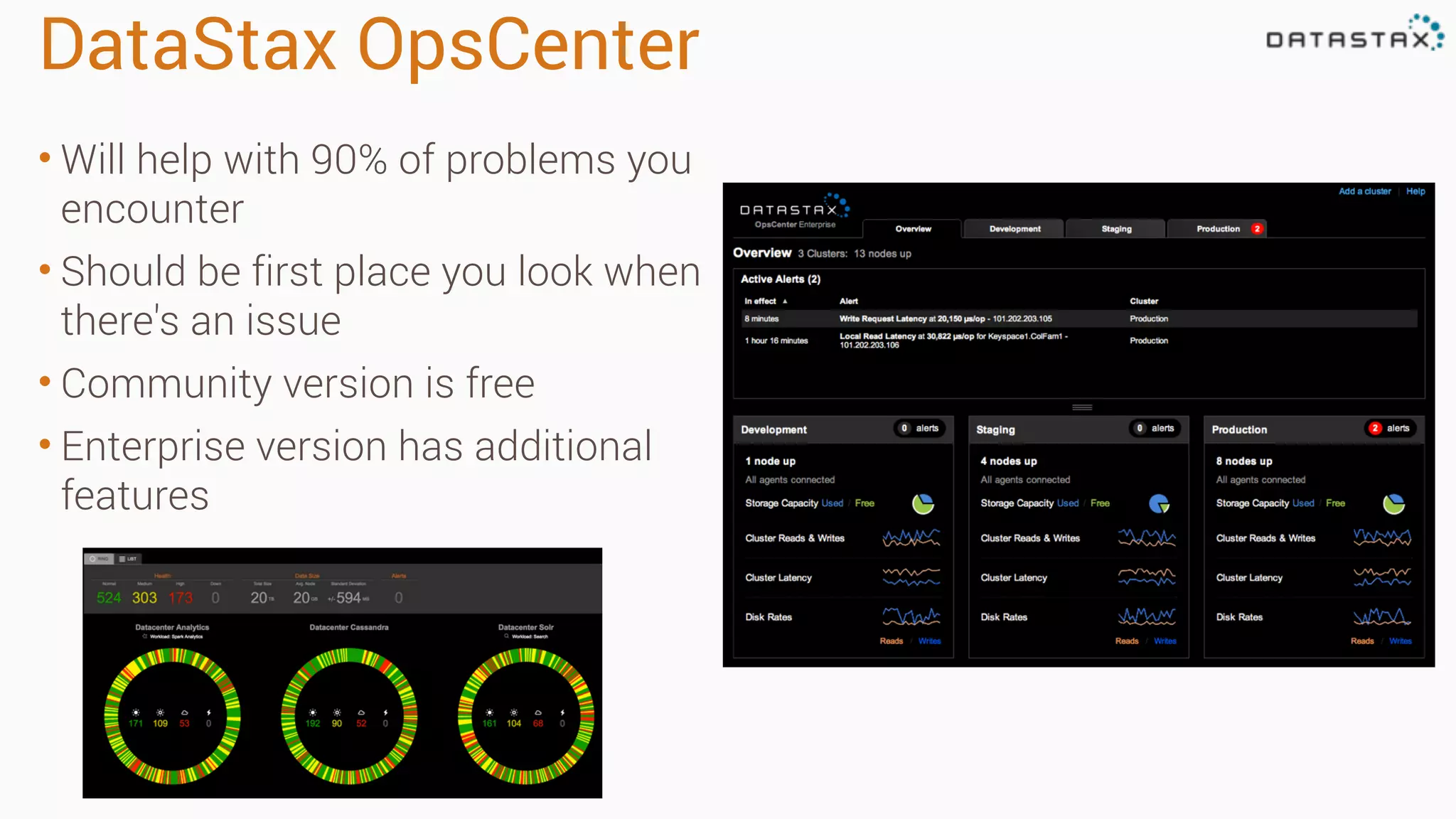
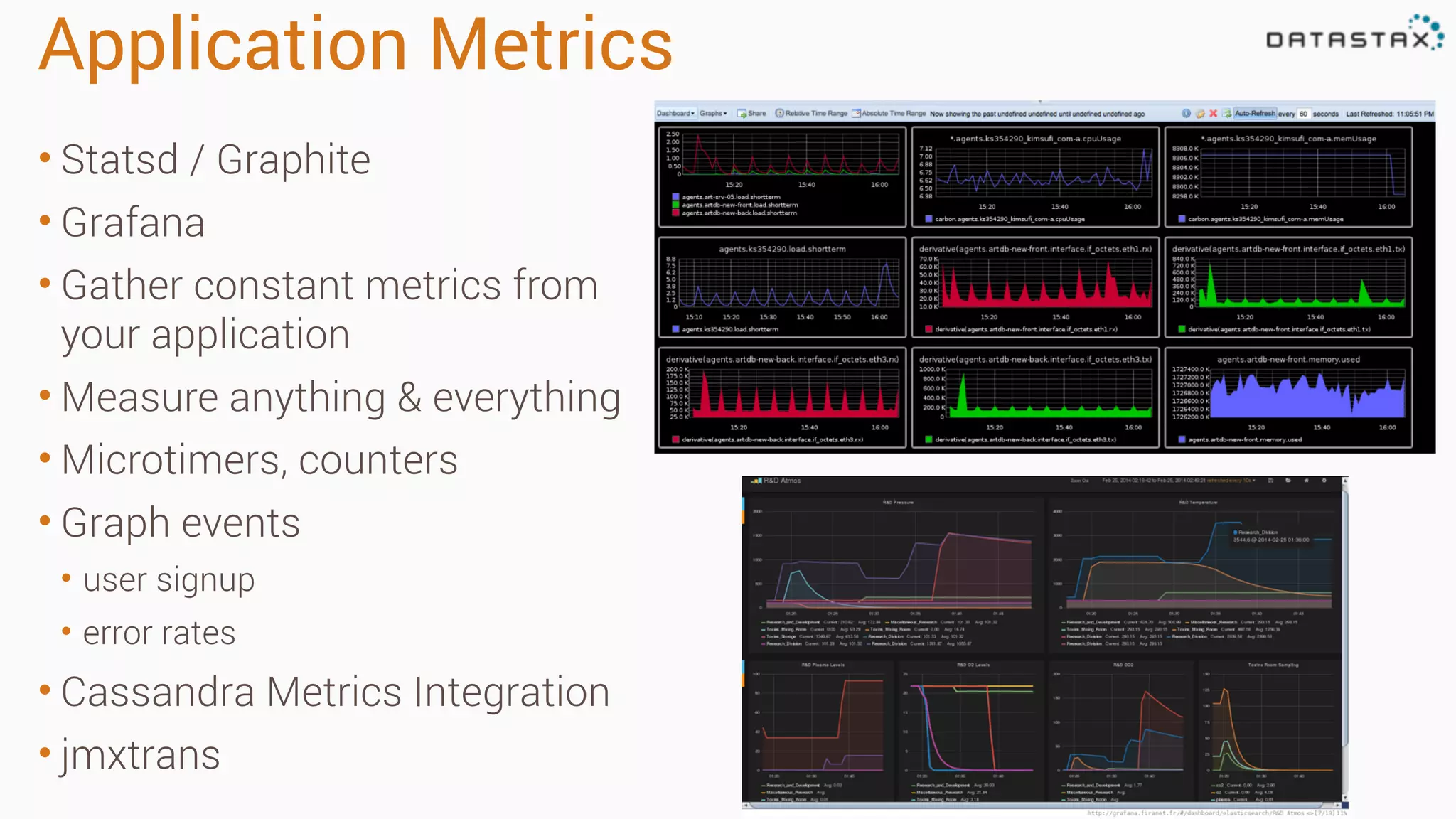
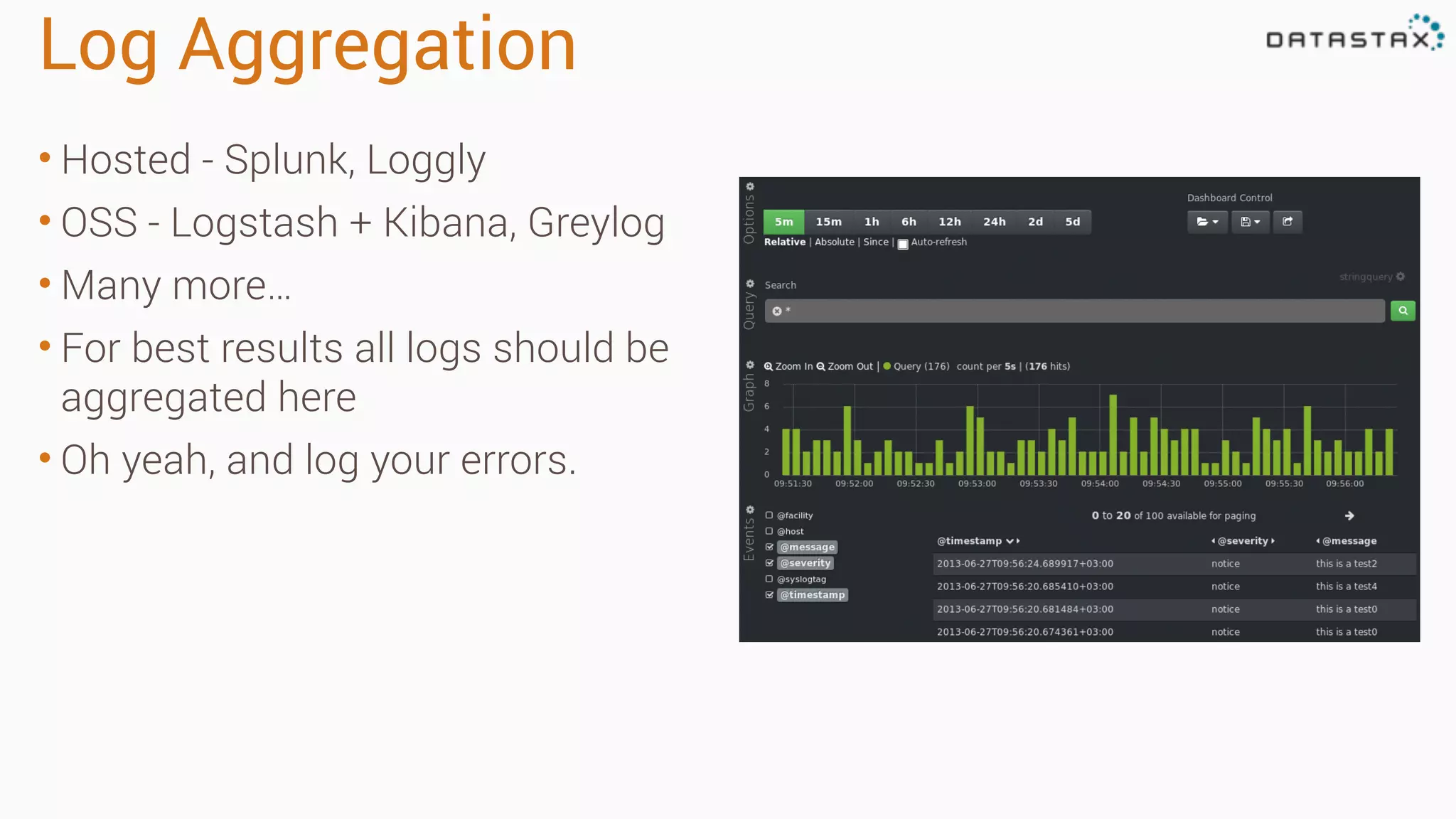
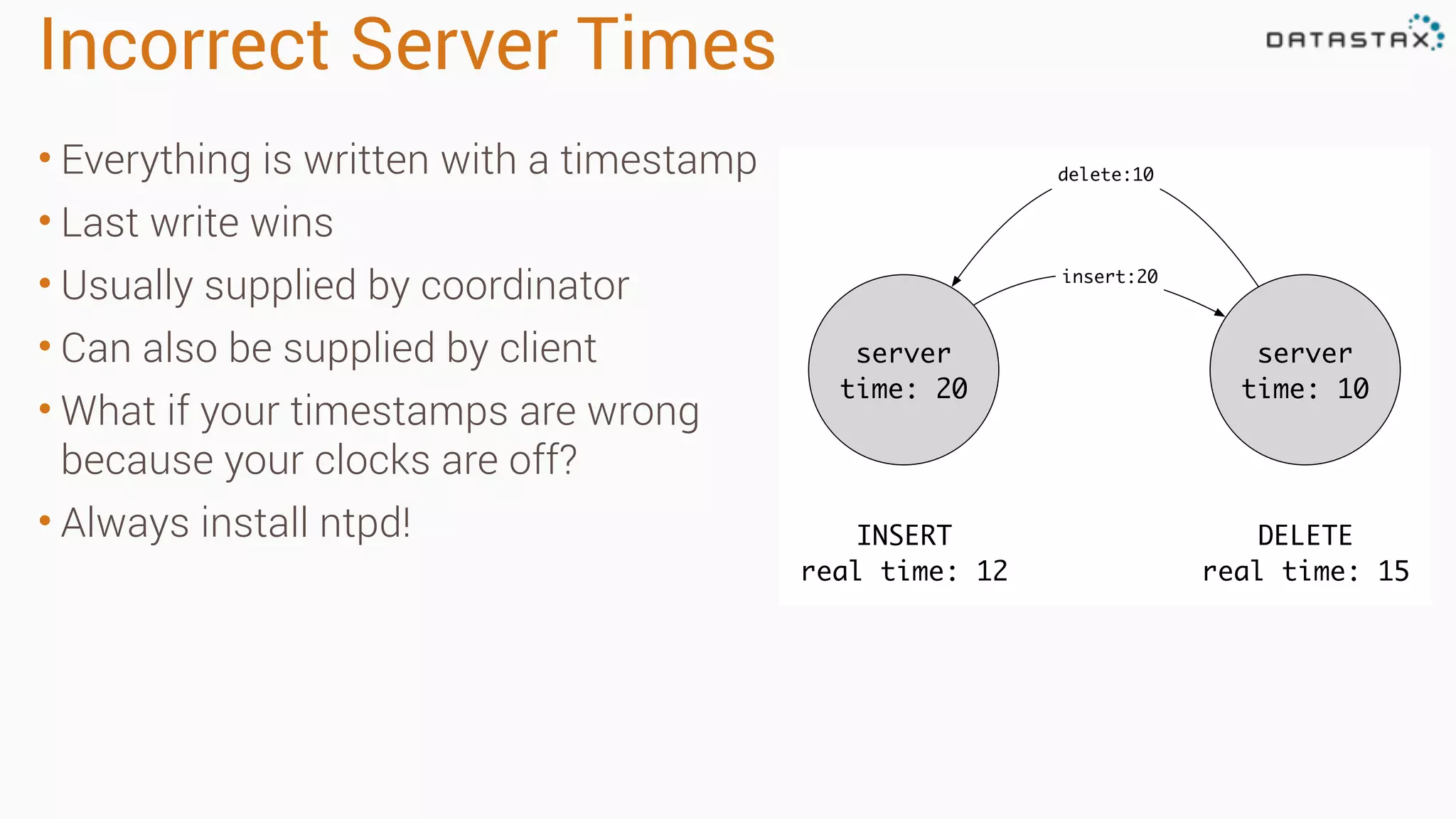
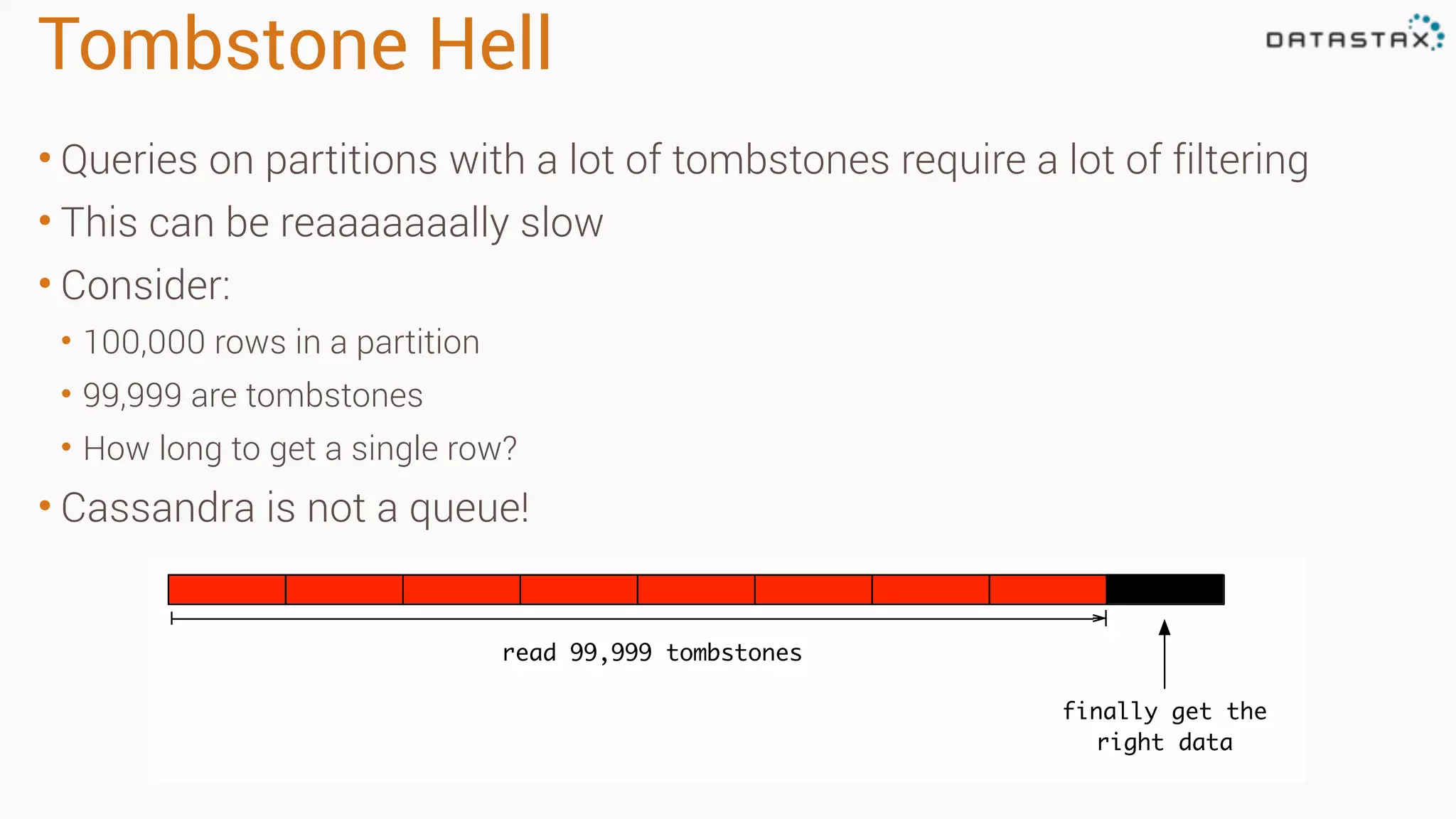
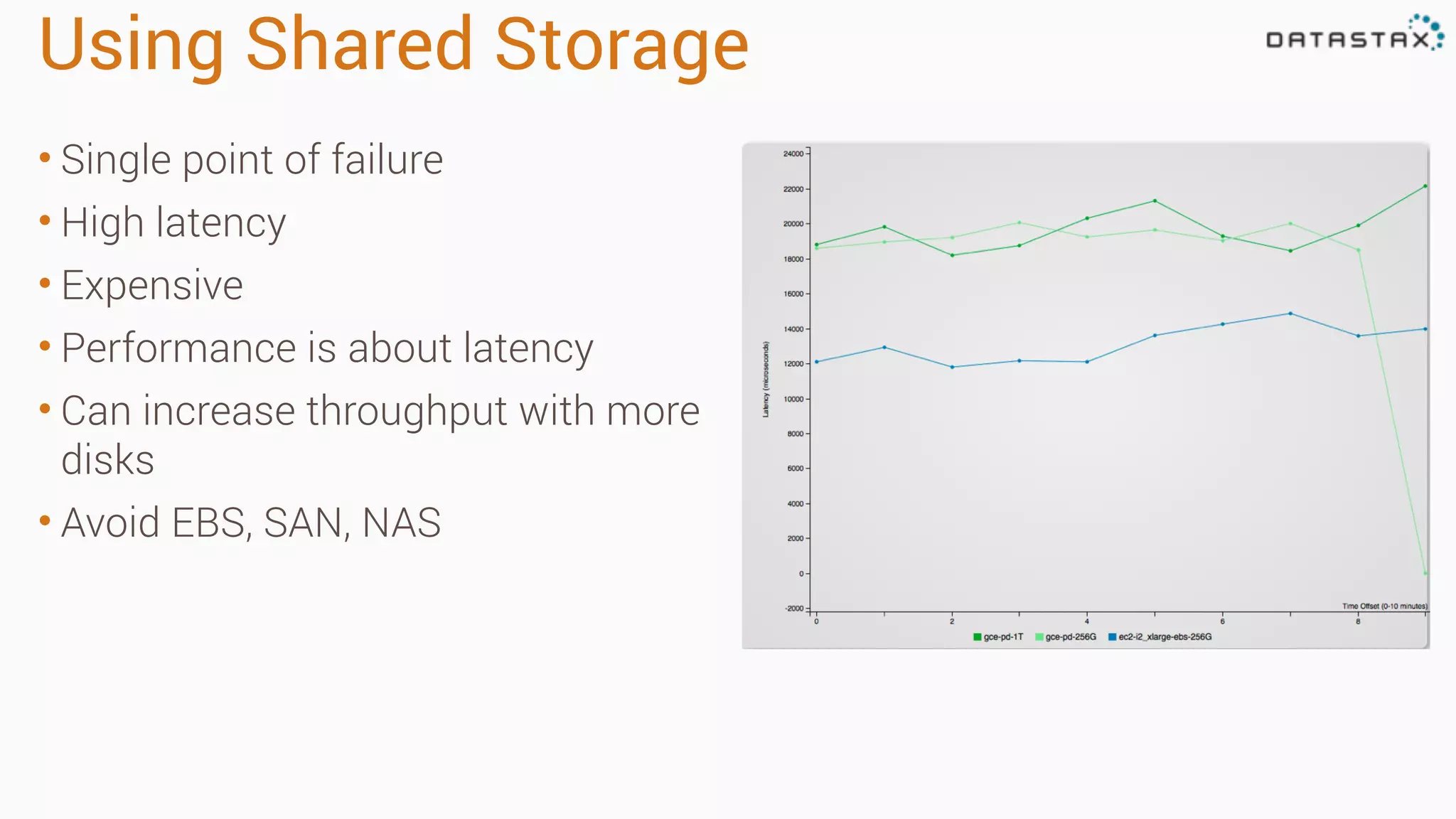
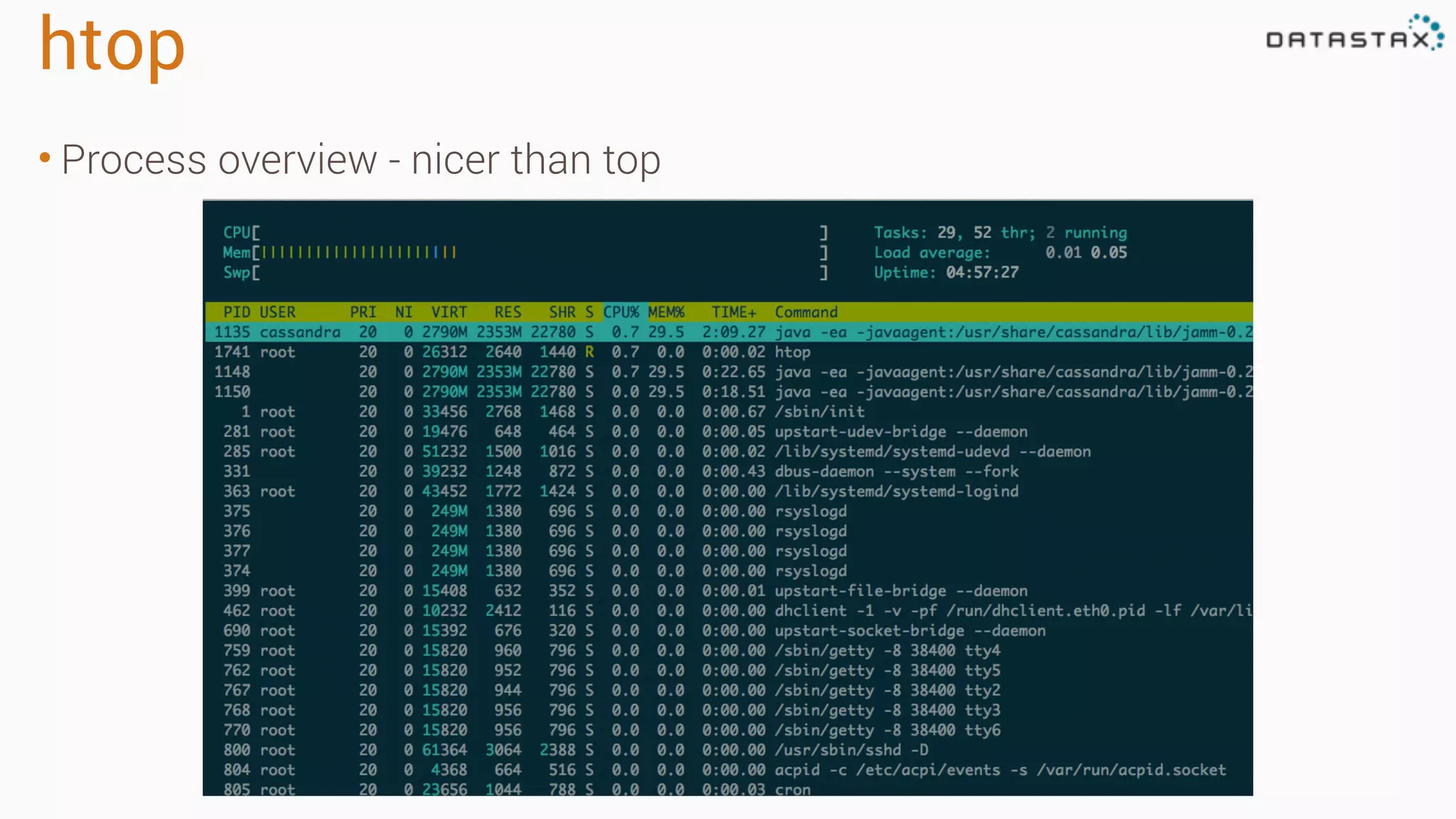
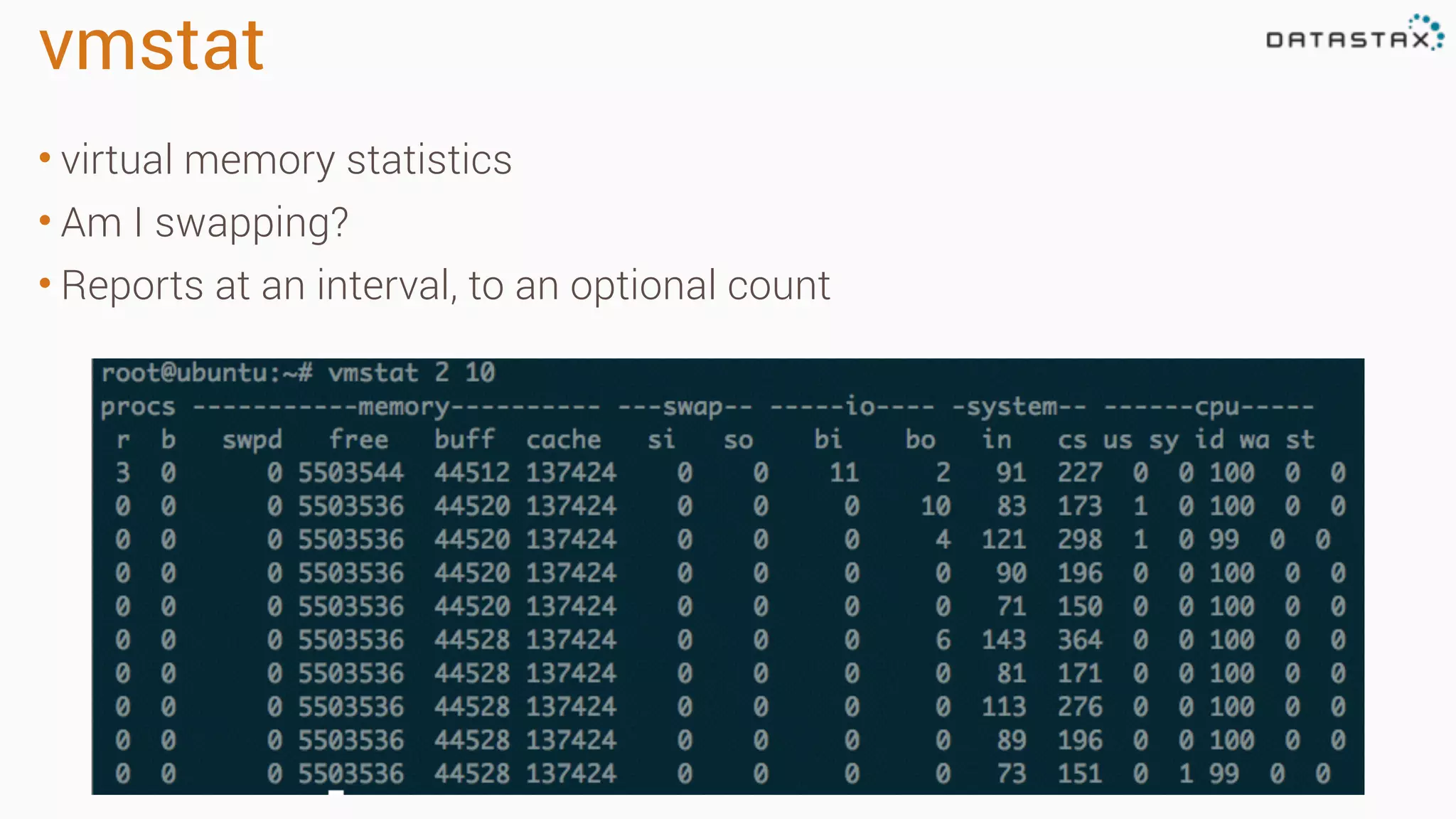
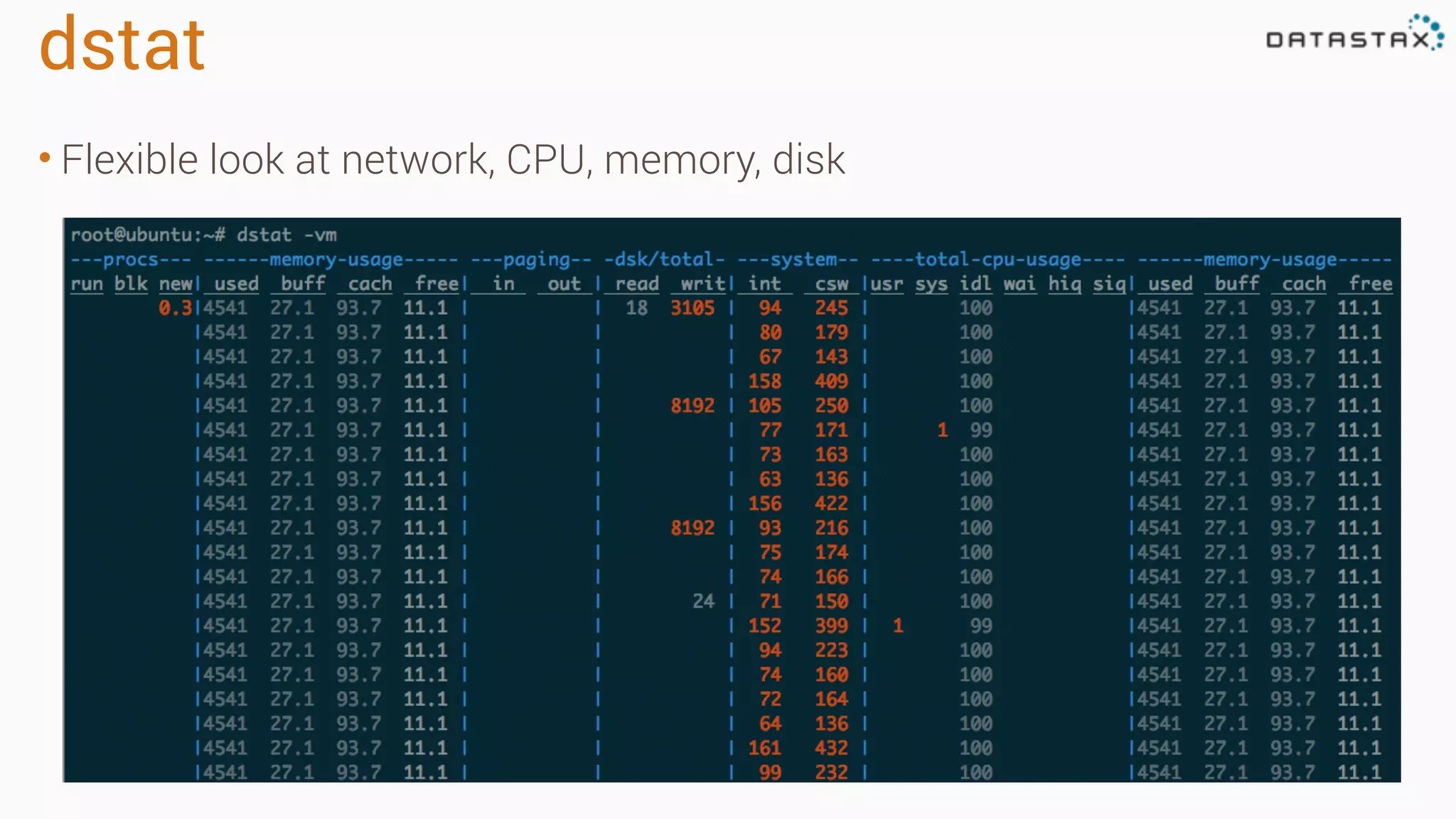
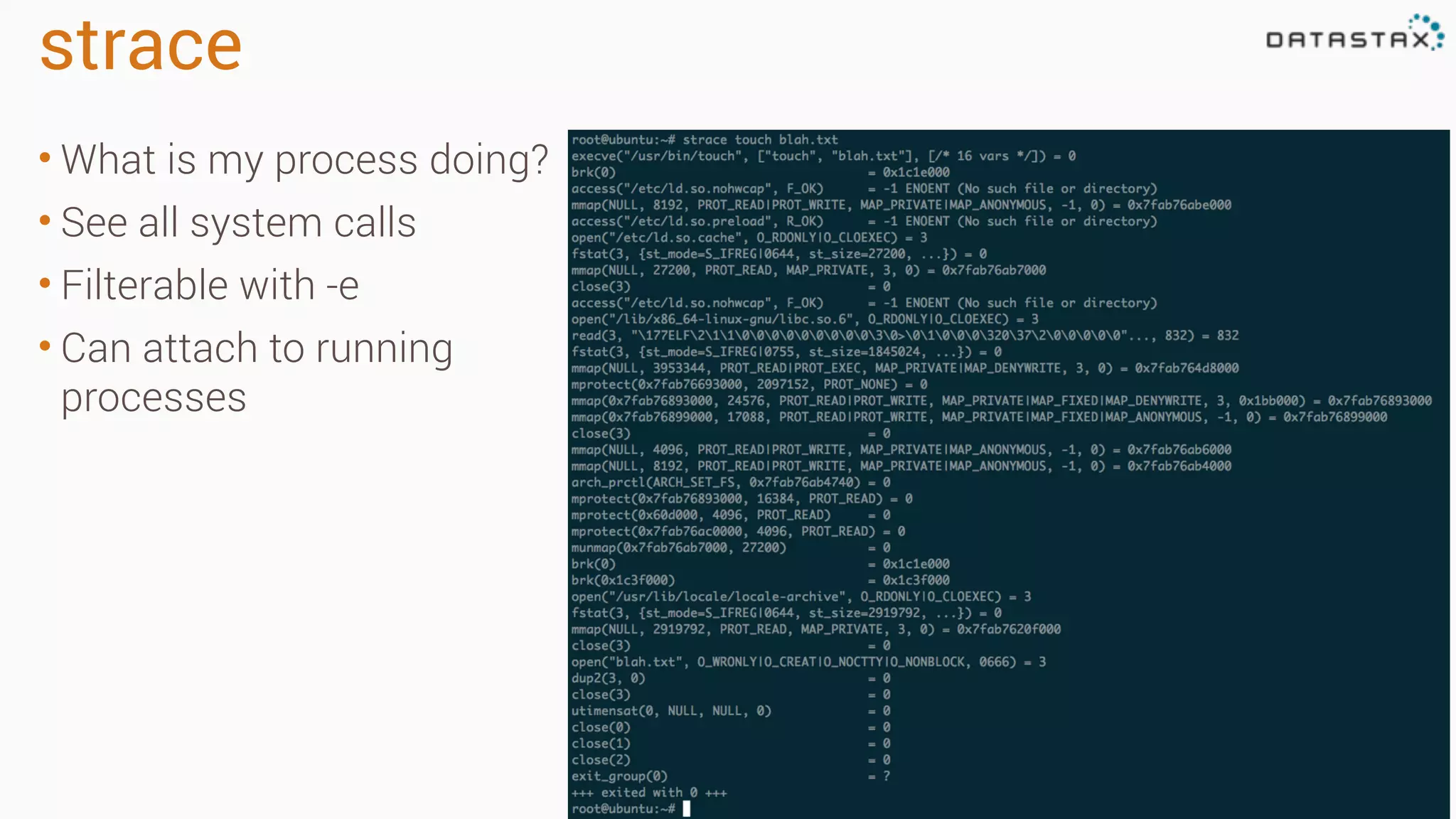
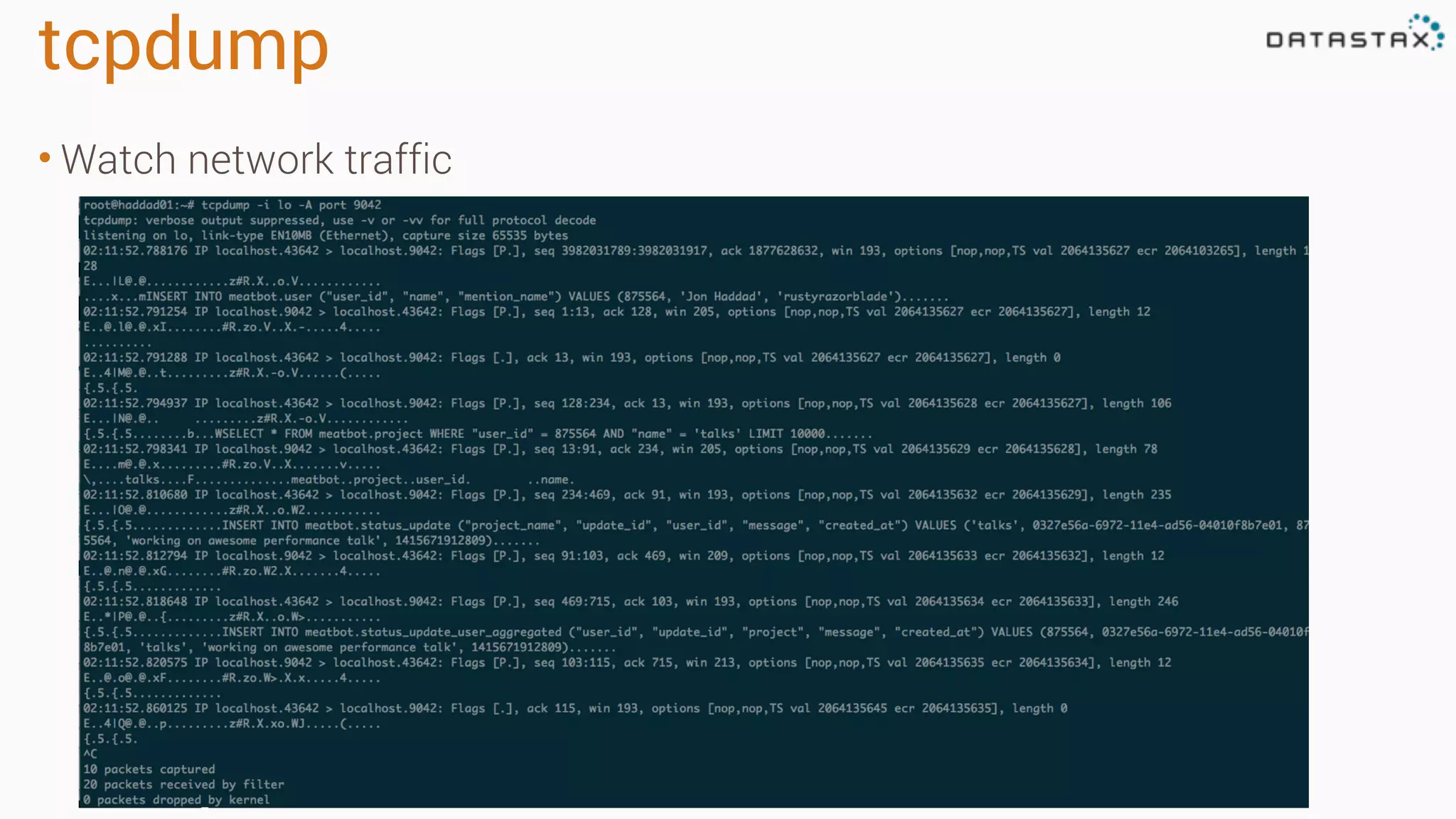
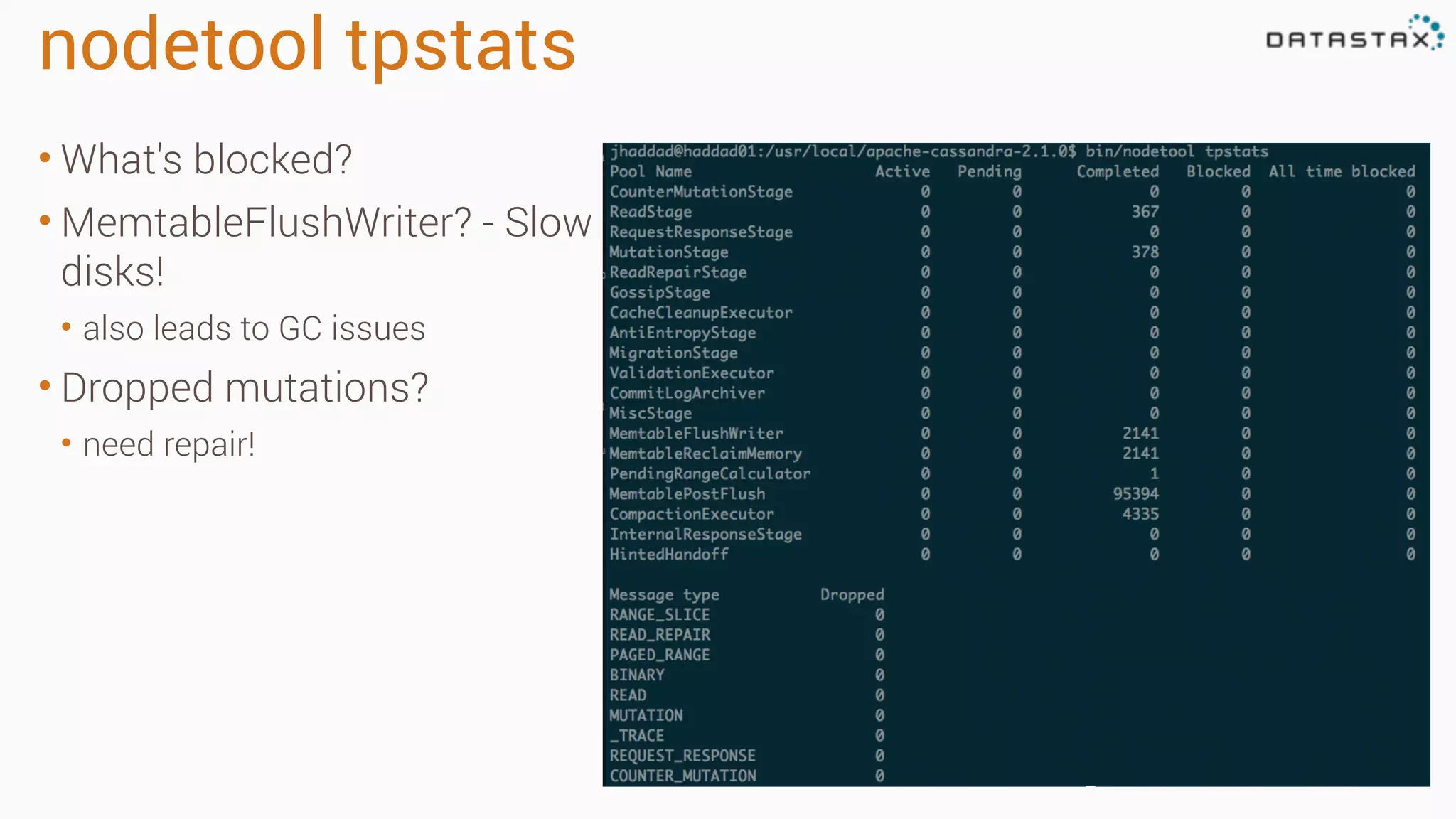
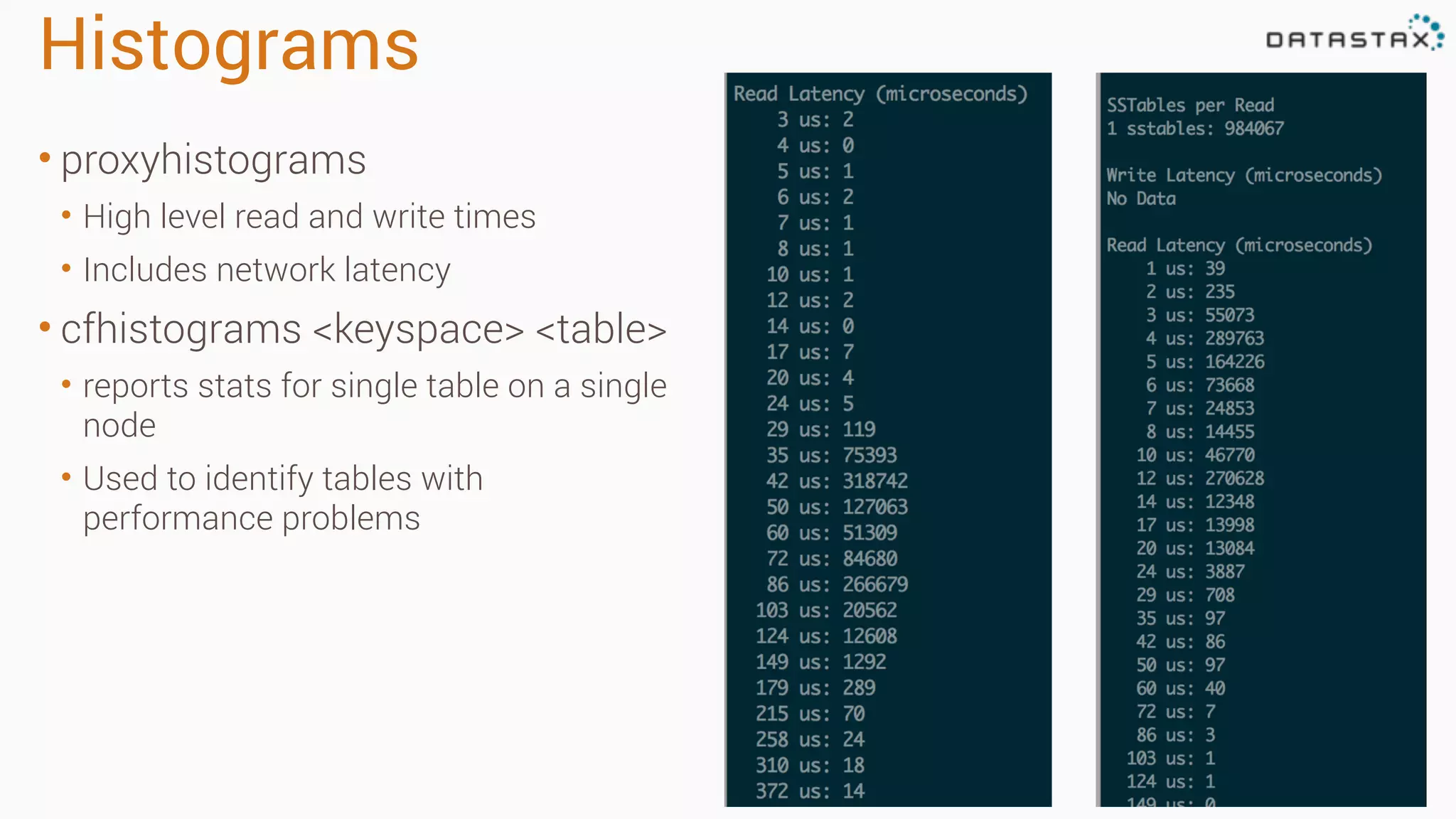
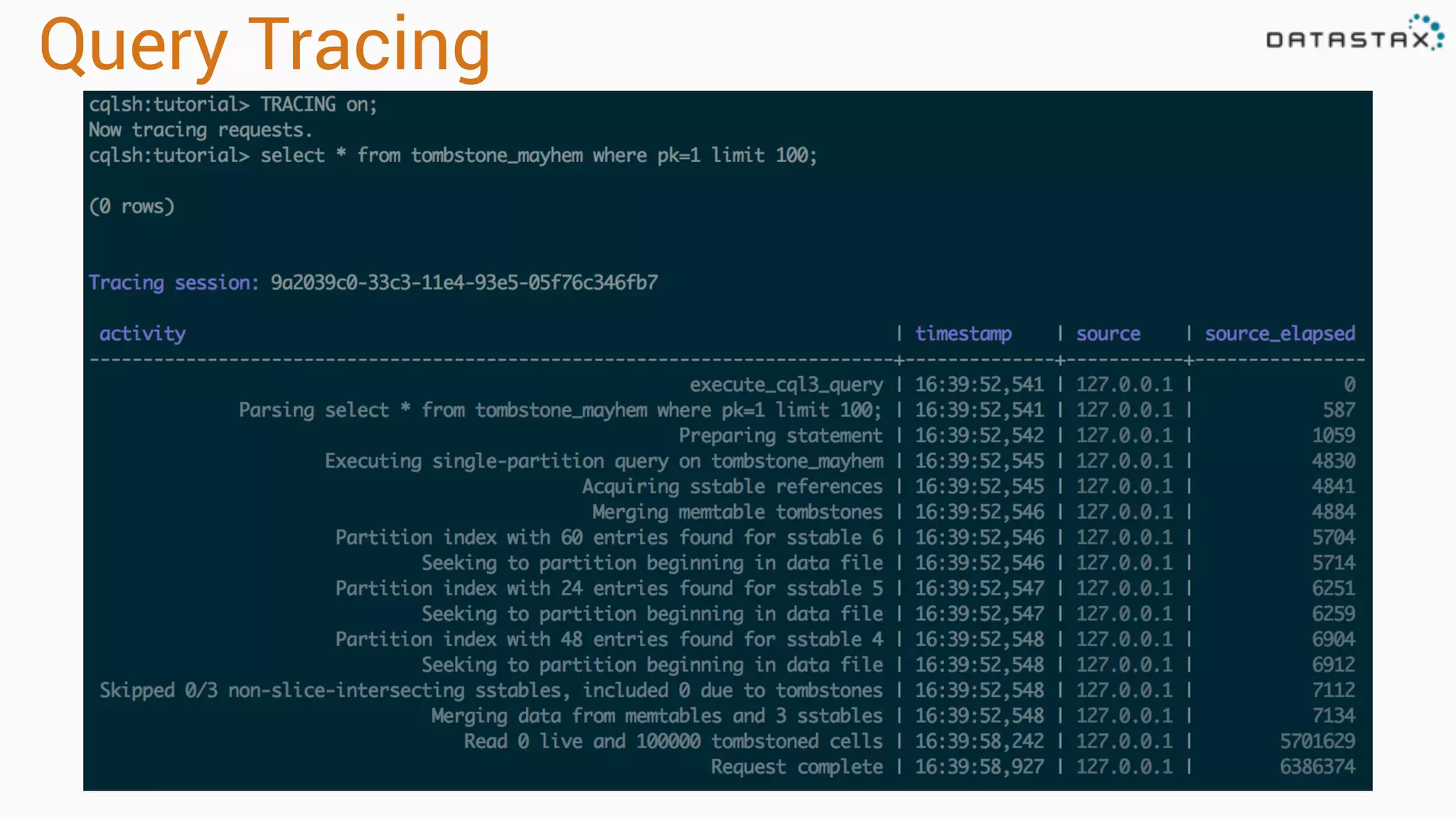
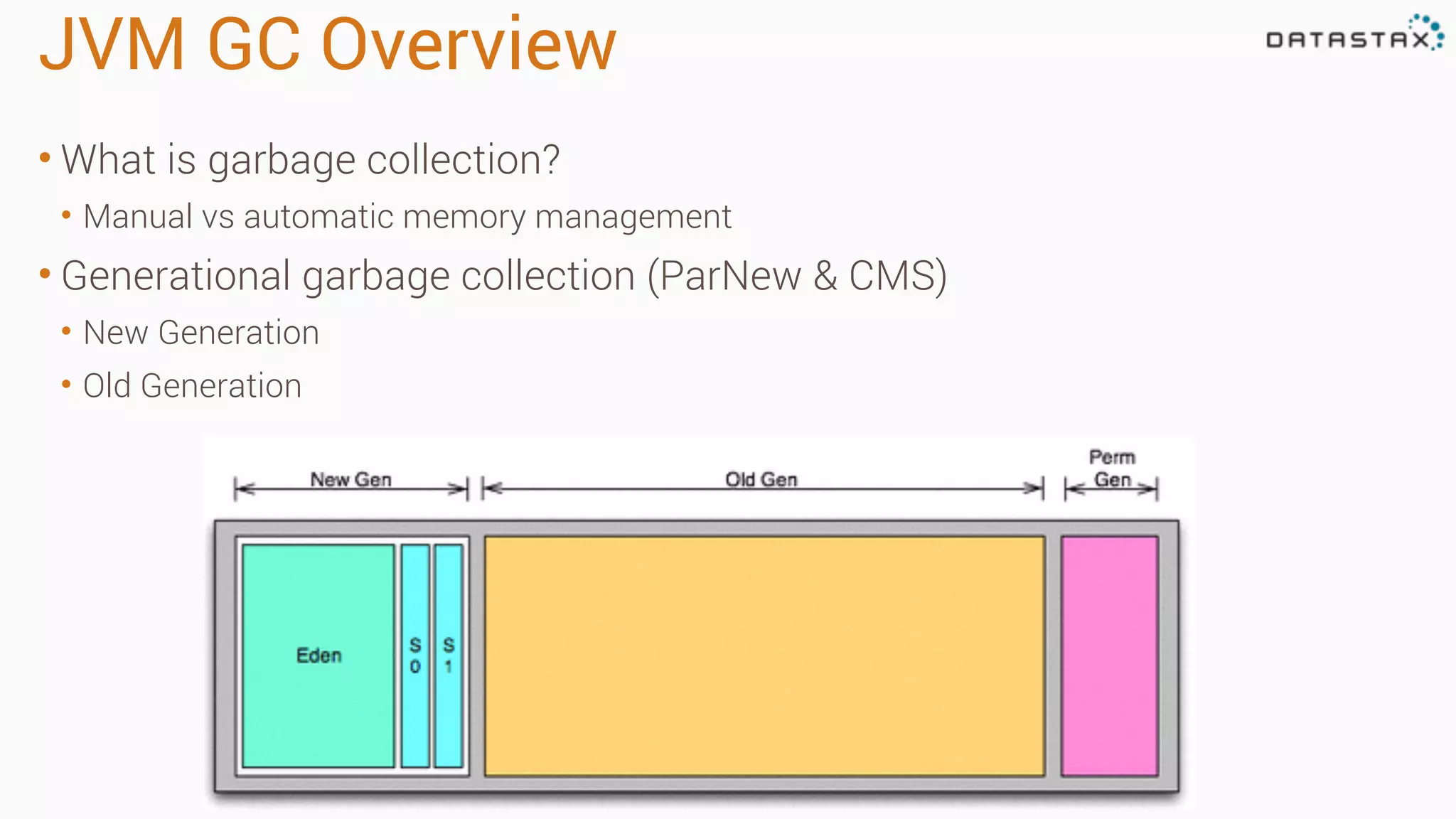
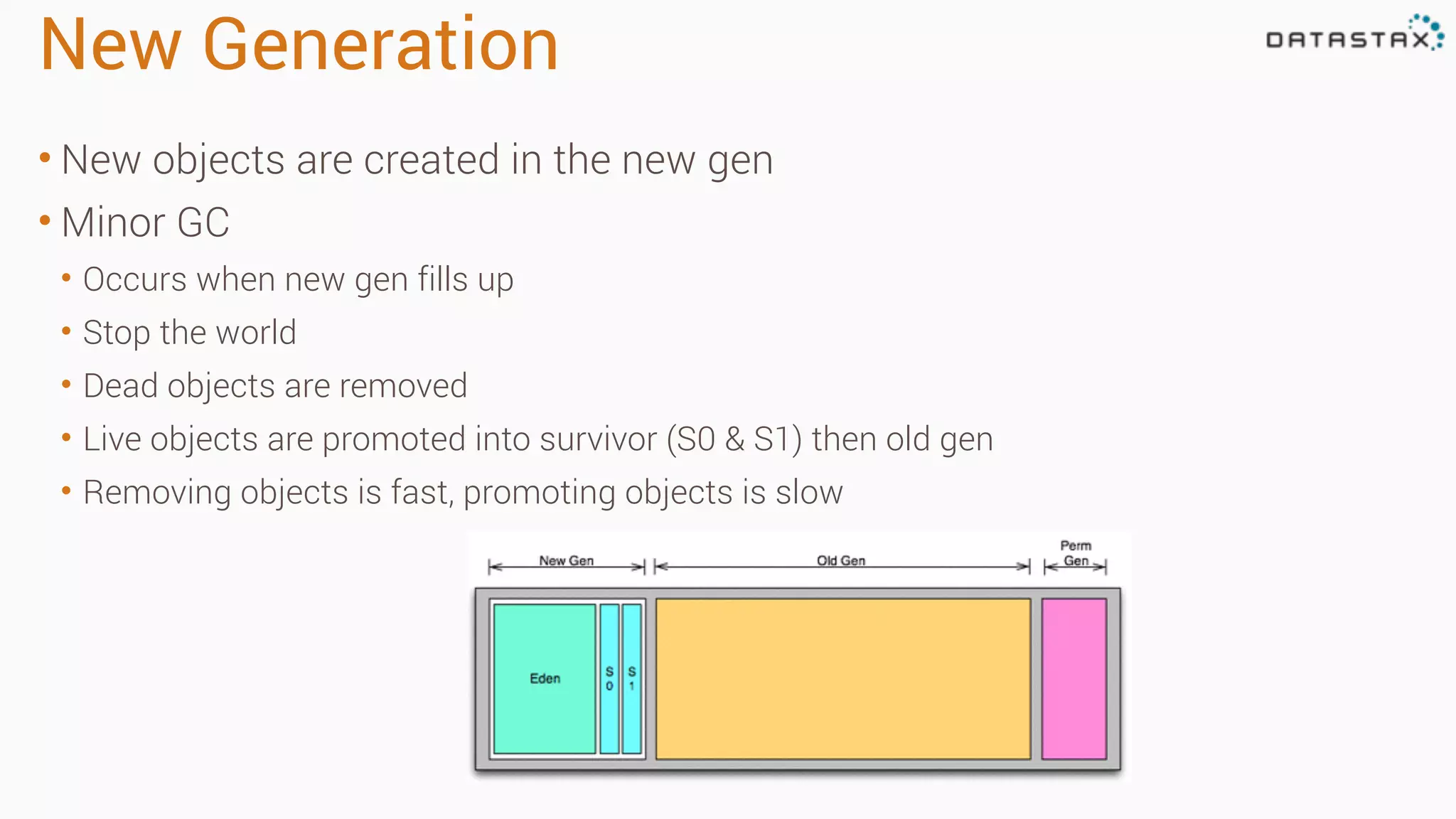
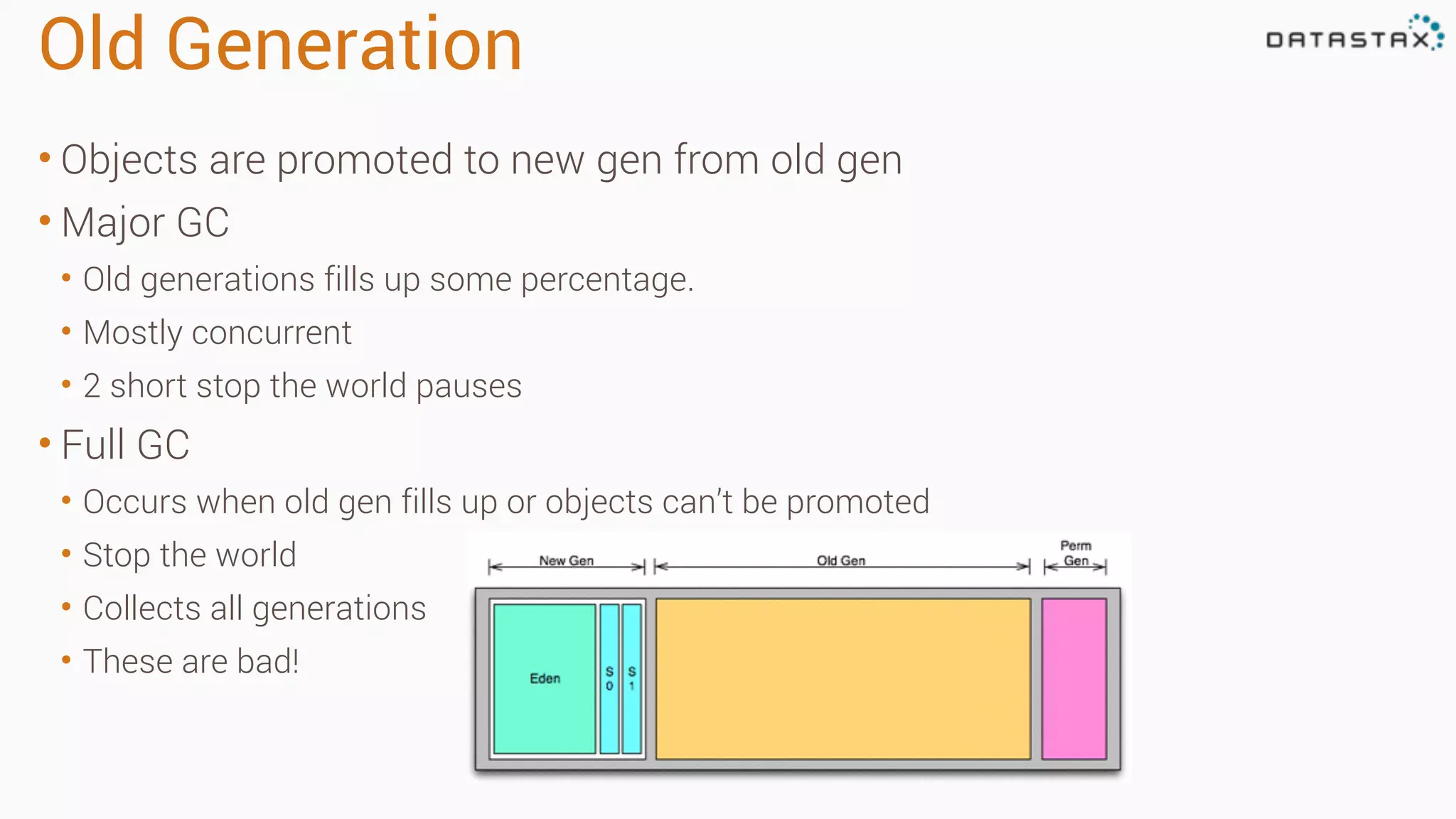
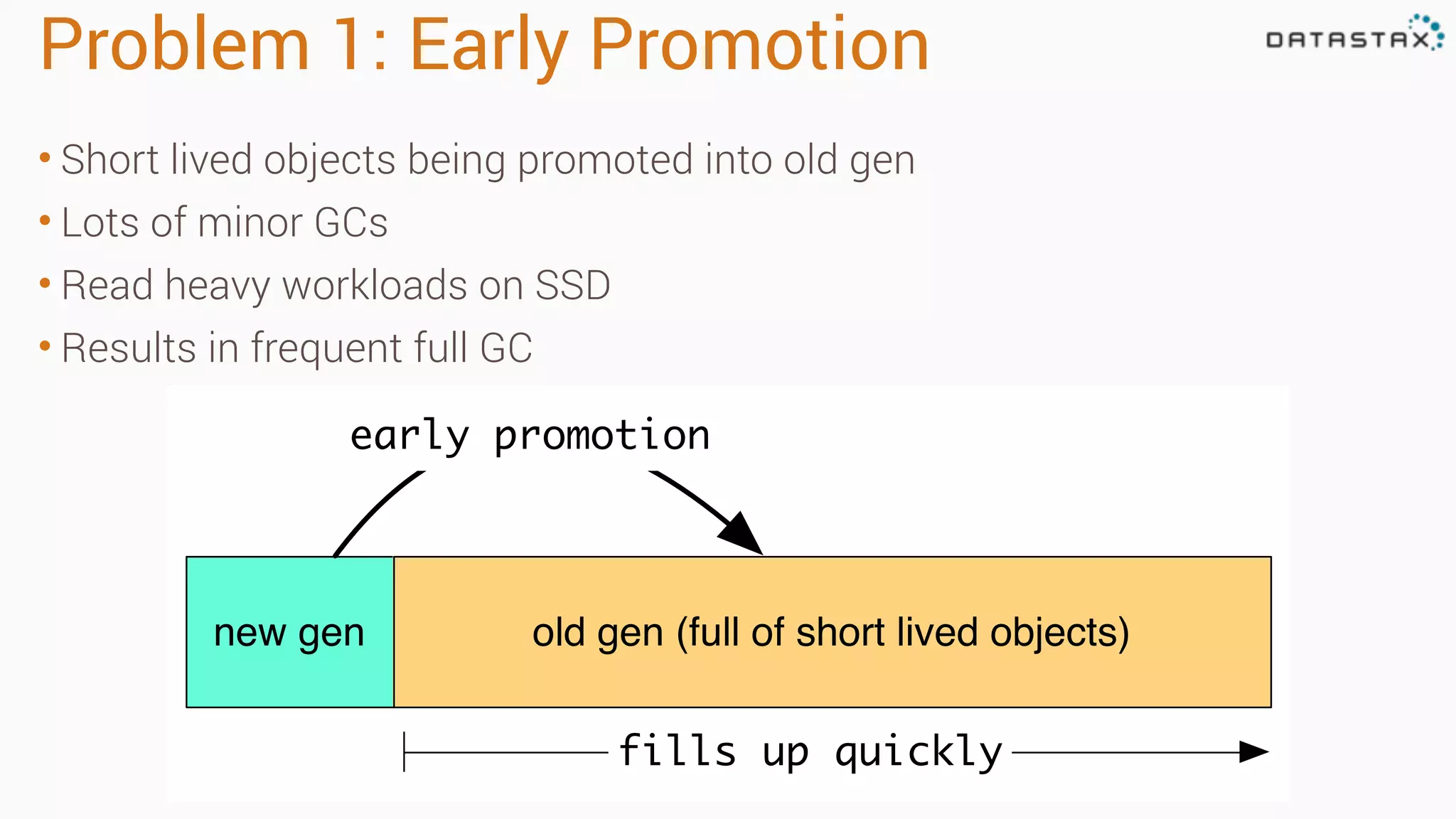
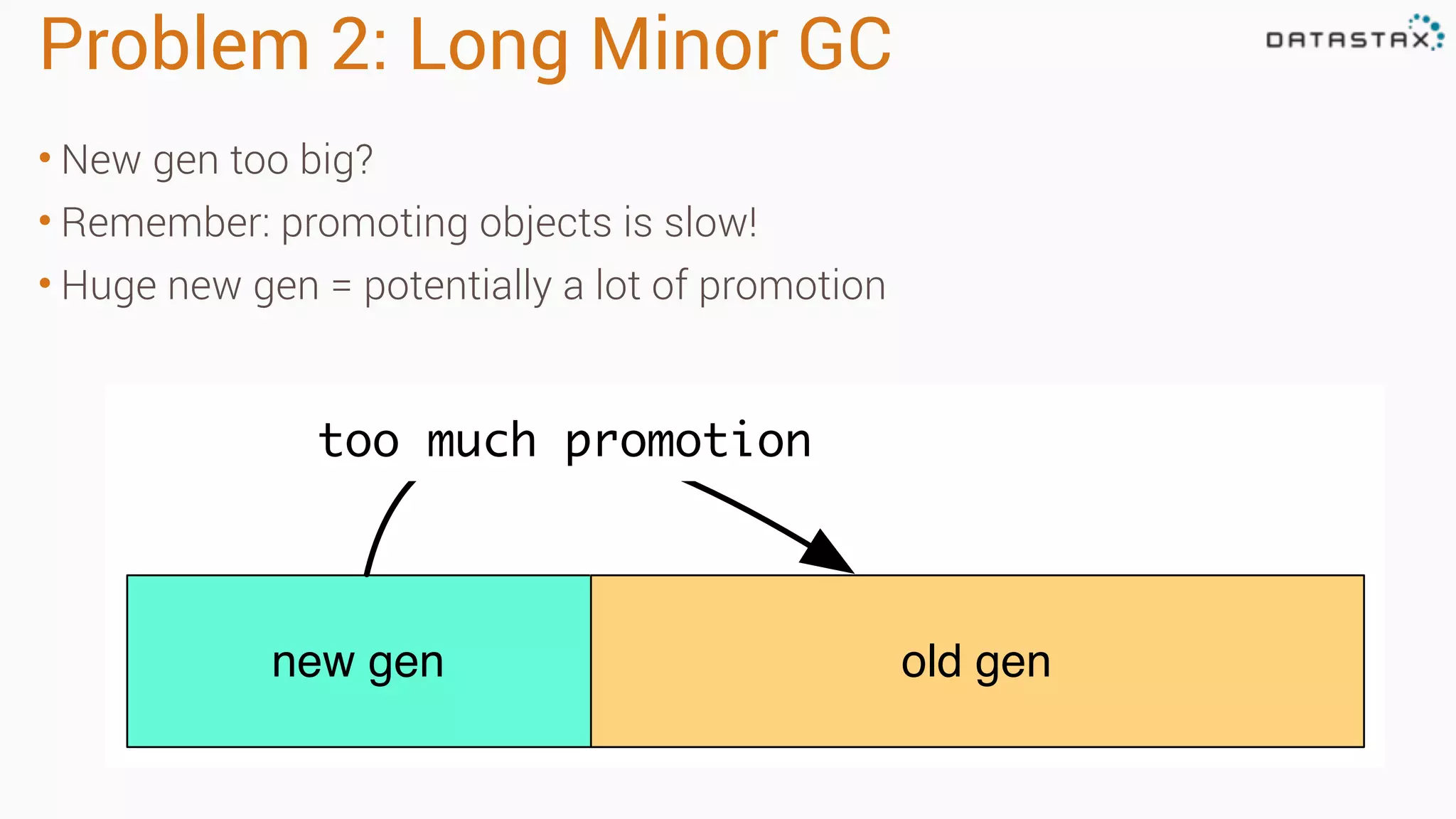
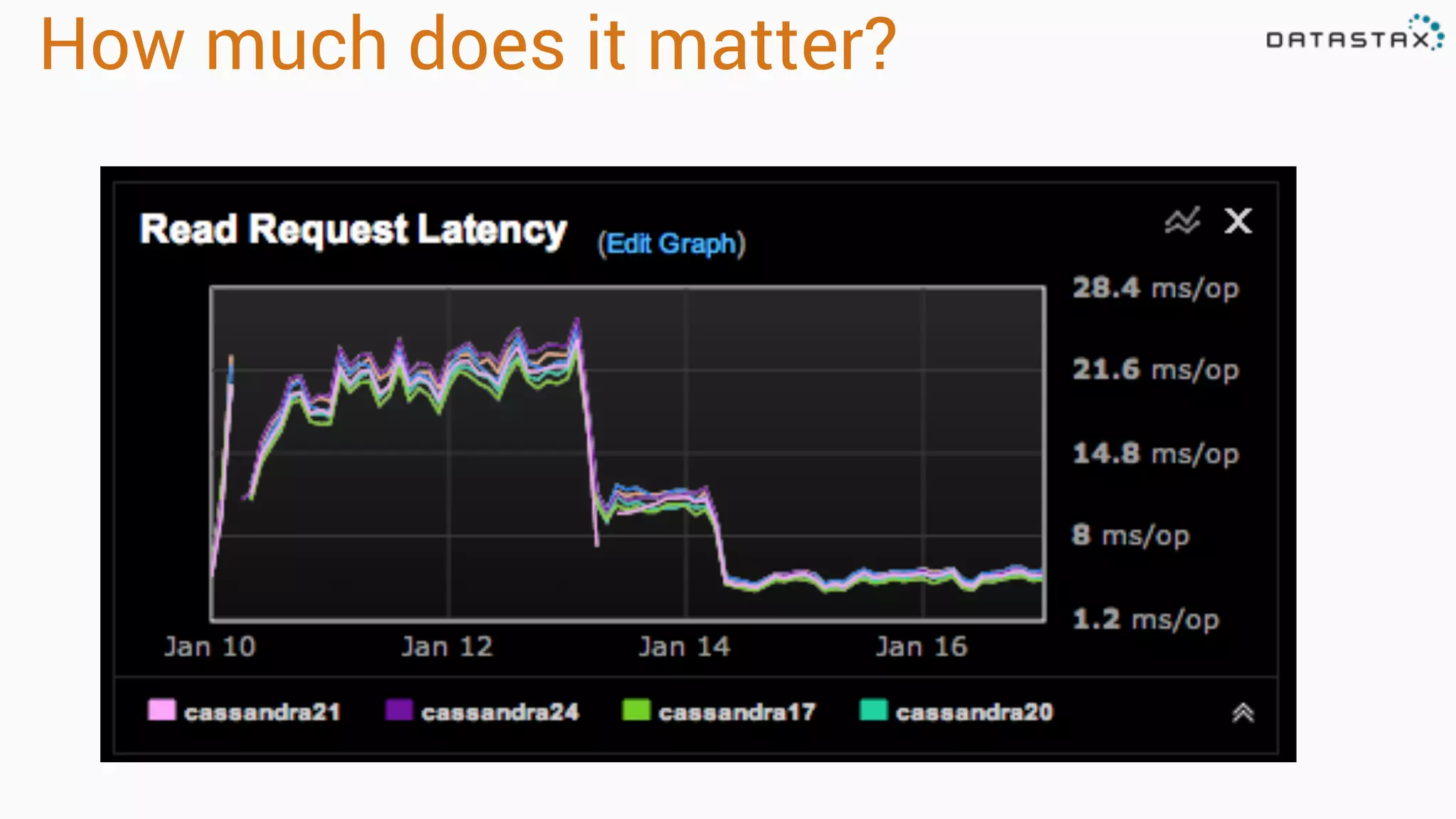
The document outlines best practices and tools for diagnosing production issues with Cassandra, emphasizing the importance of preparation and monitoring through various tools such as OpsCenter and other metrics aggregation solutions. It discusses common pitfalls like incorrect server times, insufficient handling of tombstones, version mismatches, and garbage collection problems, providing strategies for mitigation. Diagnostic tools and methods for performance monitoring, troubleshooting, and query tracing are highlighted to help identify and resolve system problems.