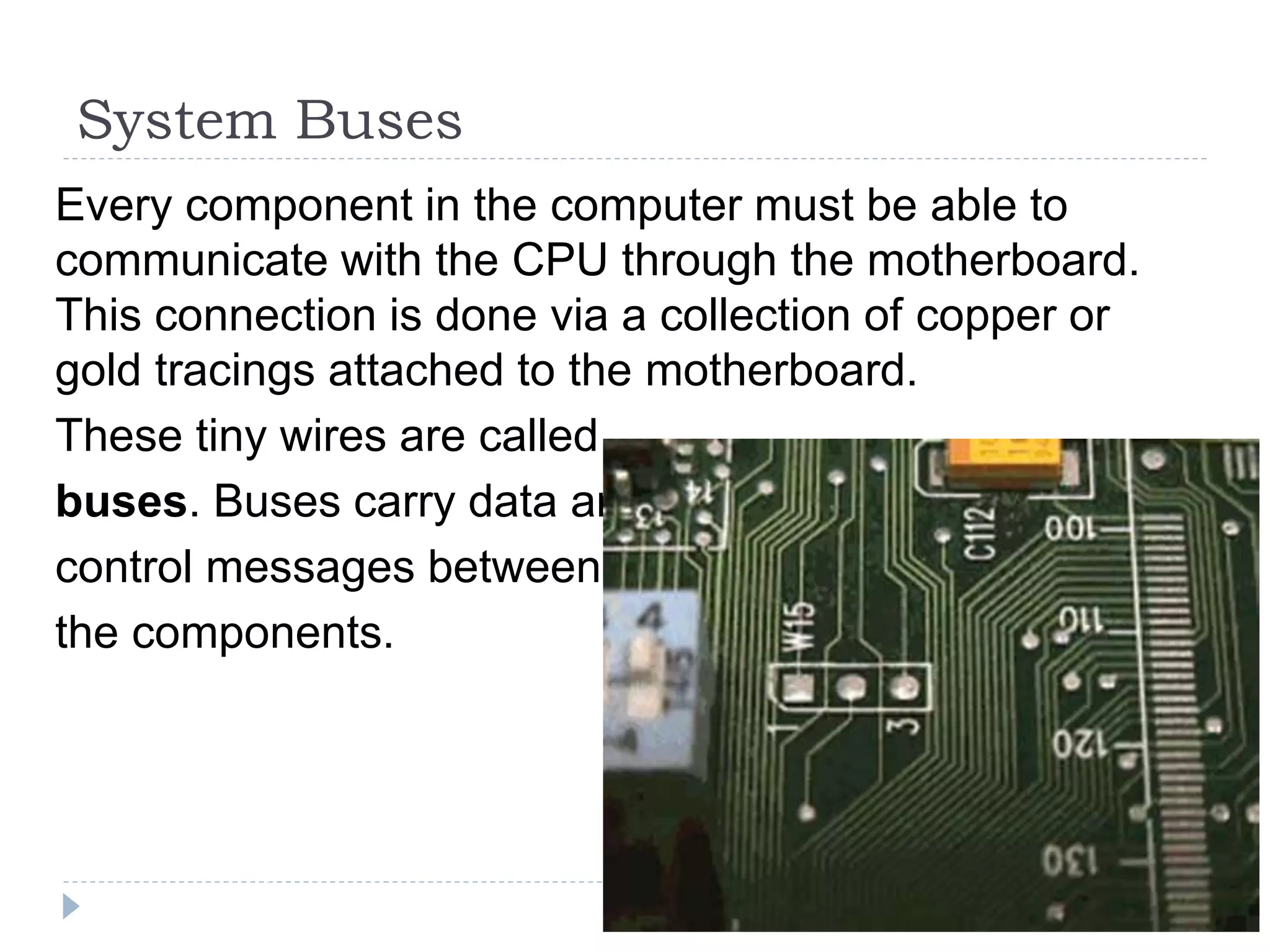
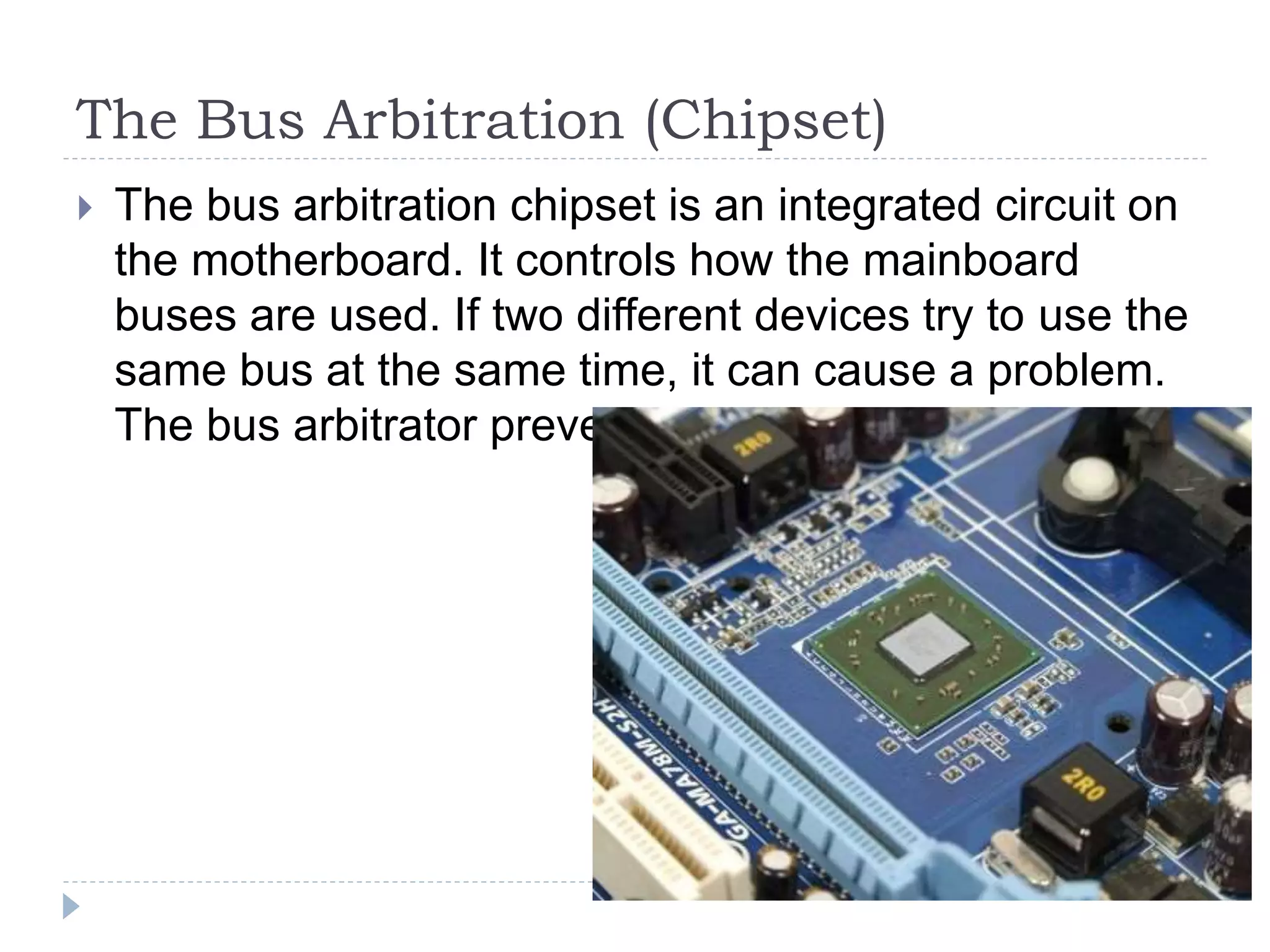
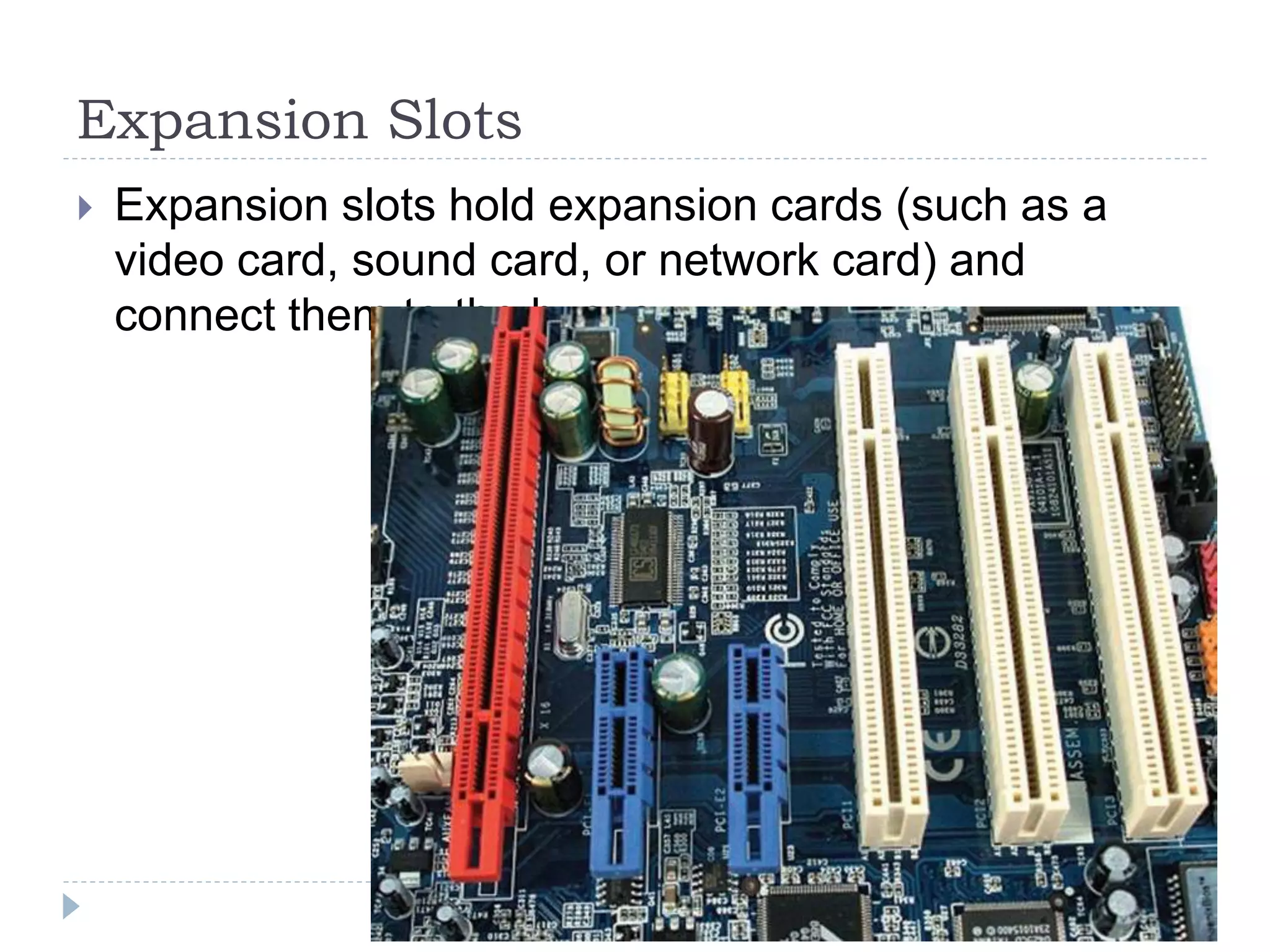
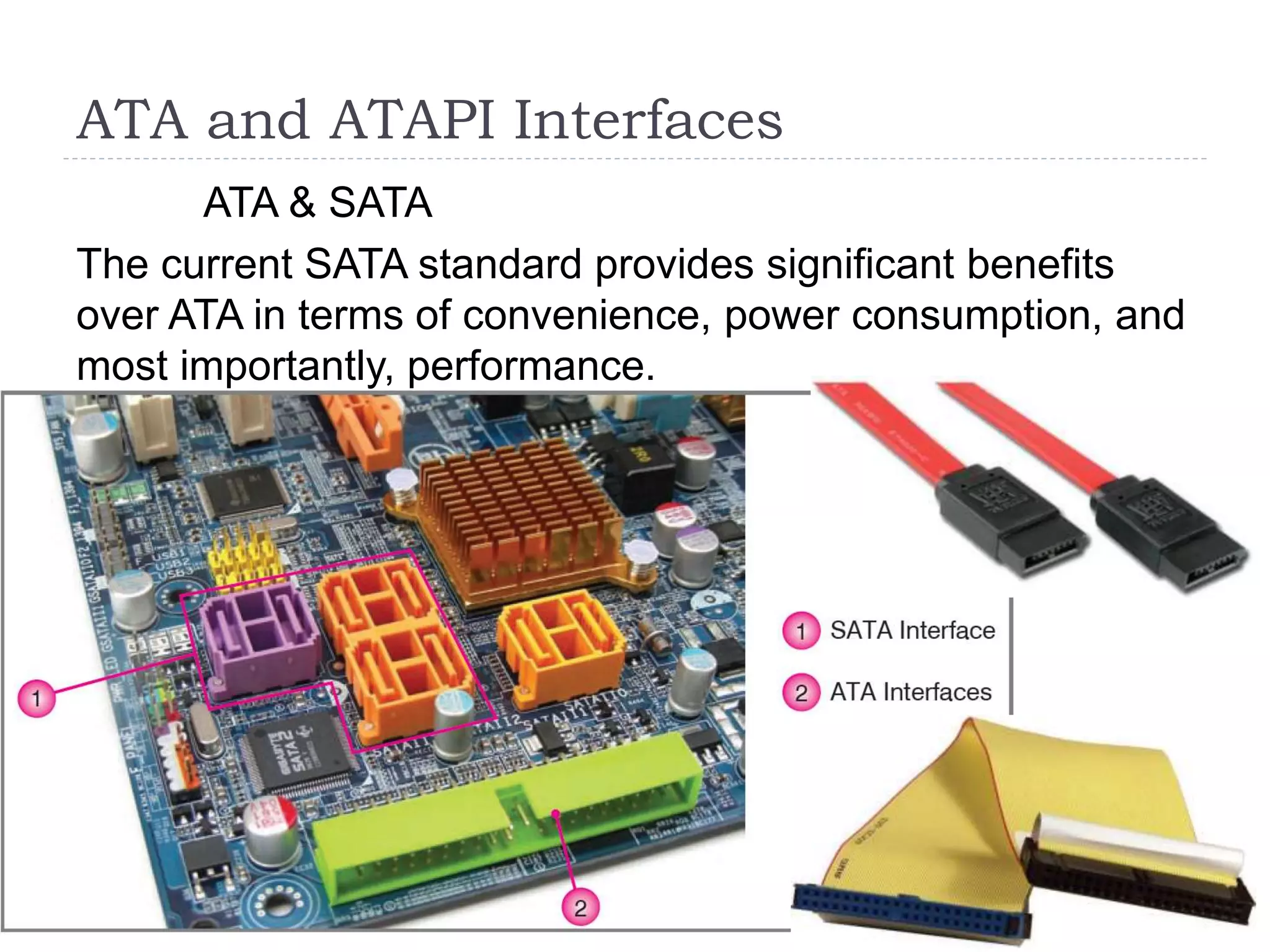
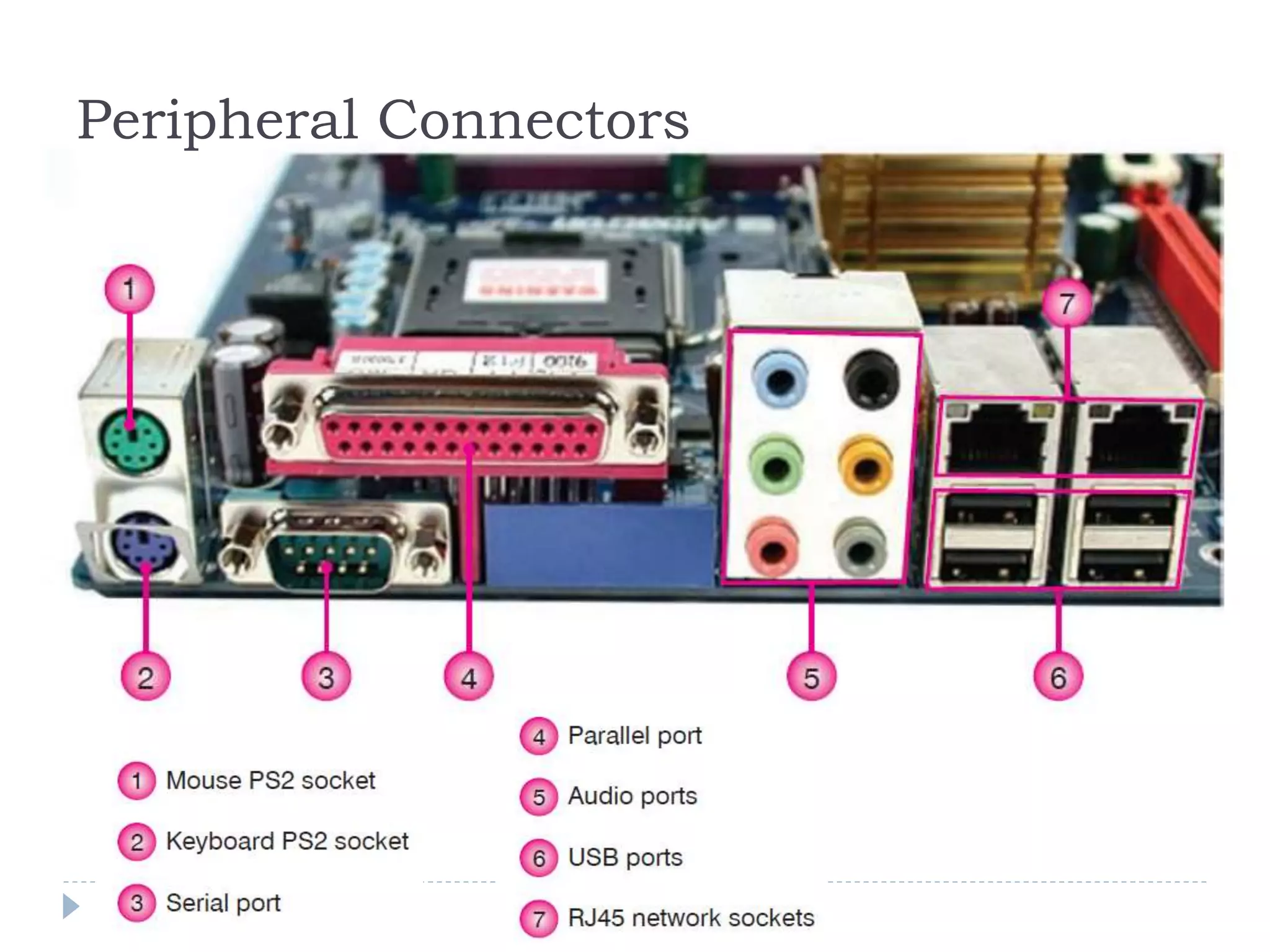
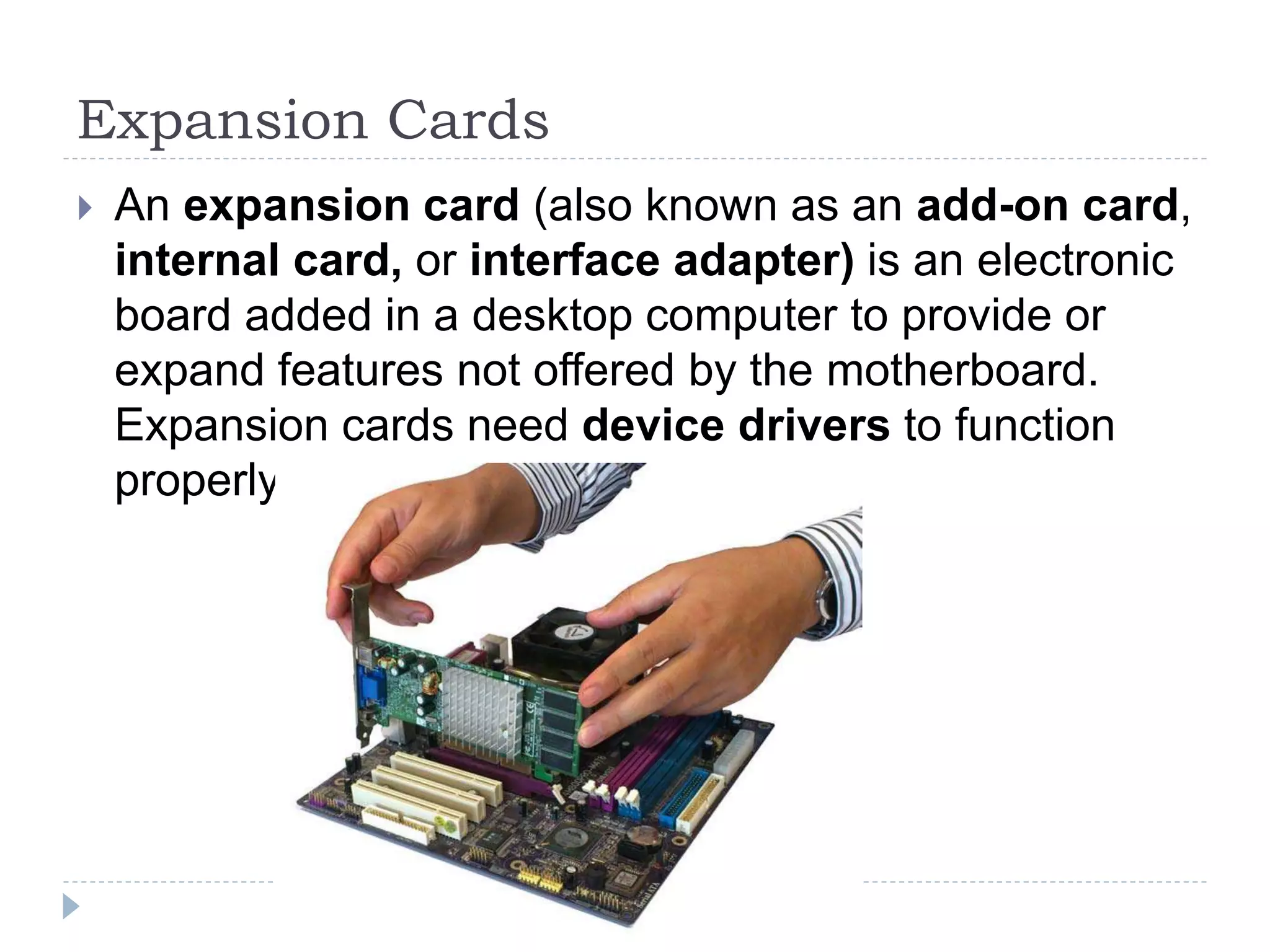
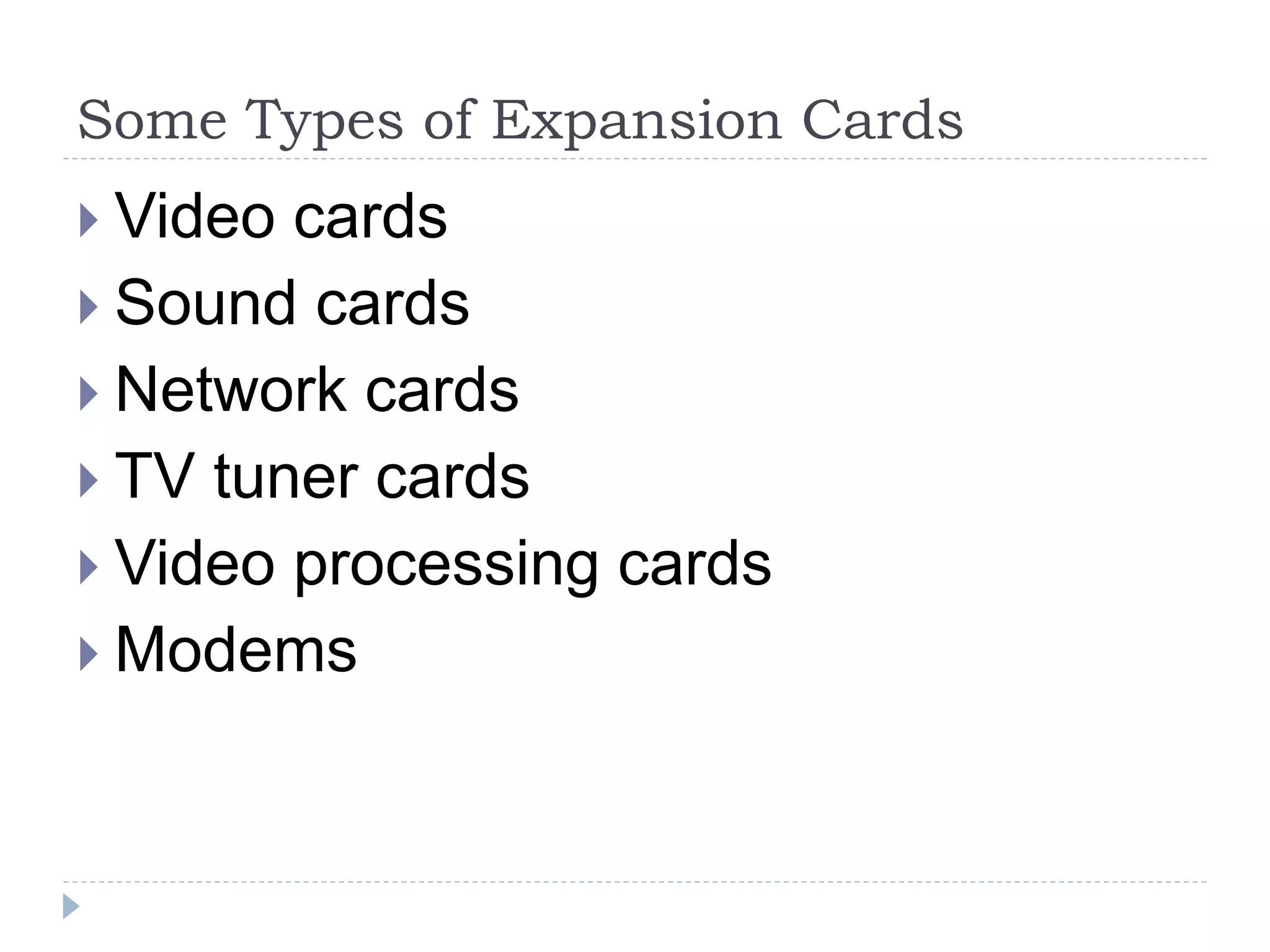
The physical components of a computer can be grouped into four categories: the system unit, input devices, output devices, and storage devices. The system unit houses the main computer components including the motherboard, CPU, RAM, expansion cards, and connections for other components. The motherboard serves as the central component that connects the other parts of the computer including storage devices, expansion cards, and buses that allow communication between all components.