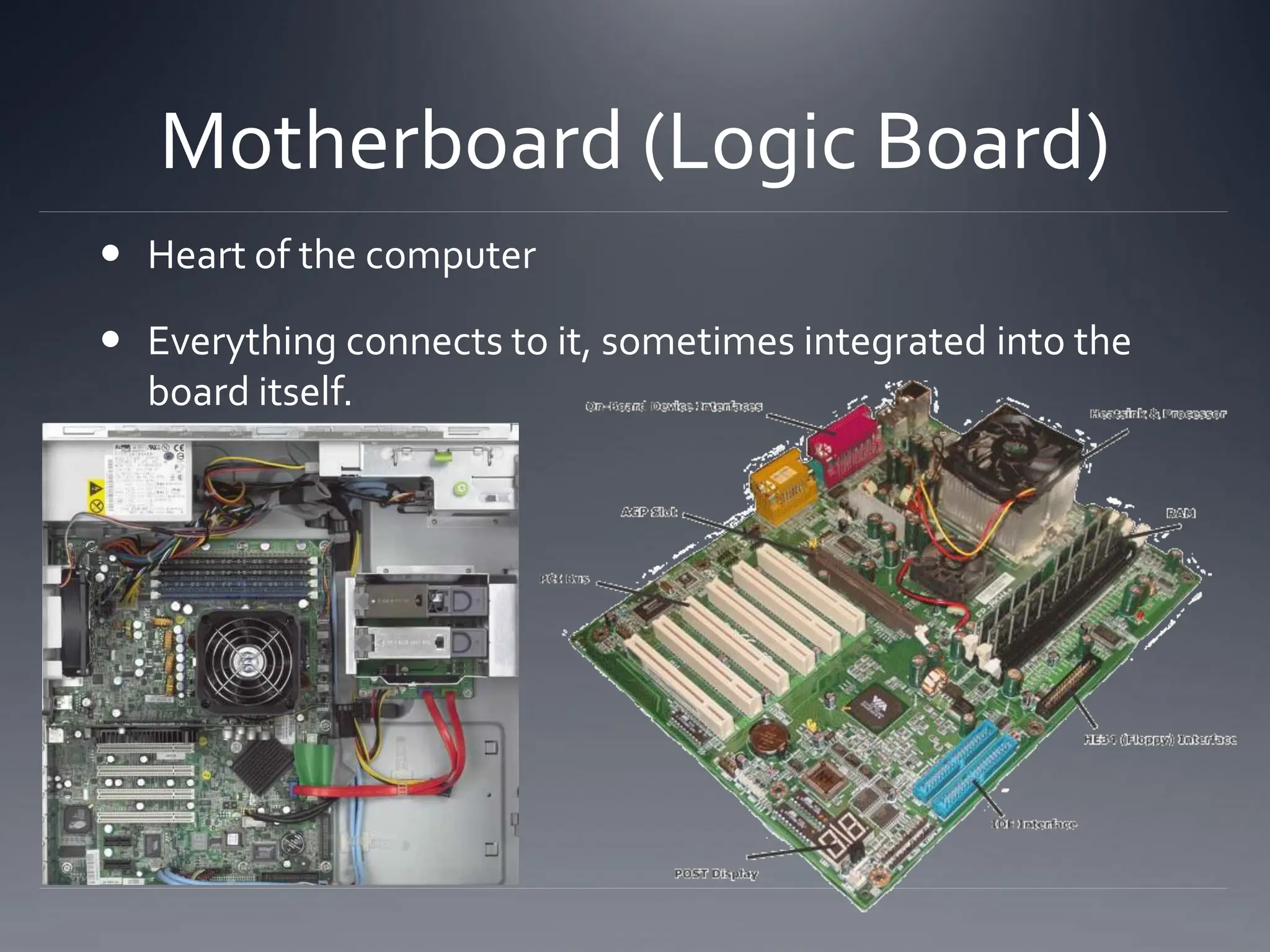
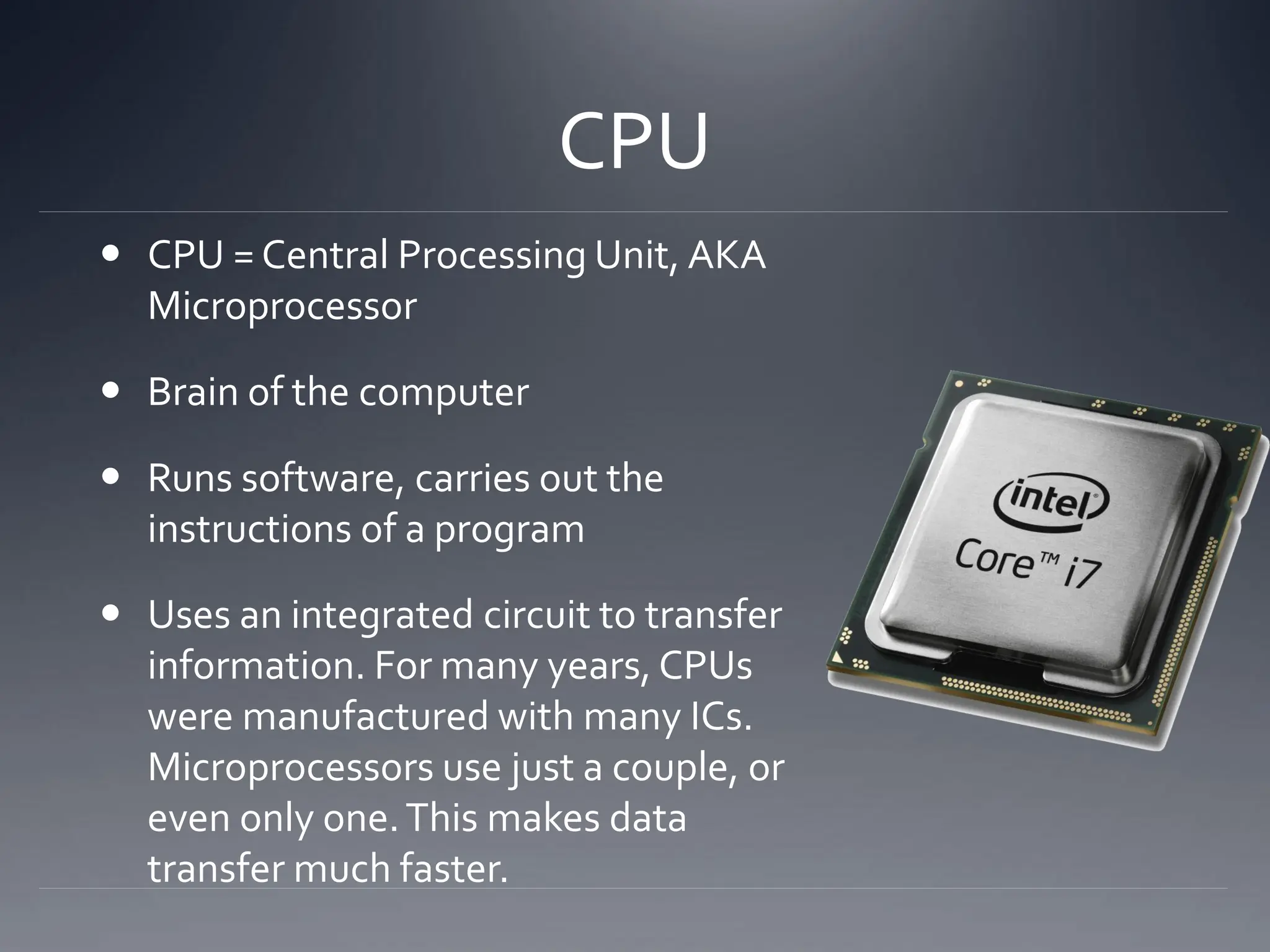
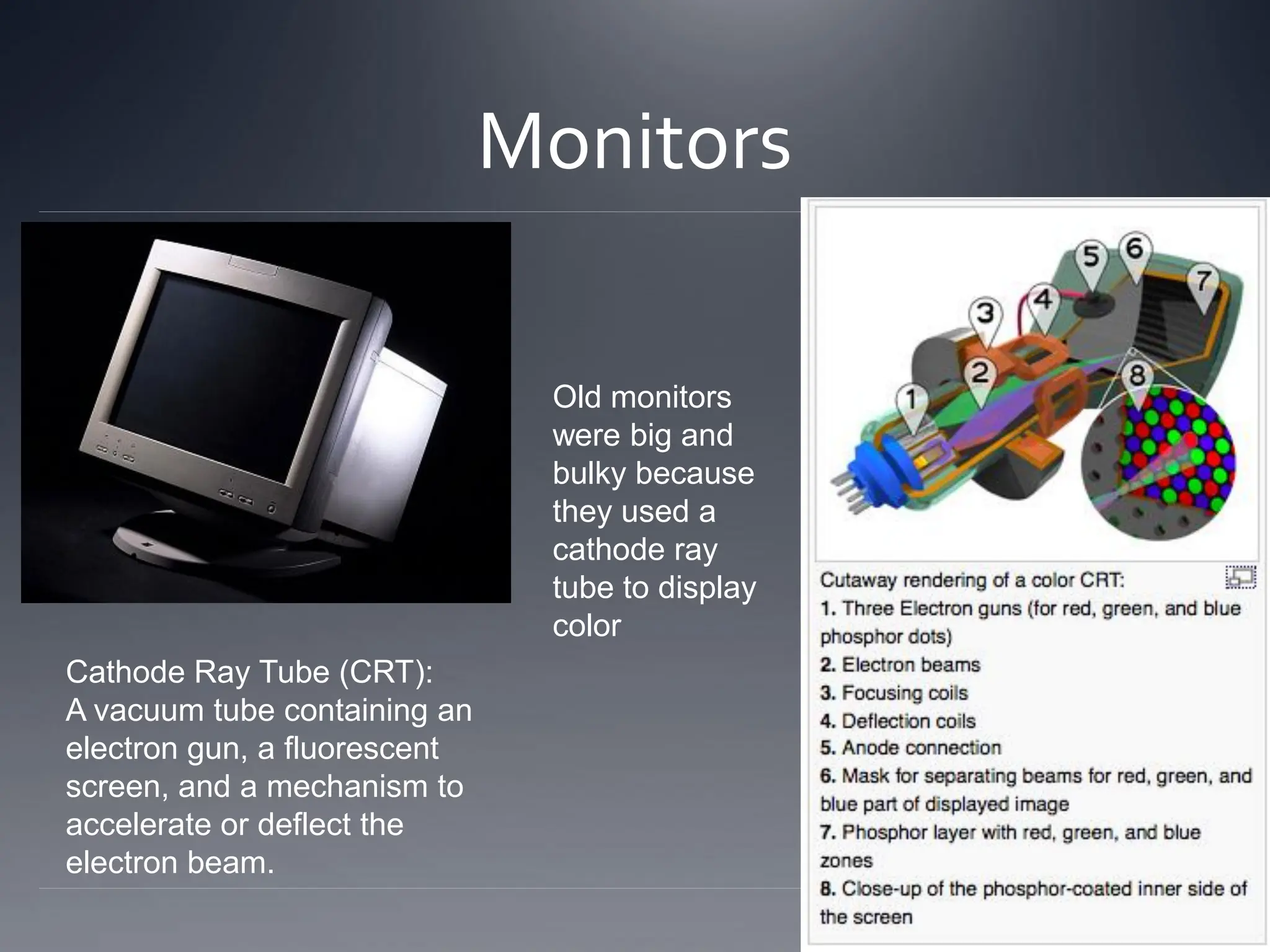
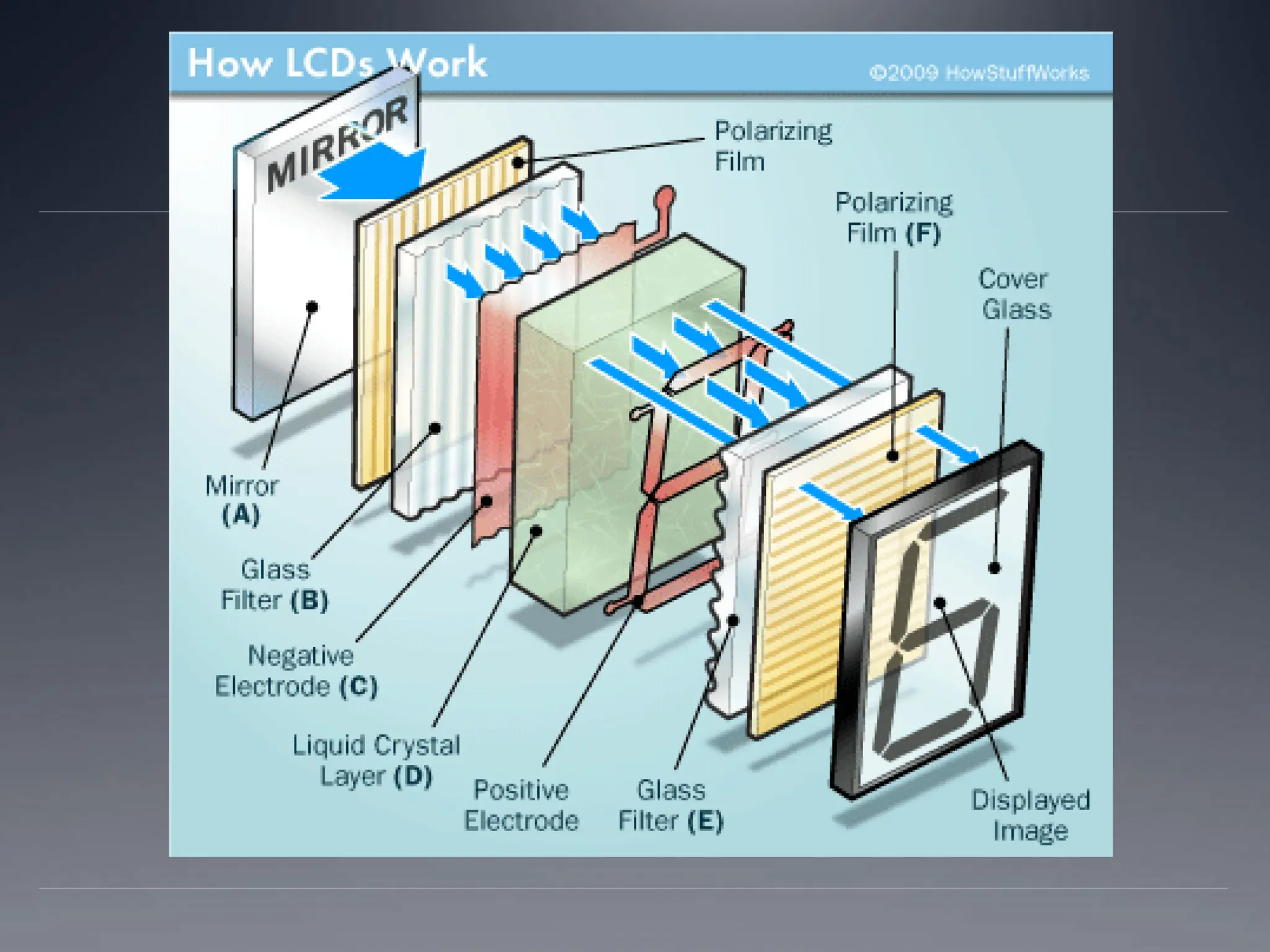
The document outlines the essential hardware components inside a computer, including the motherboard, CPU, hard disk, memory (RAM and ROM), video card, sound card, ethernet card, optical drive, power supply, and cooling system. It explains the functions of each component as well as concepts like Moore's Law, which predicts the growth of data density in CPUs and the transition to multi-core designs. Additionally, it discusses various input and output devices, highlighting their roles in computer interaction and communication.