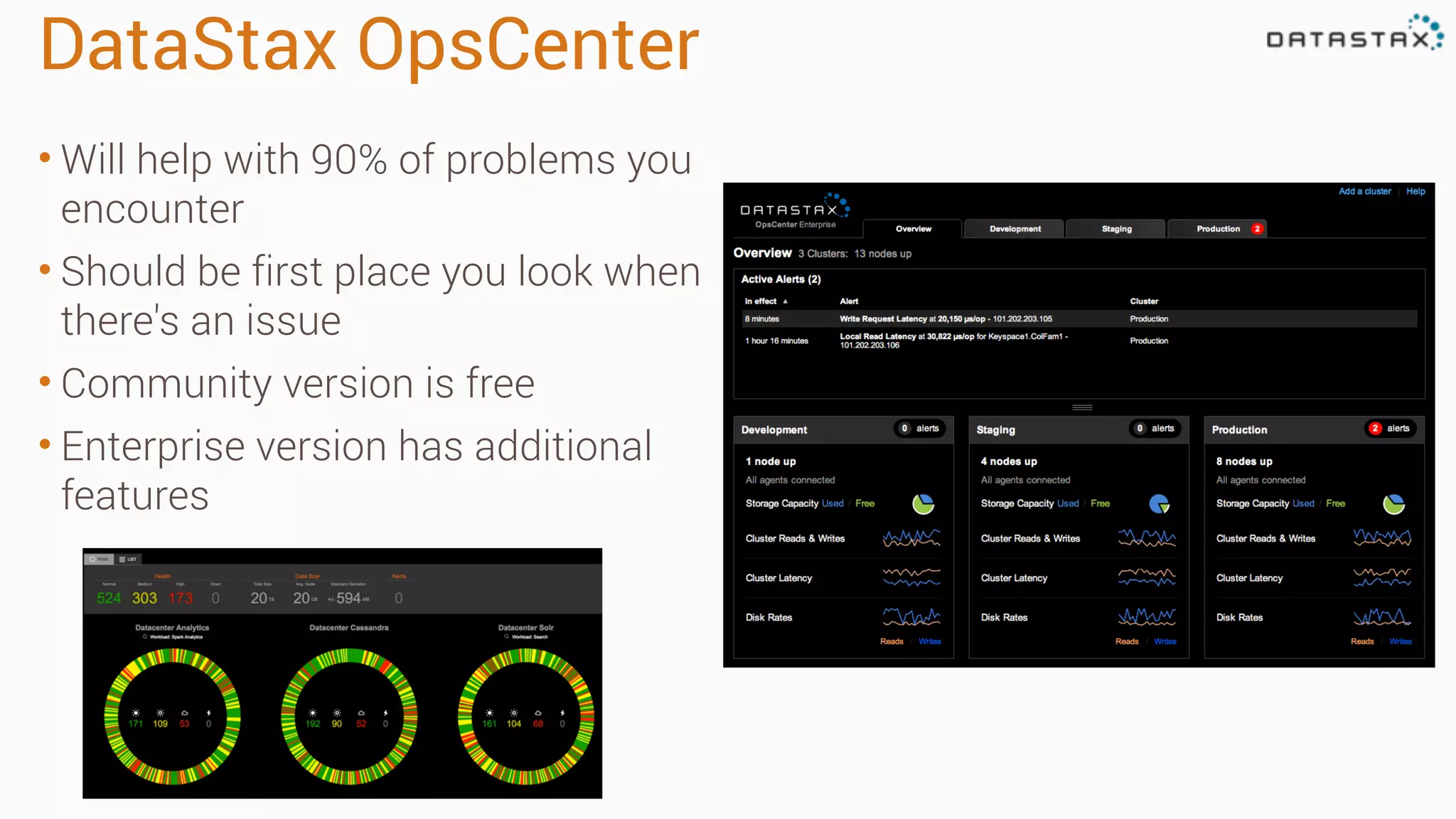
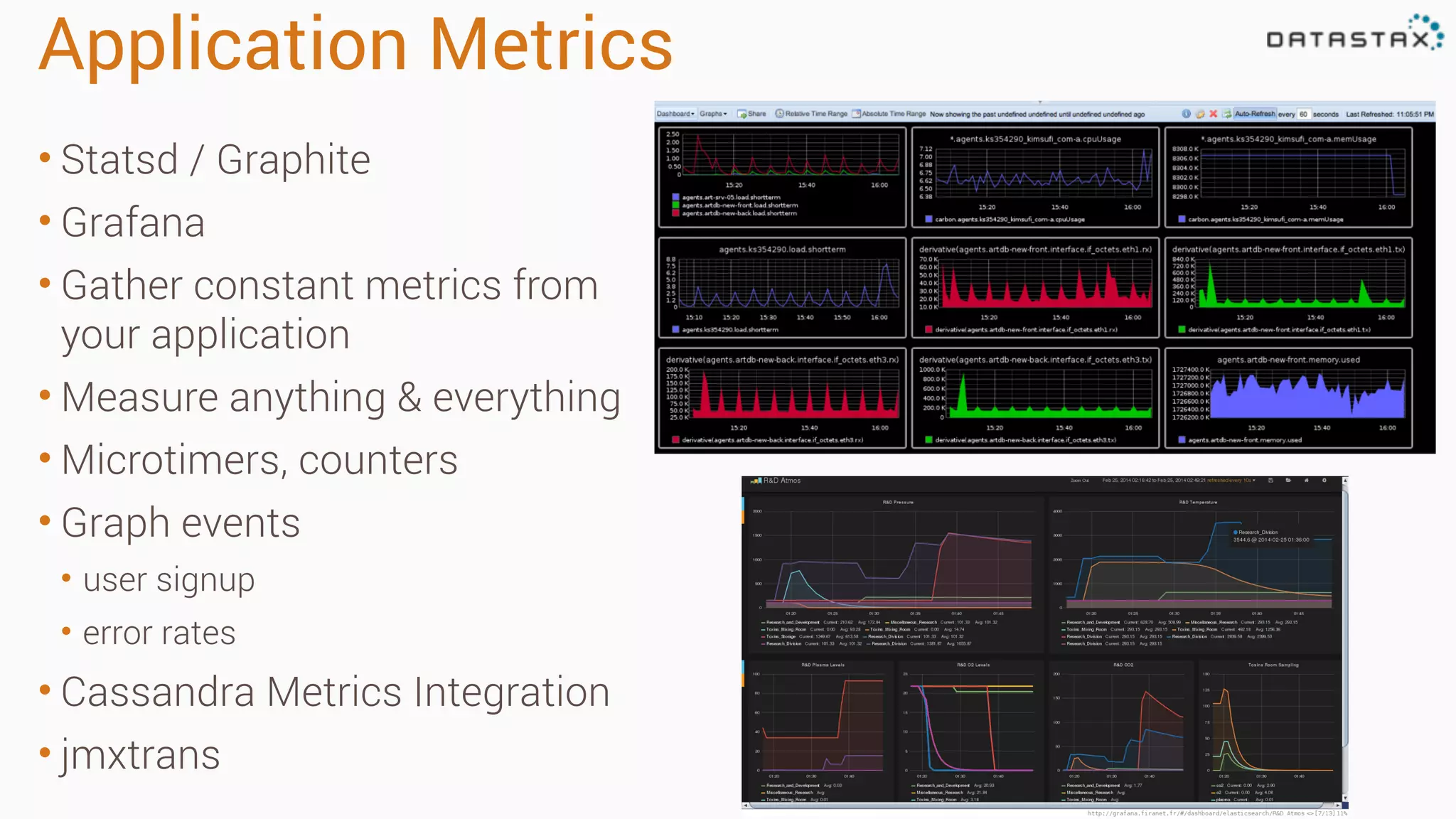
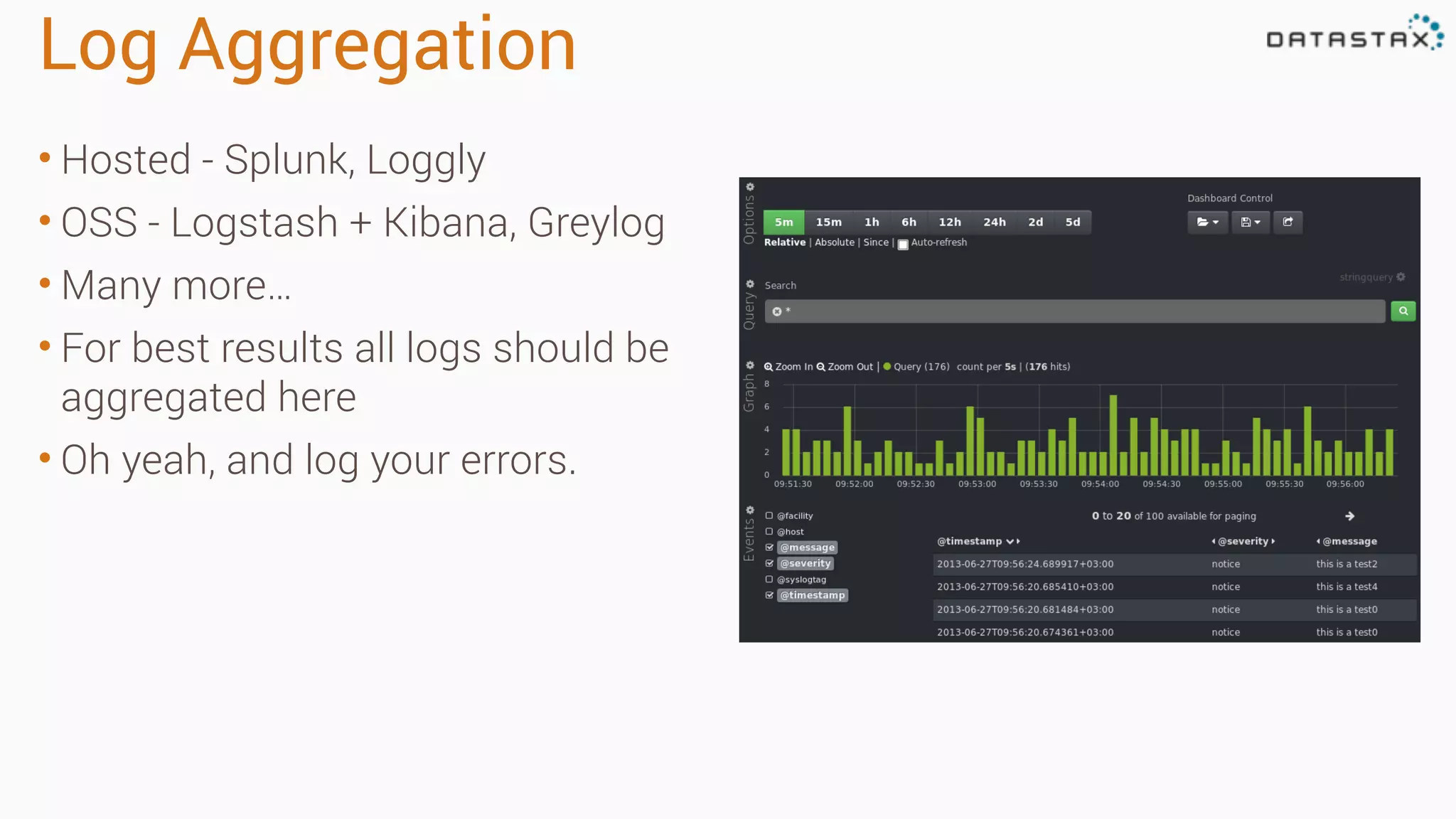
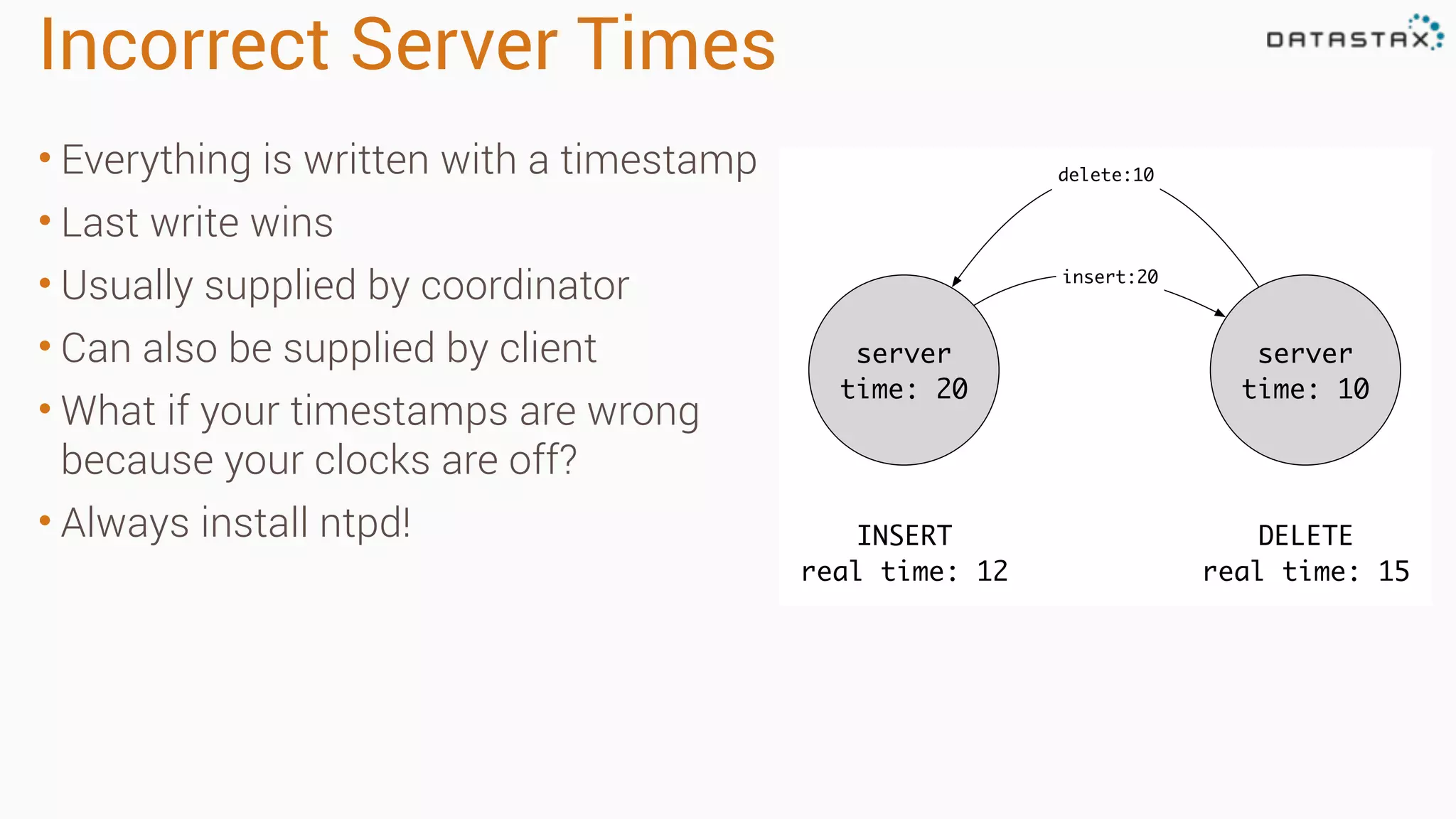
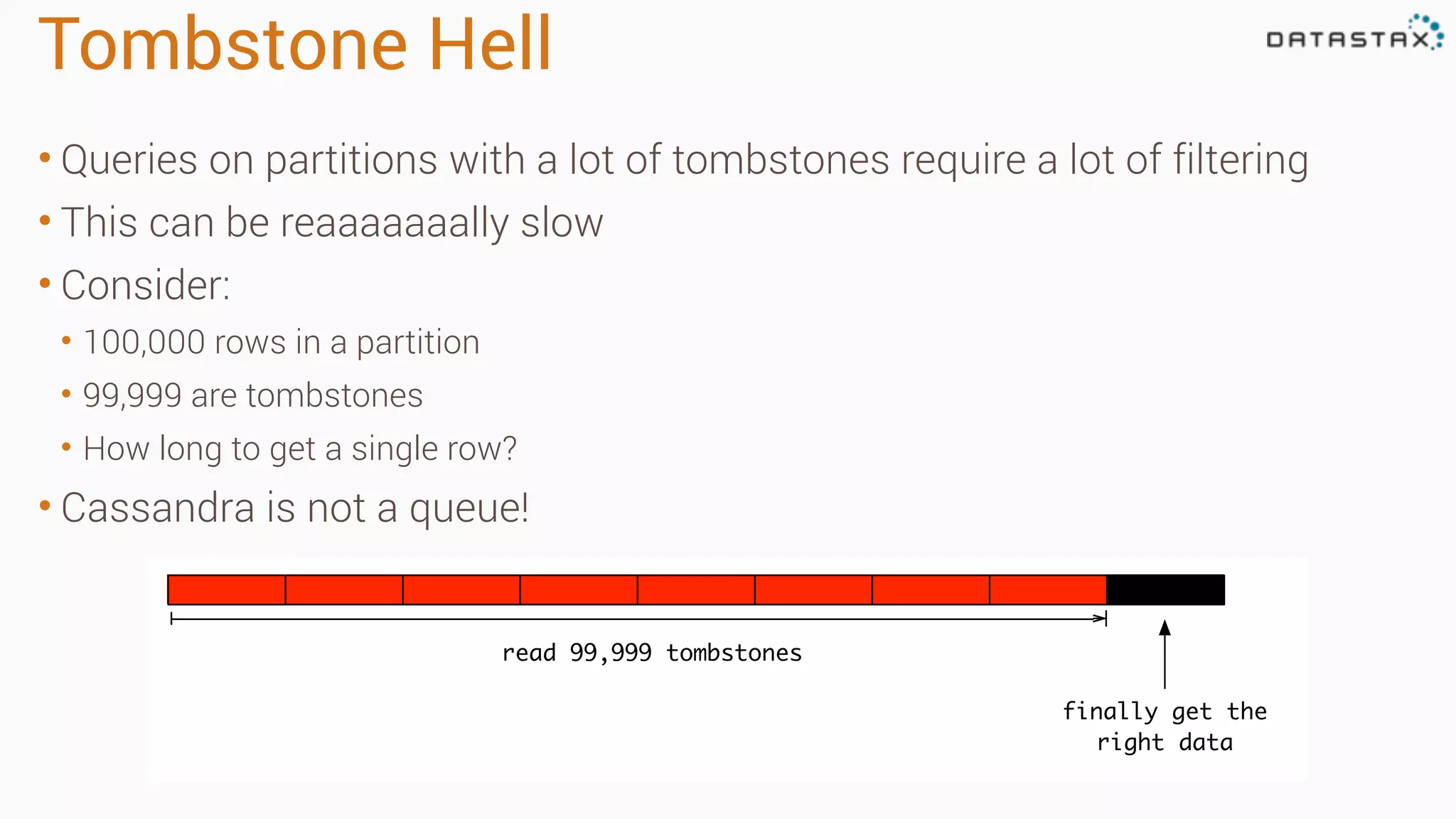
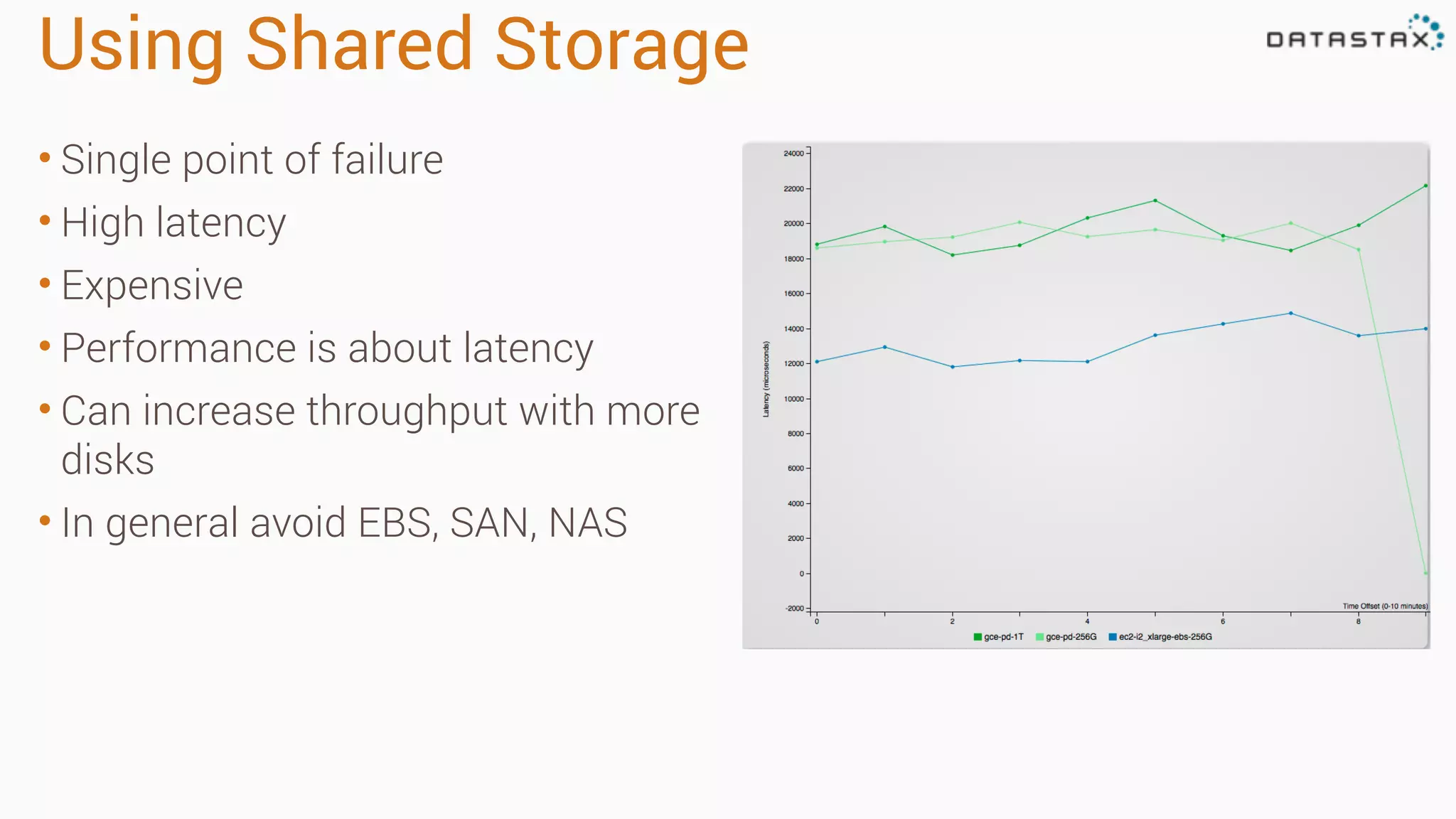
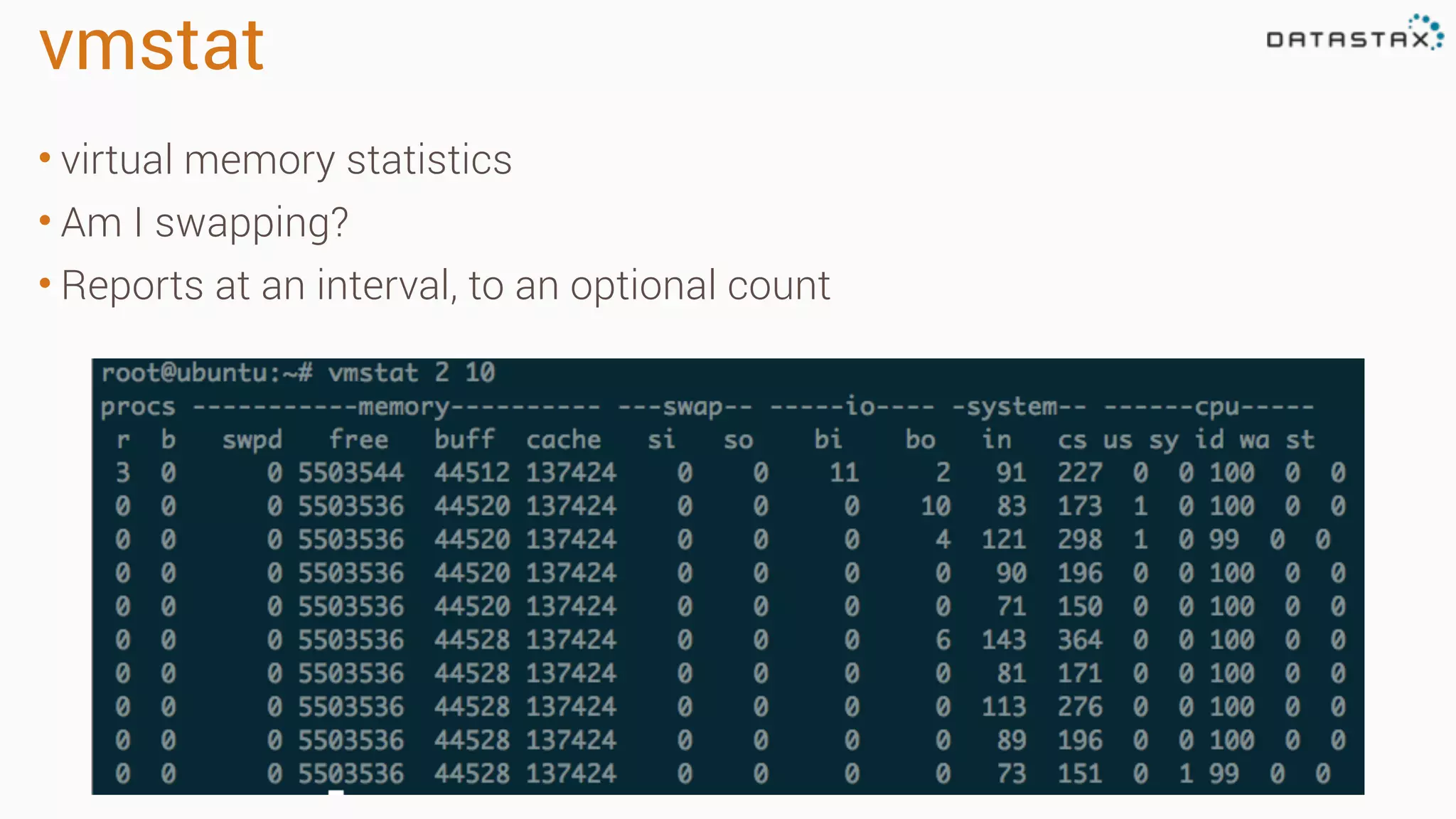
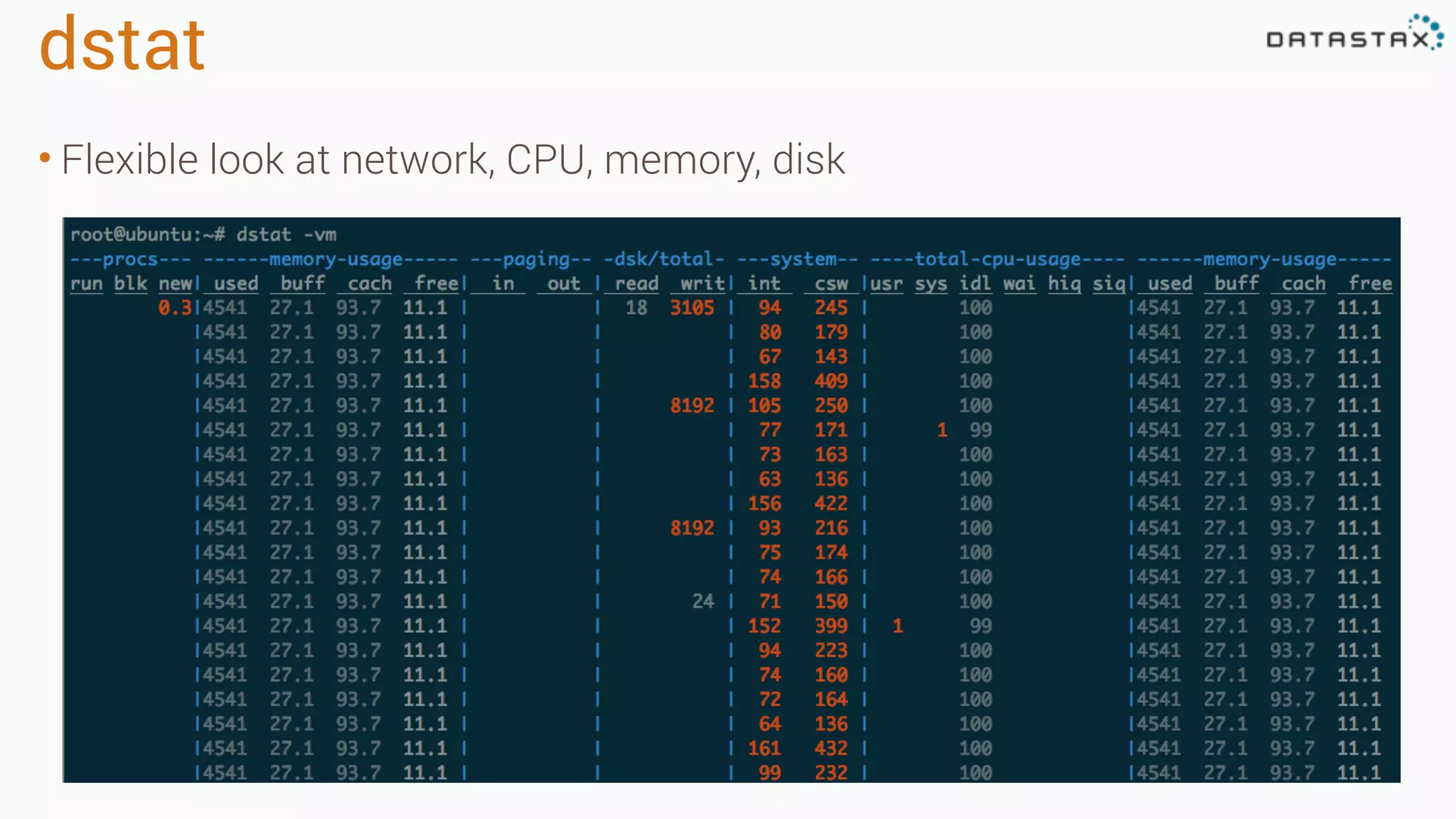
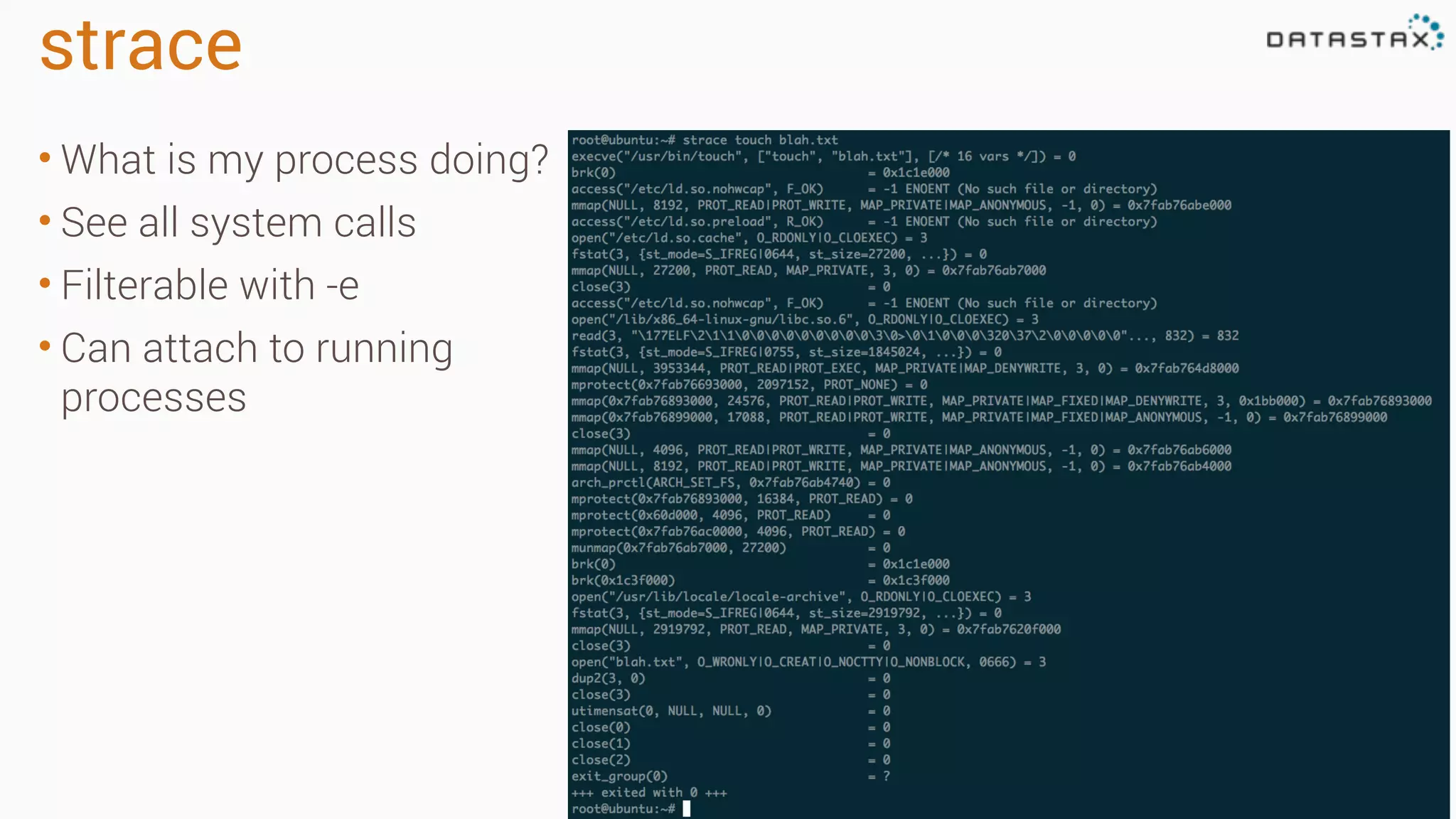
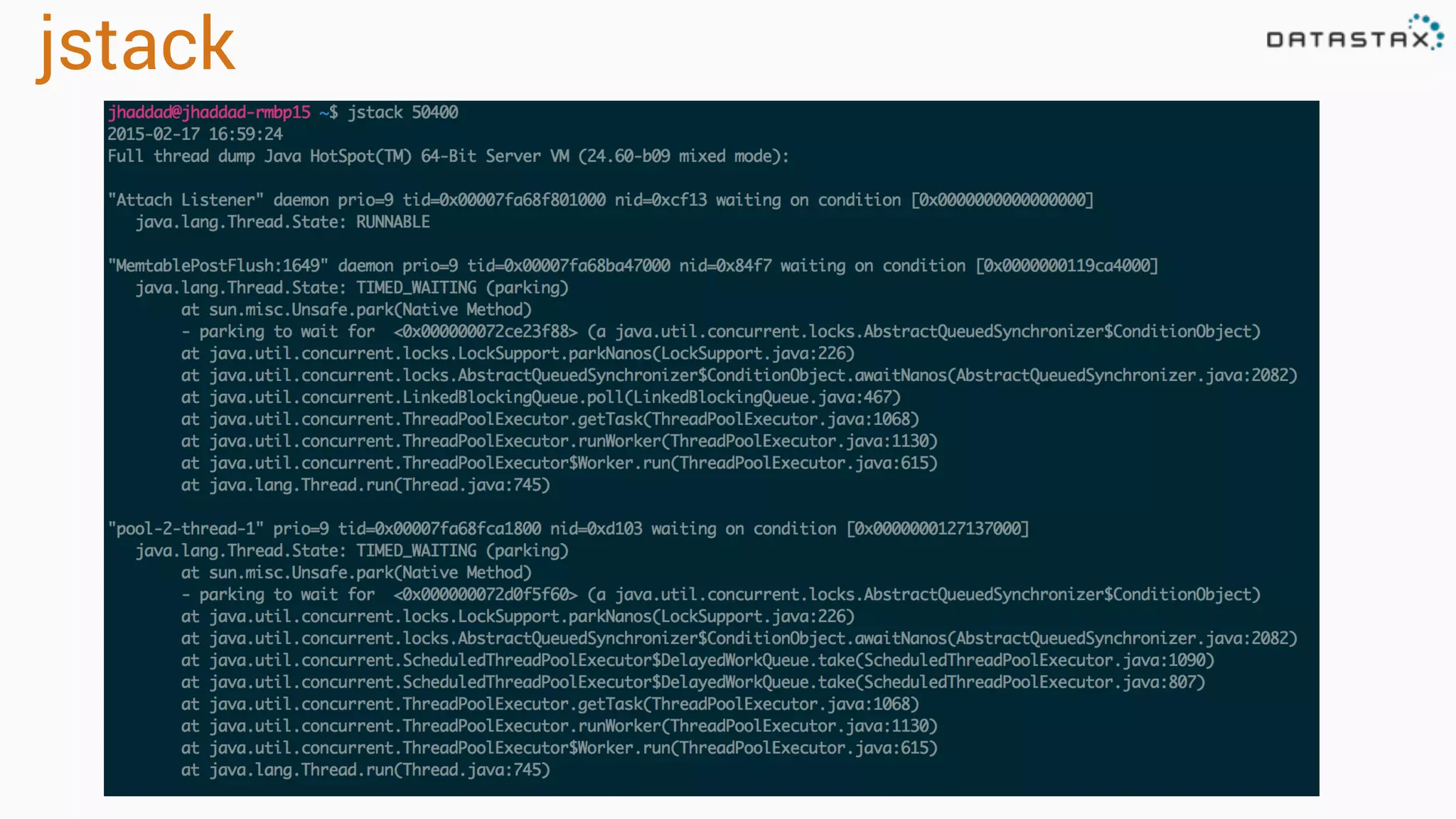
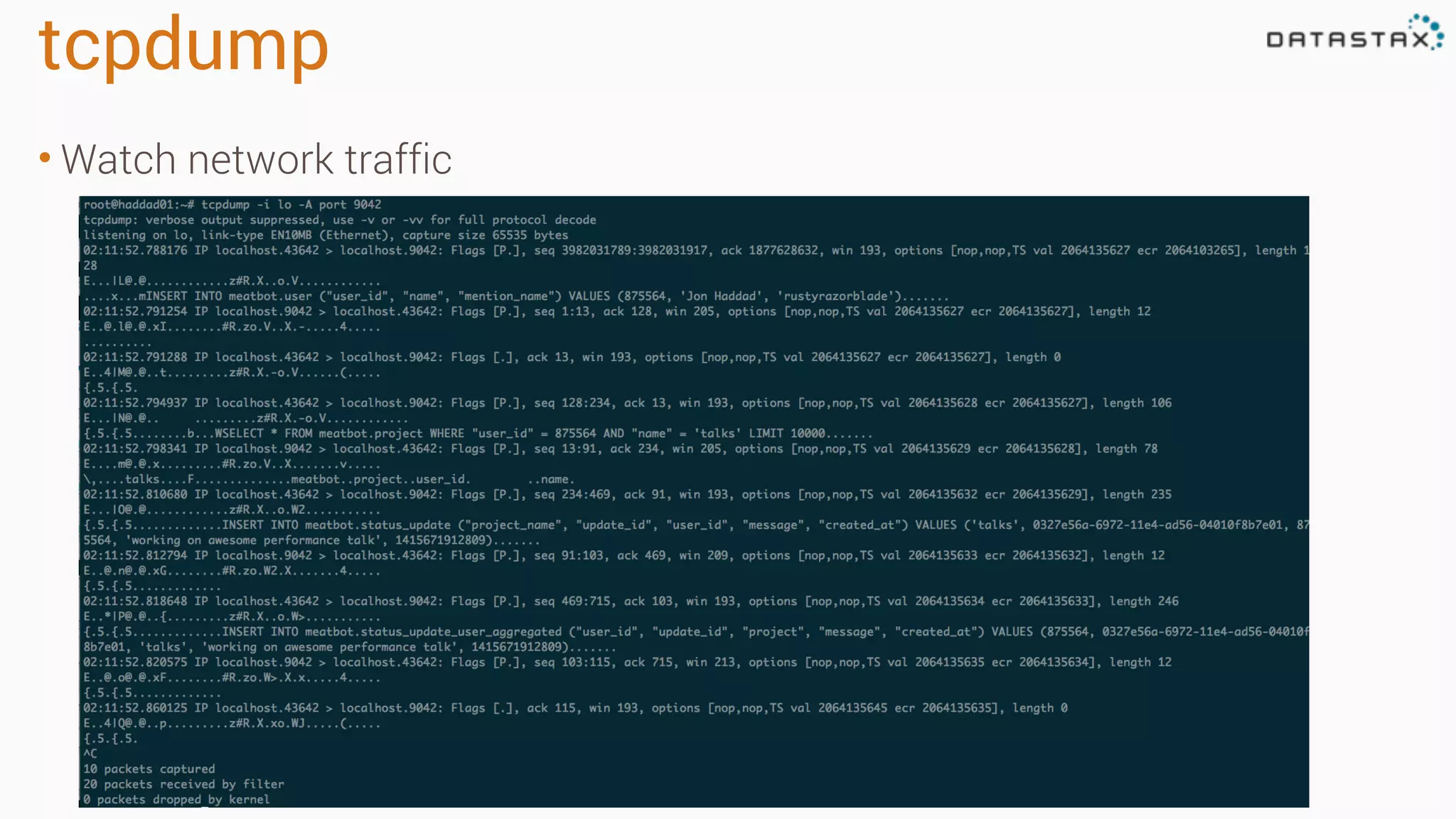
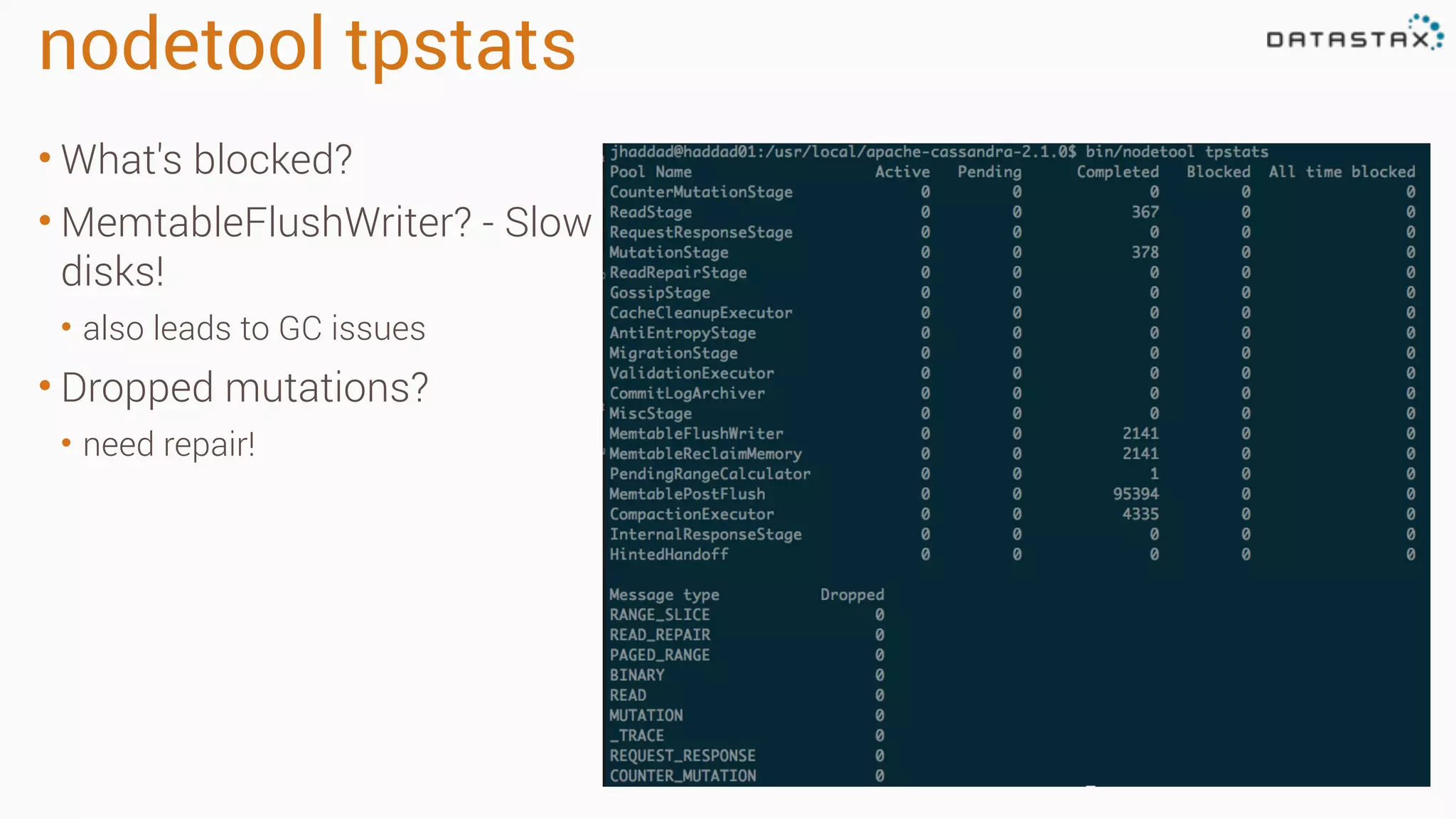
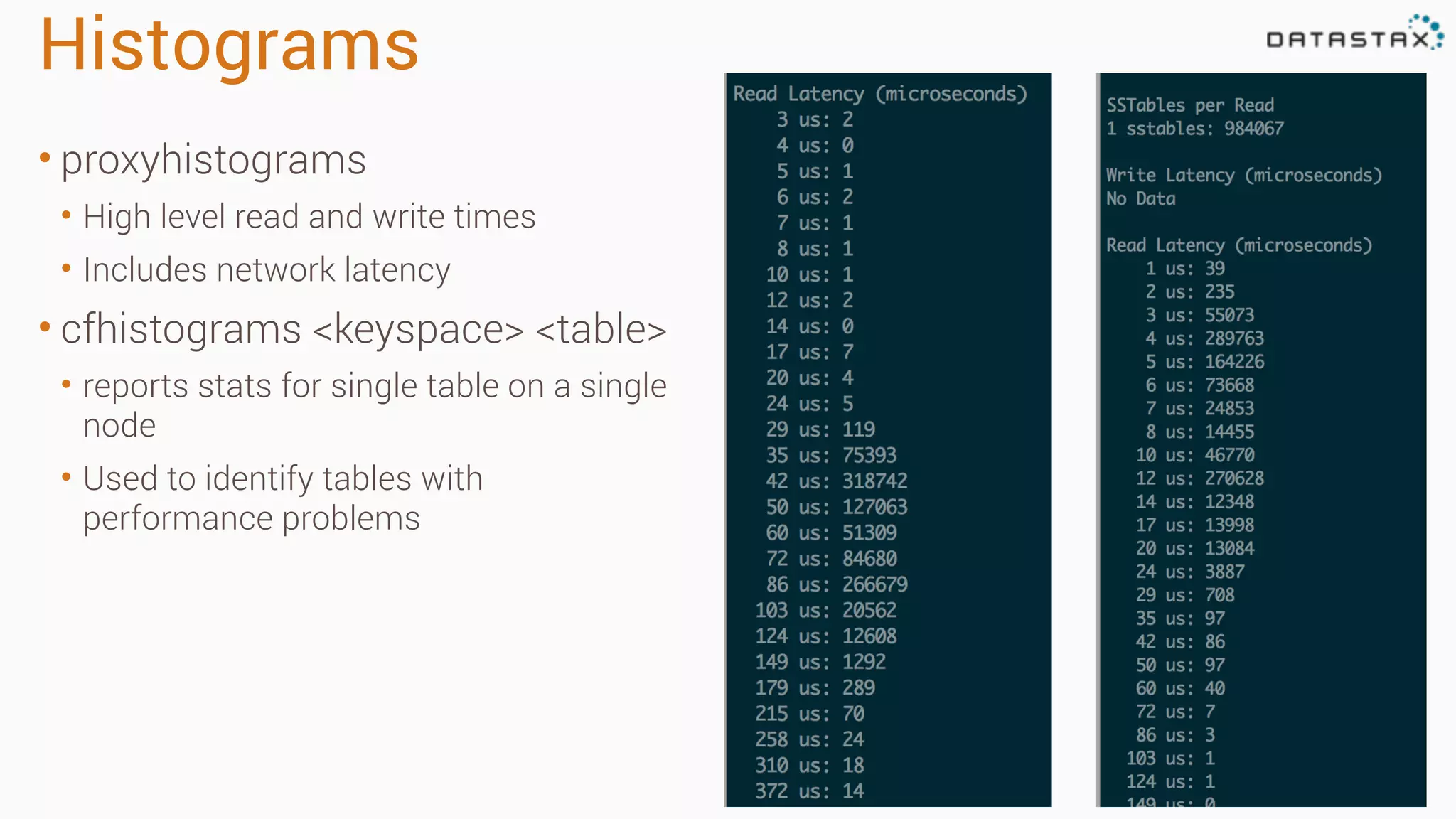
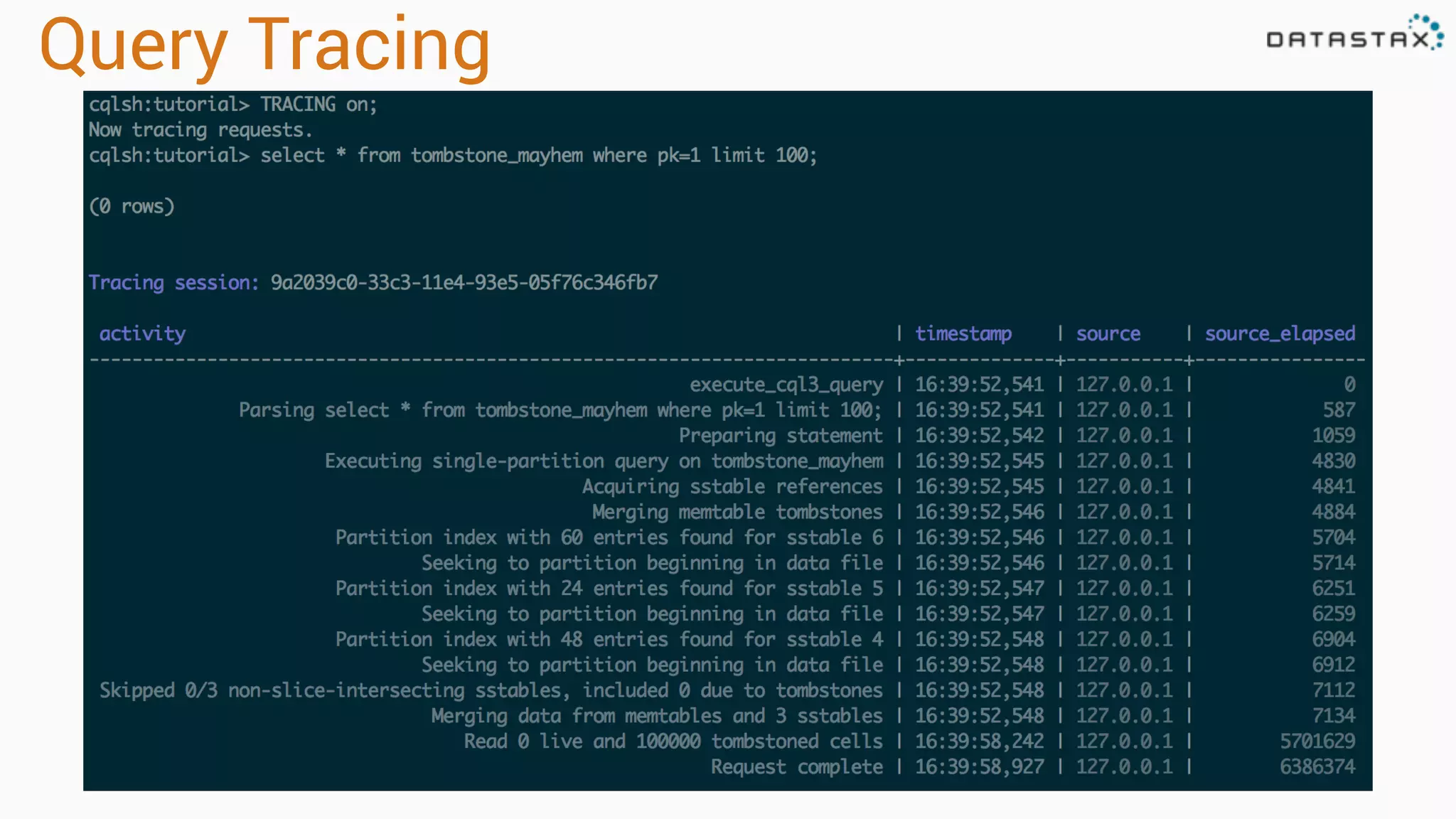
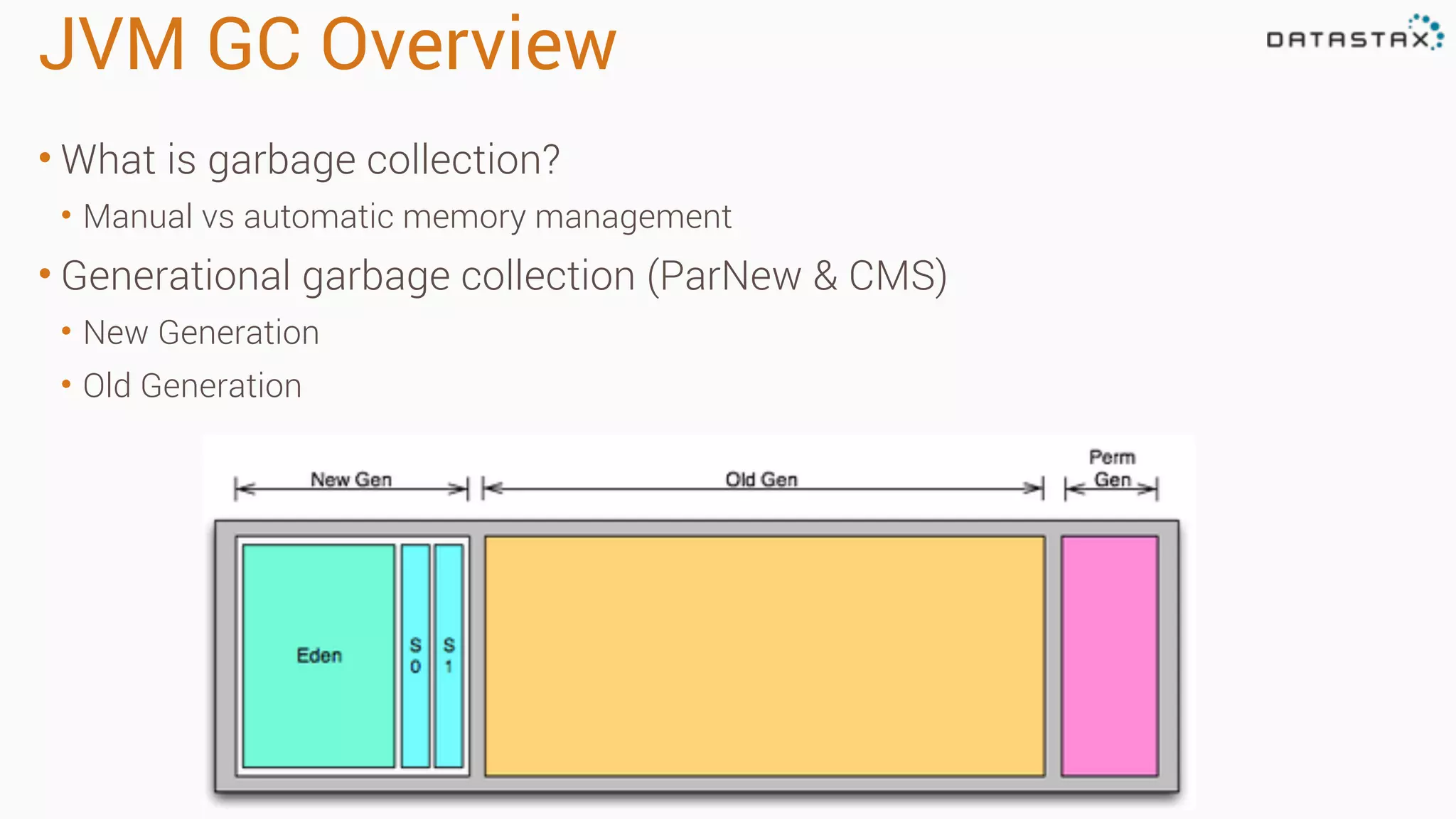
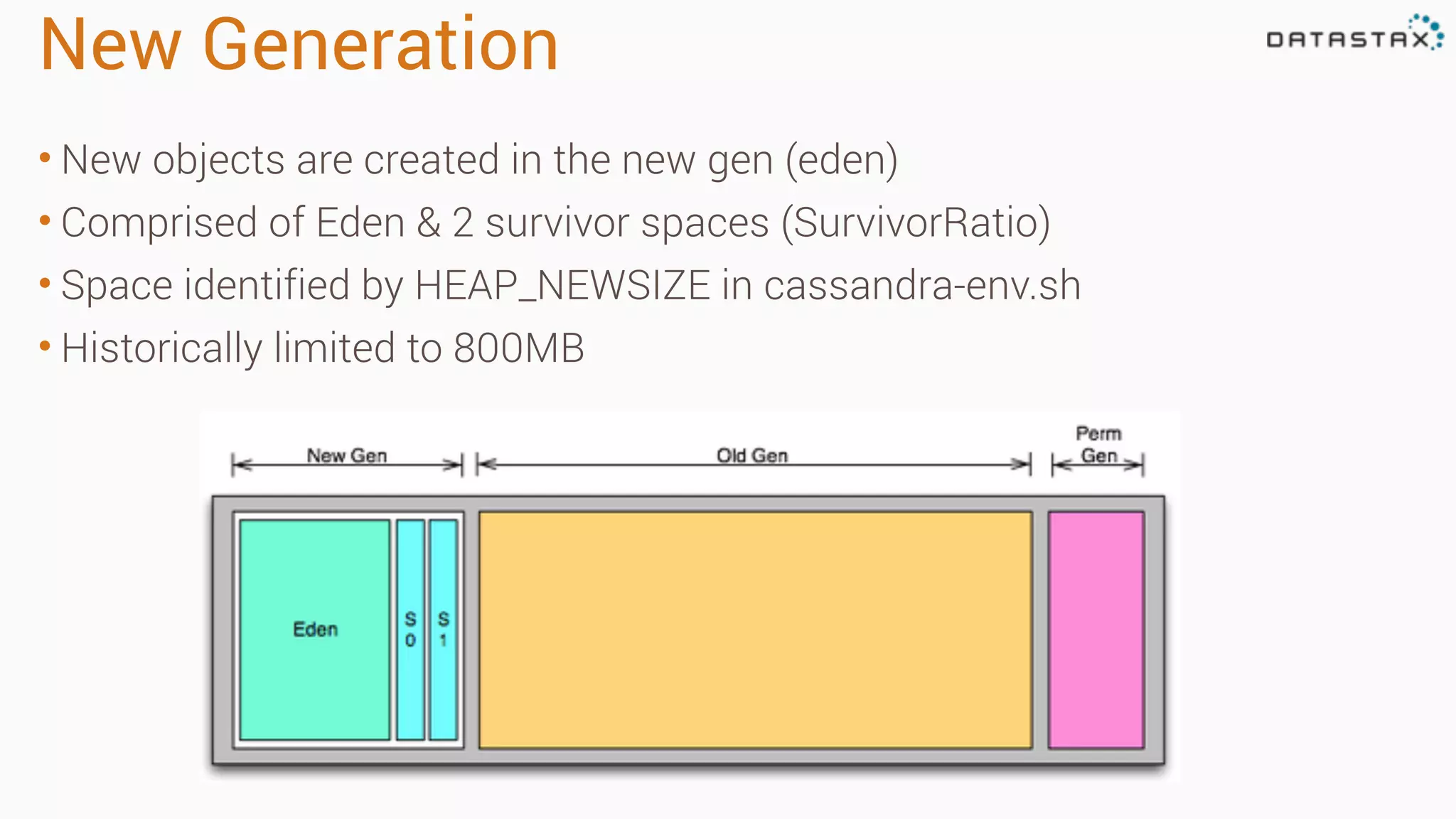
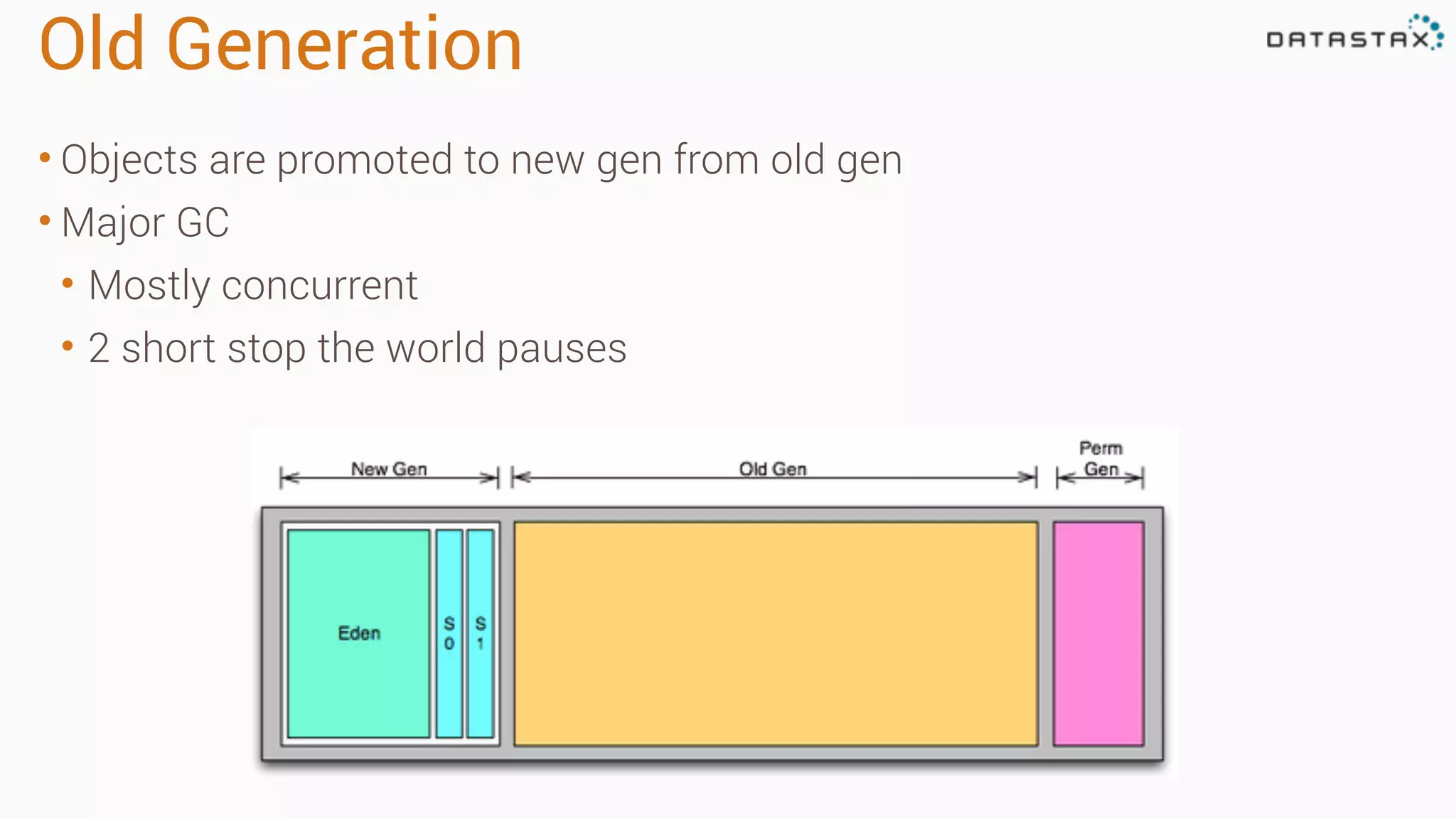
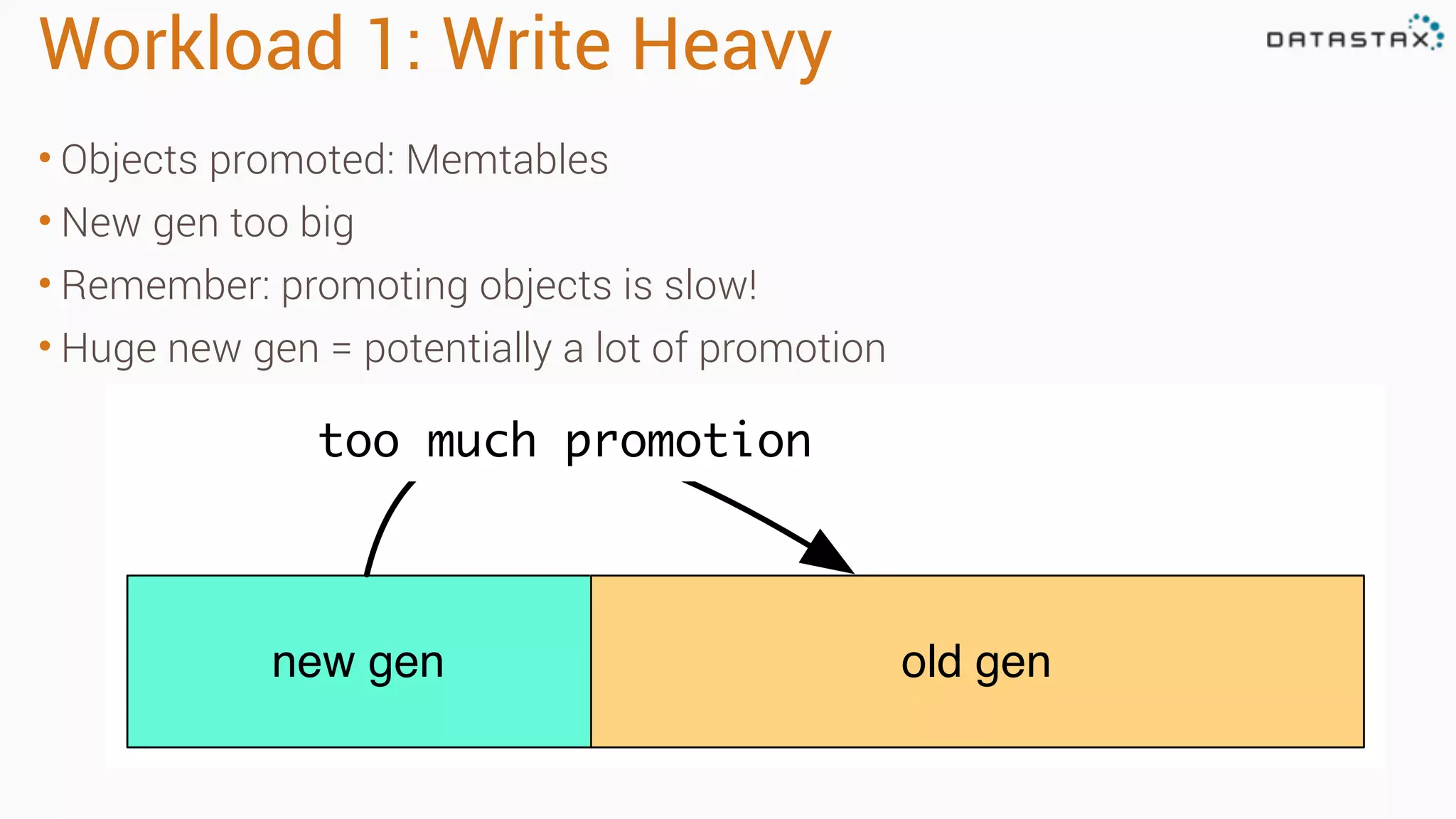
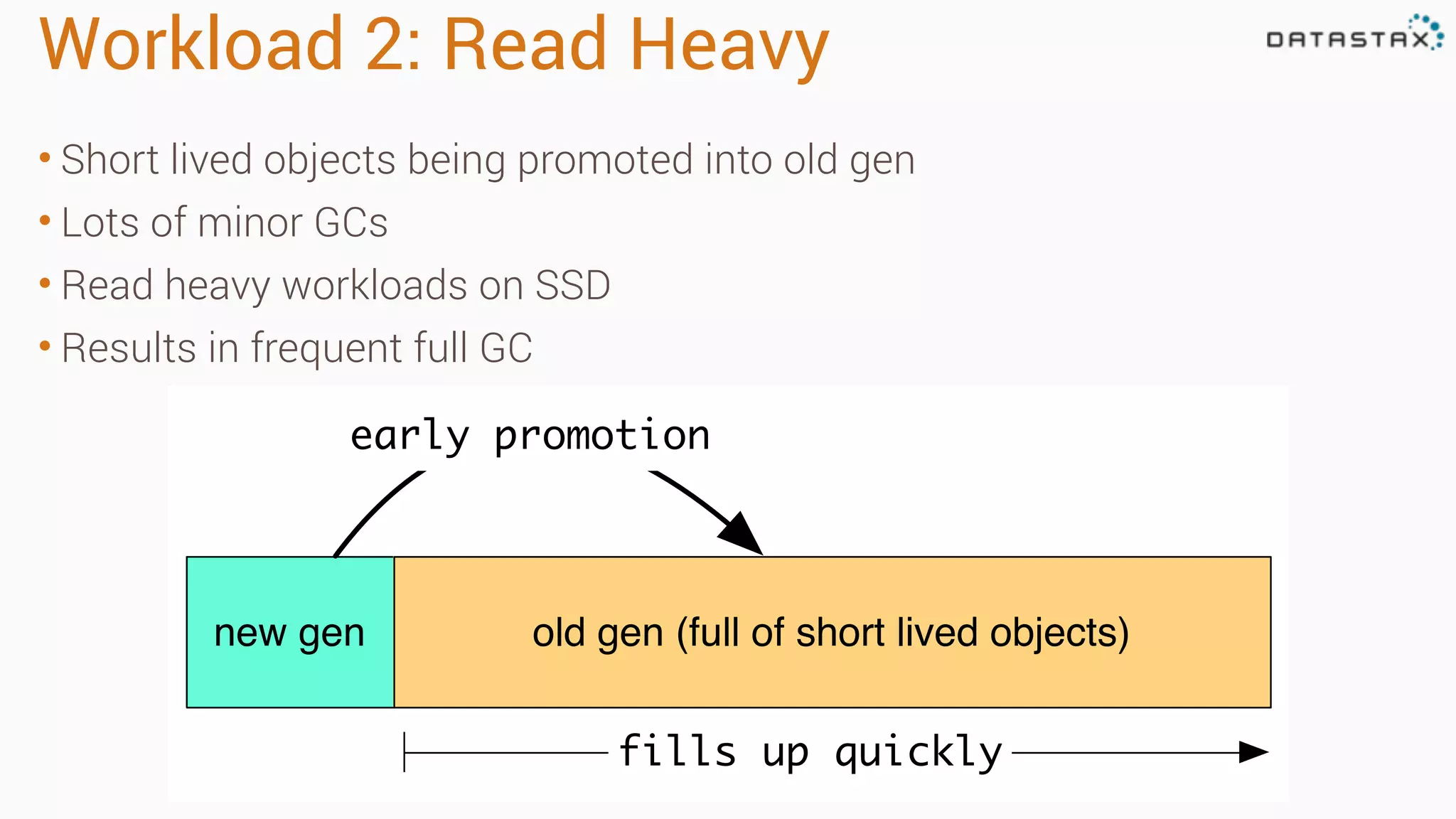
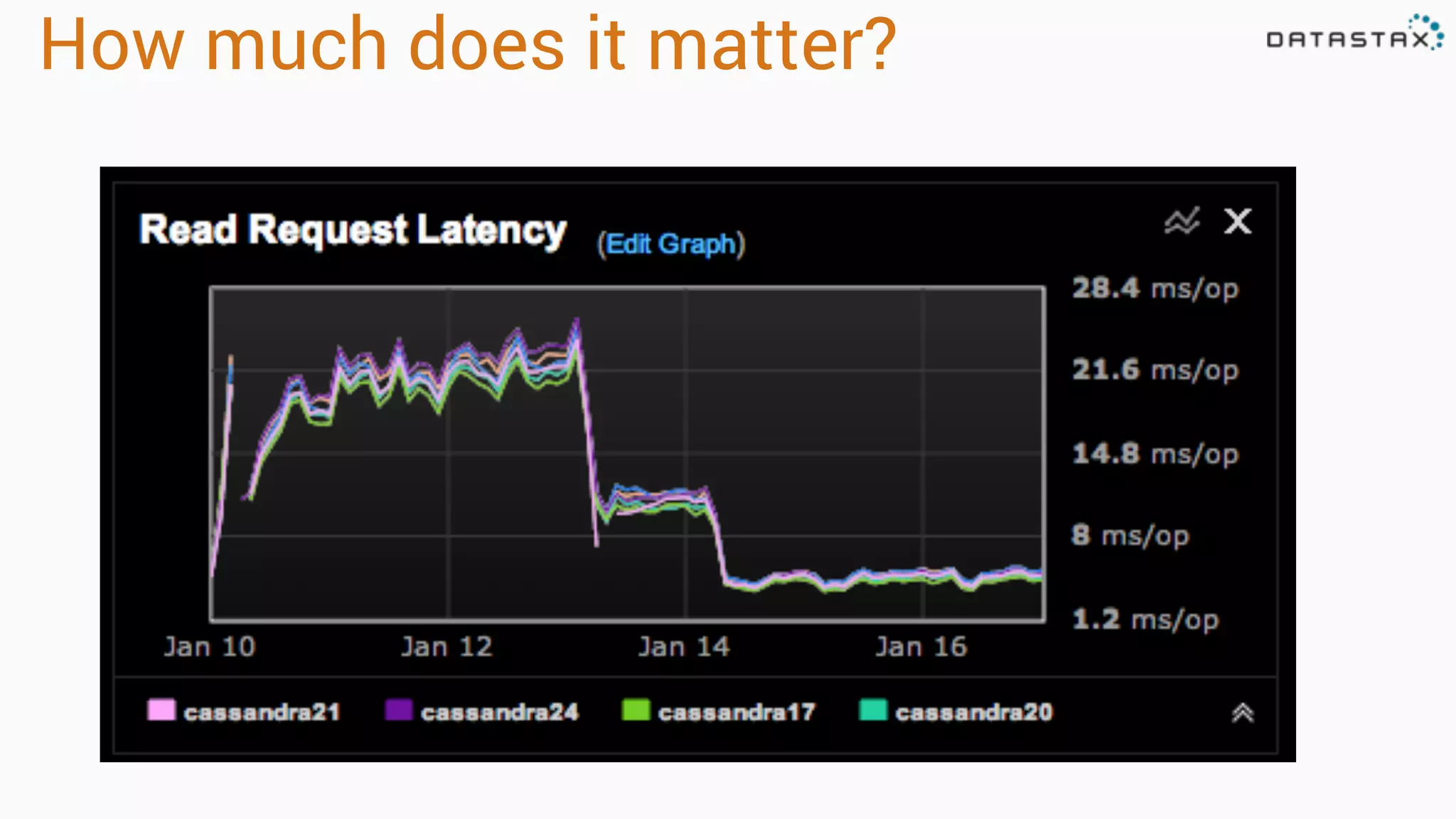
Diagnosing Problems in Production involves first preparing monitoring tools like OpsCenter, Server monitoring, Application metrics, and Log aggregation. Common issues include incorrect server times causing data inconsistencies, tombstone overhead slowing queries, not using the right snitch, version mismatches breaking functionality, and disk space not being reclaimed properly. Diagnostic tools like htop, iostat, vmstat, dstat, strace, jstack, tcpdump and nodetool can help narrow down issues like performance bottlenecks, garbage collection problems, and compaction issues.