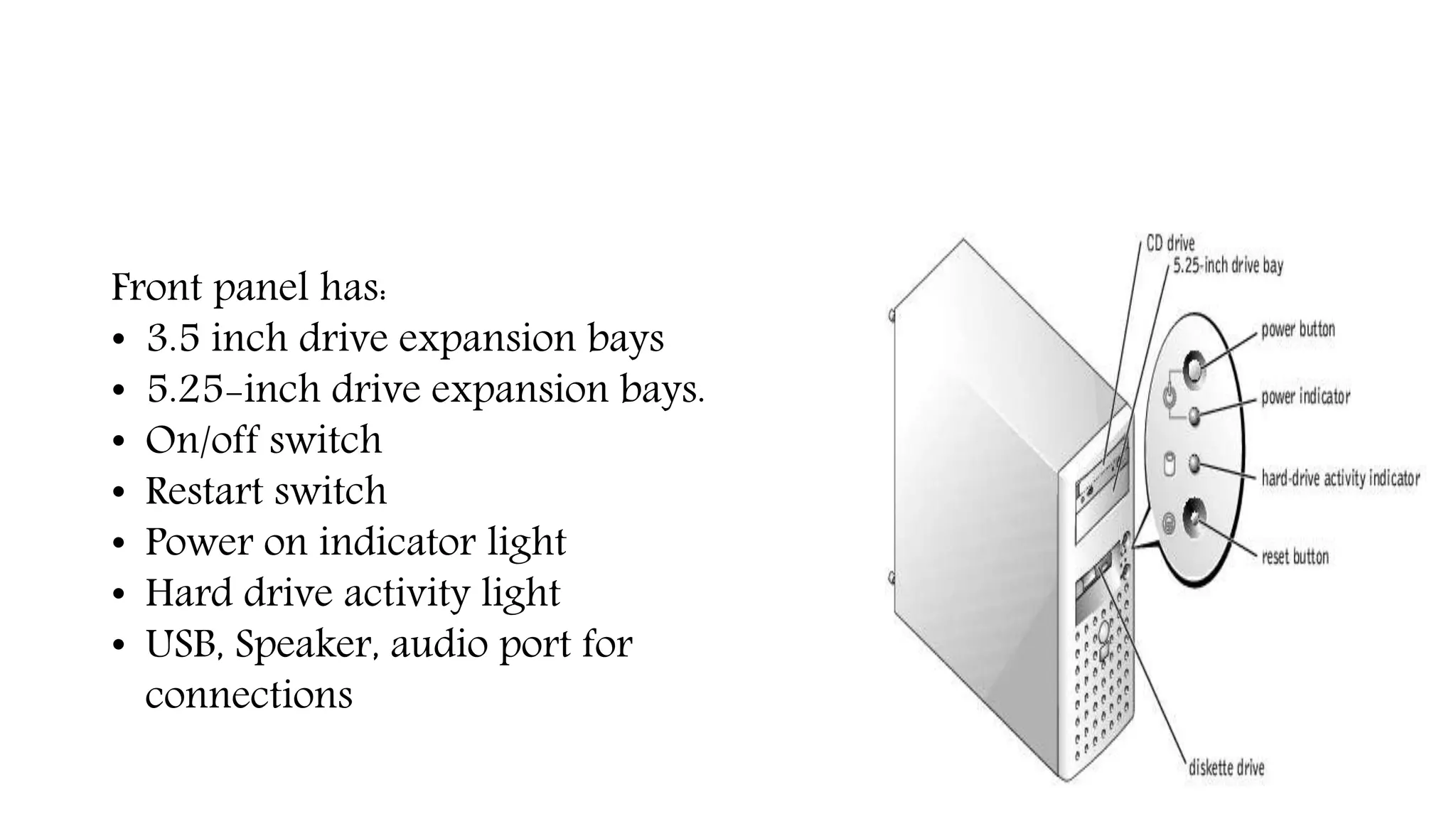
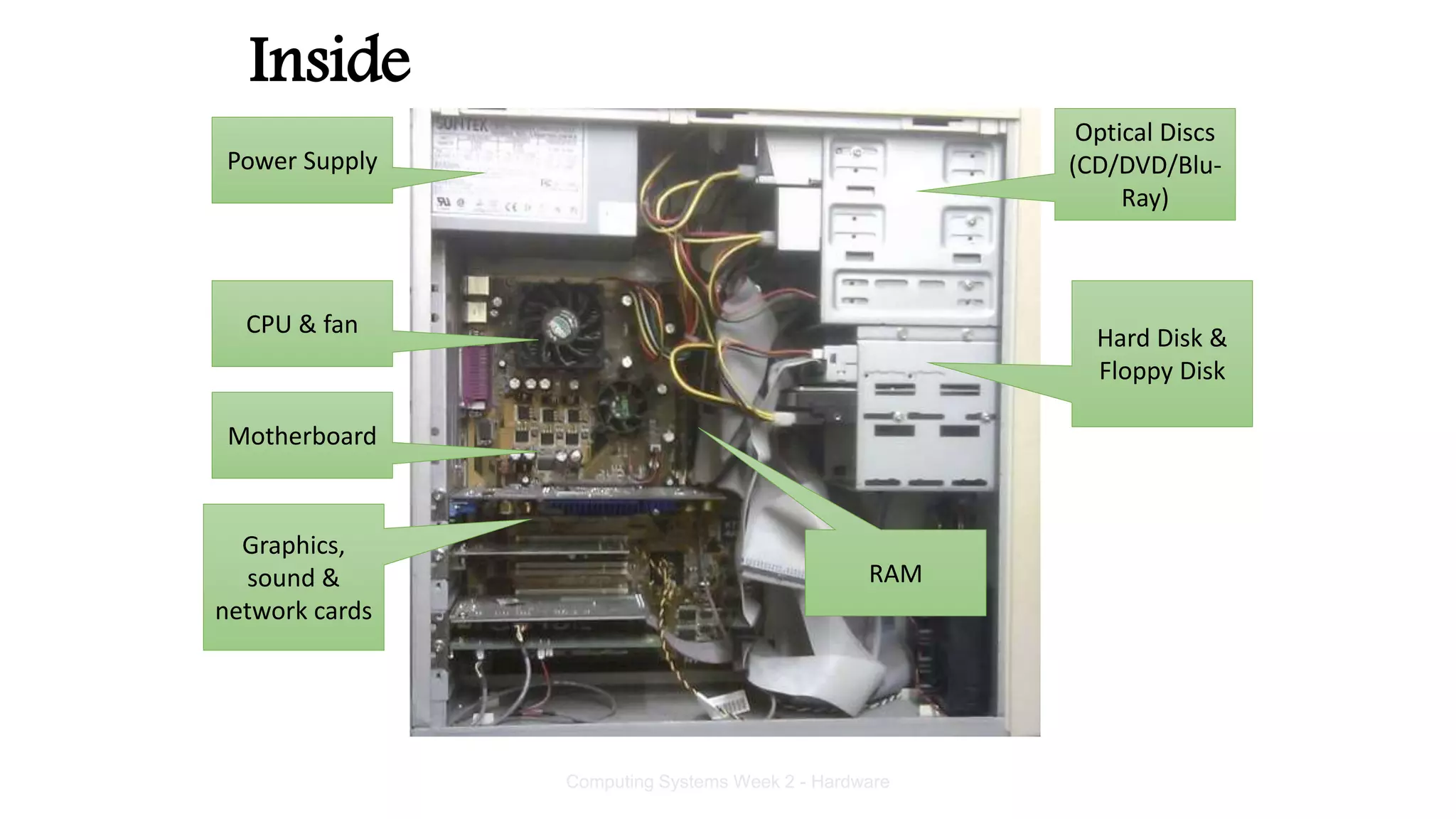
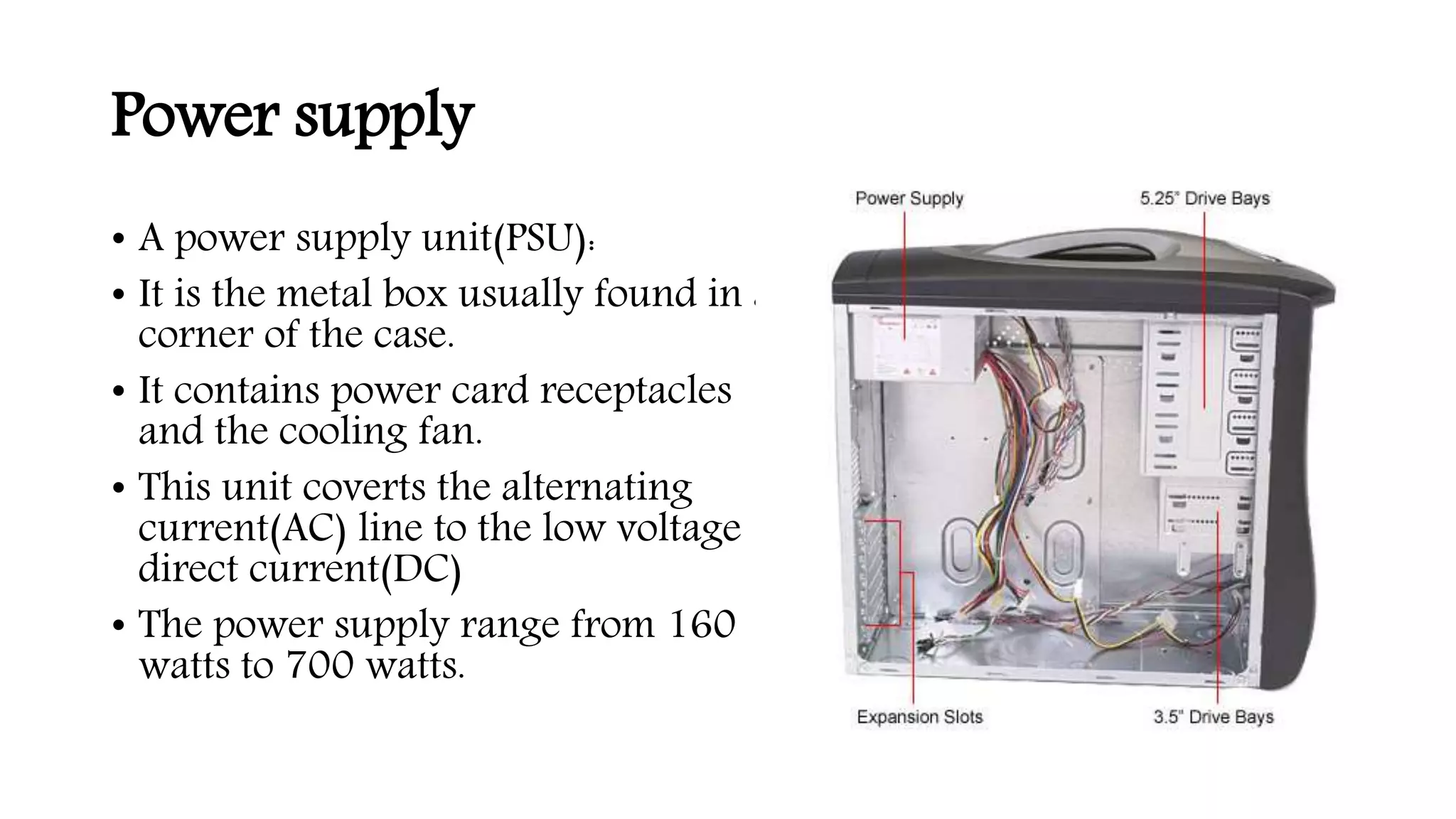
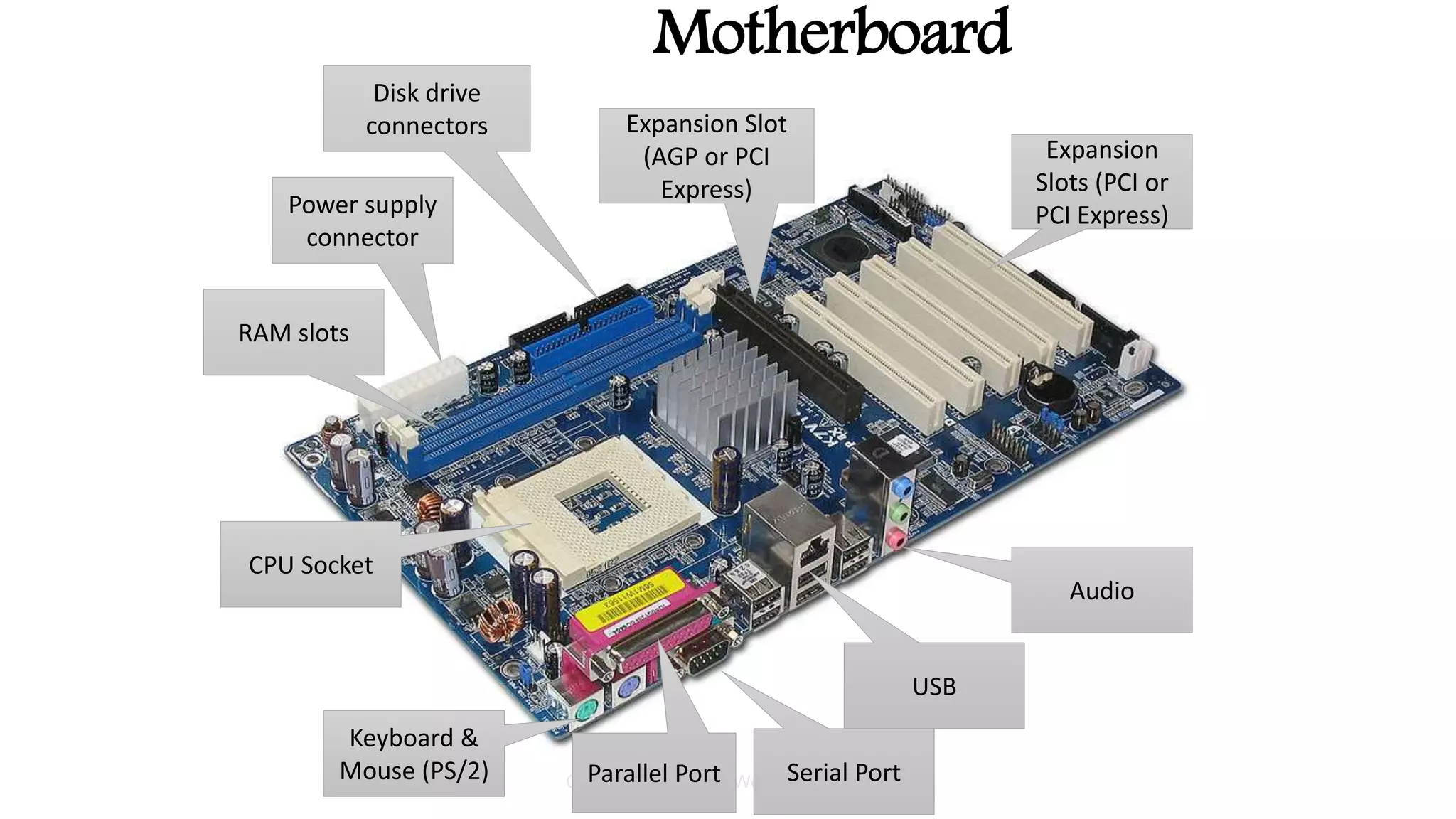
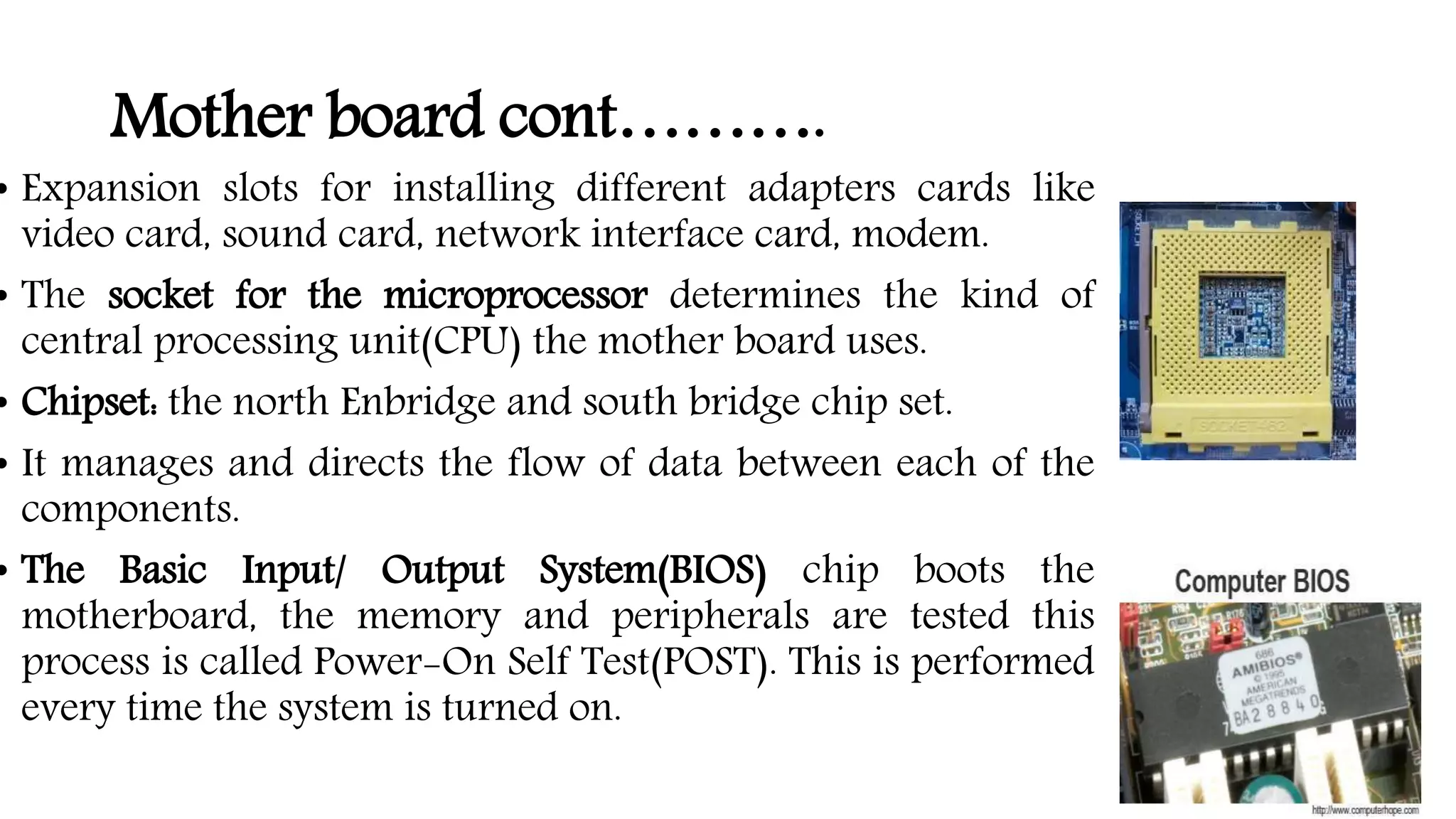
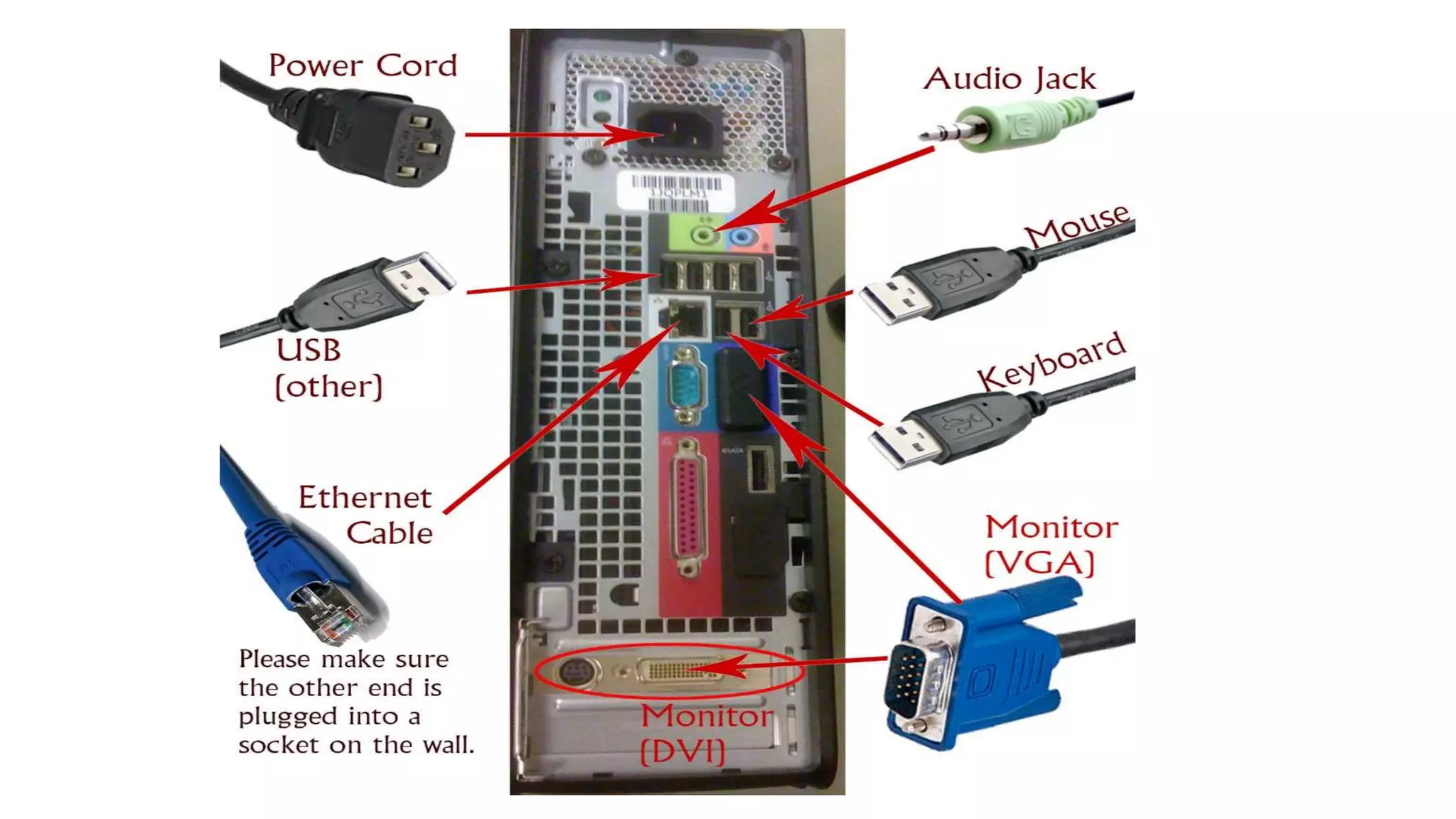
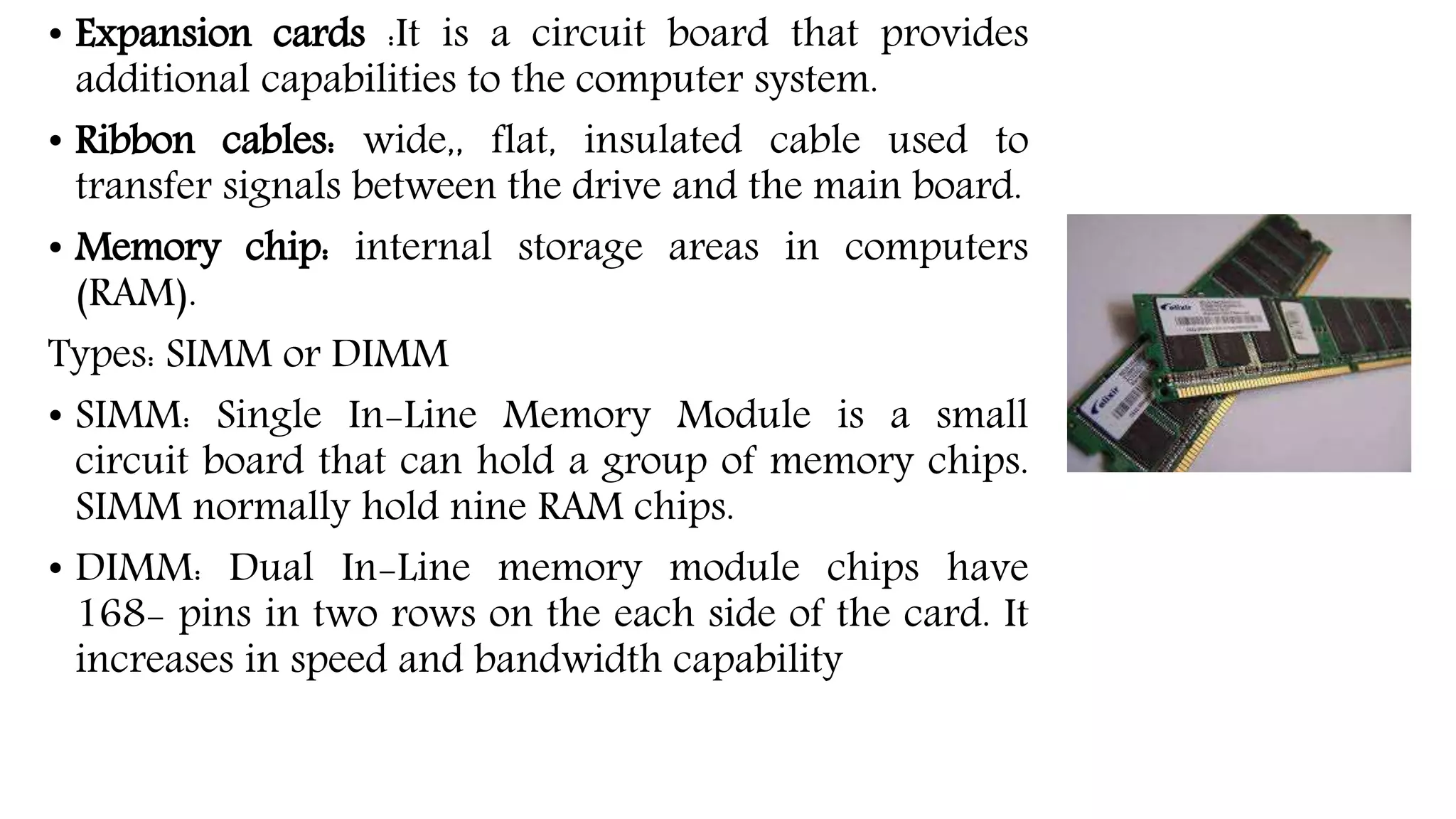
The system case contains and protects the main computer components. It has expansion bays for drives and ports on the front panel. The power supply converts AC to DC power for components. The motherboard connects all components using buses and contains the CPU, memory, chipset and expansion slots. Storage devices like hard drives and optical drives store programs and data. Ports allow connection of peripherals and expansion cards add capabilities.