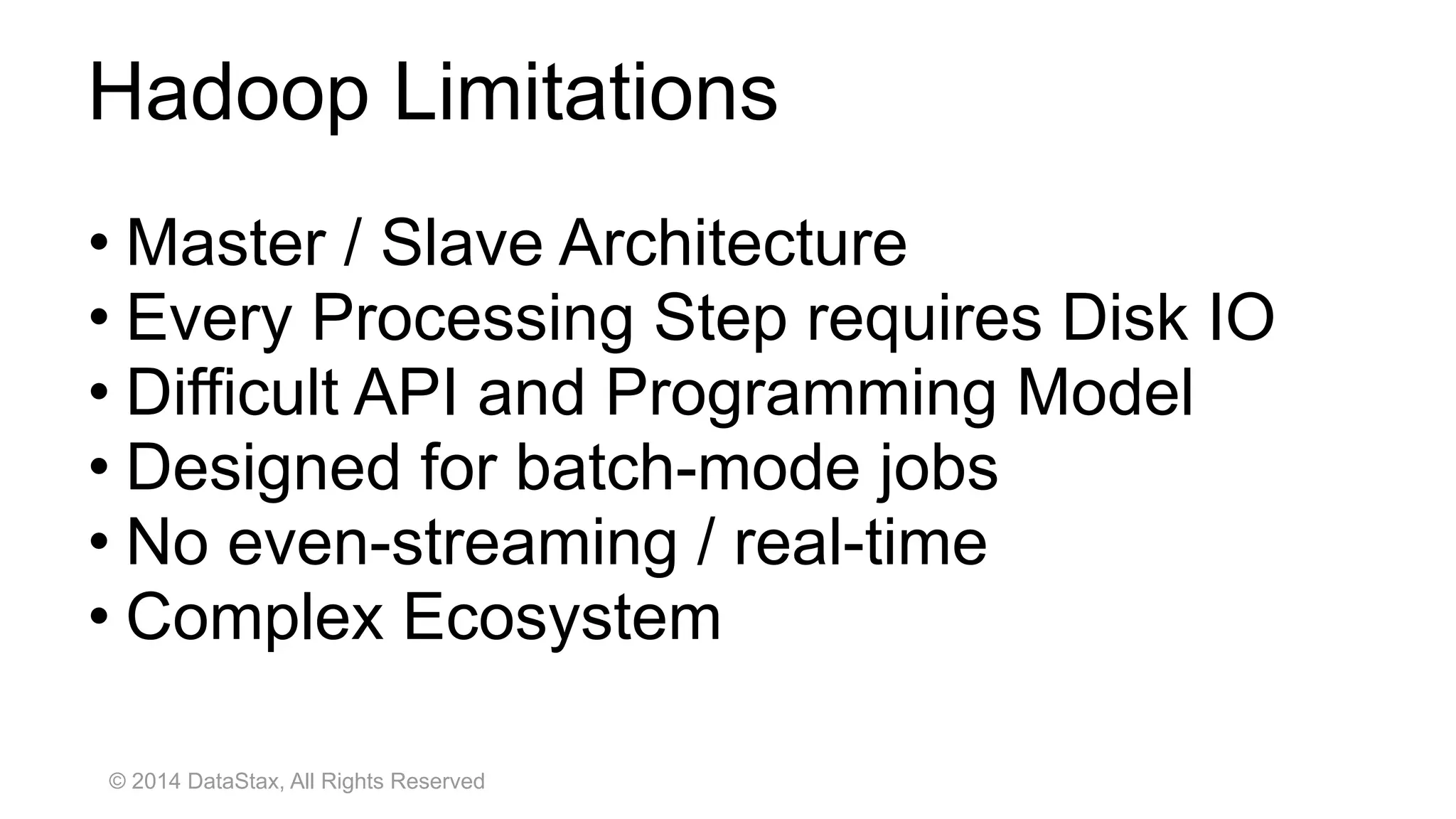
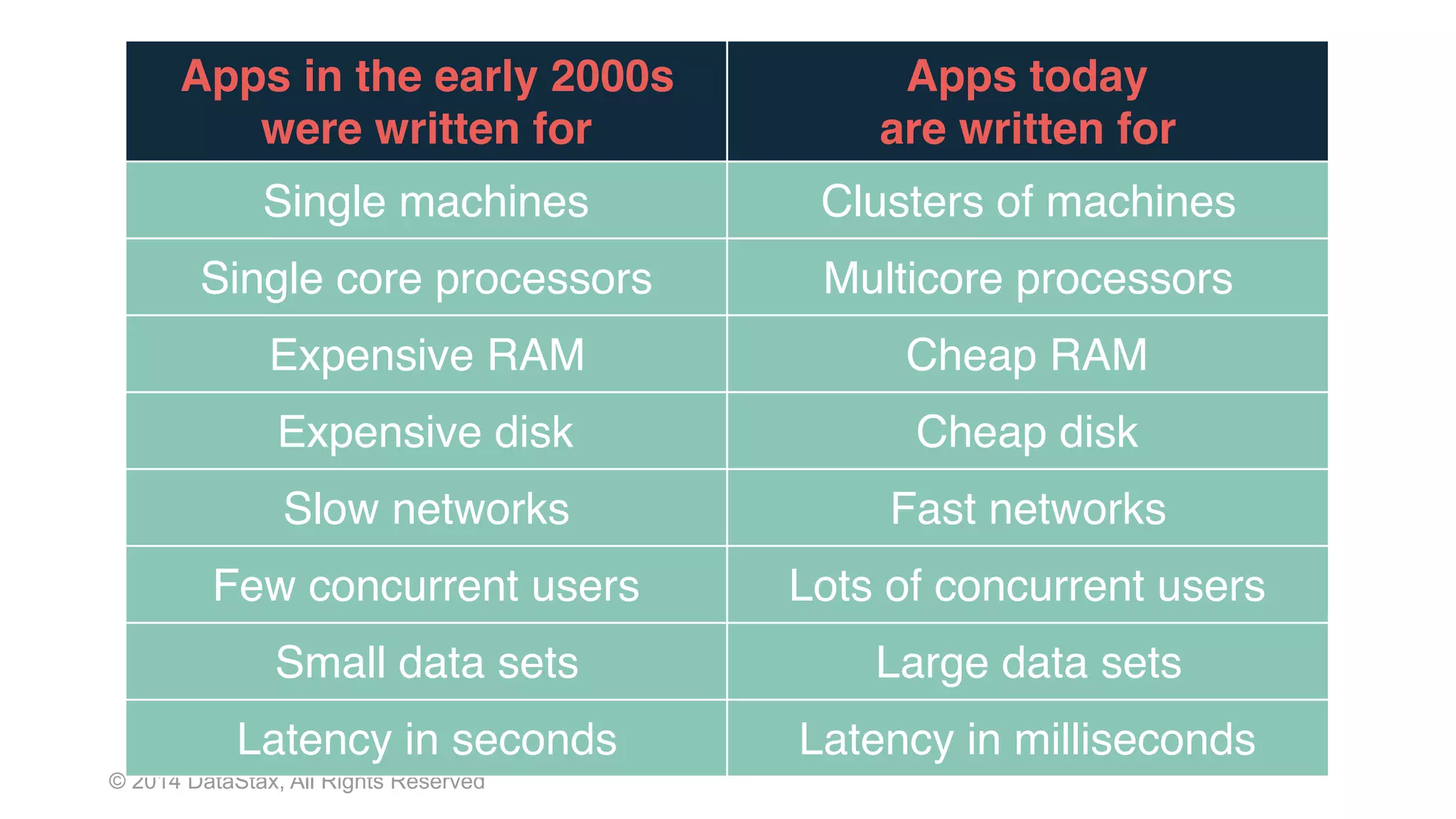
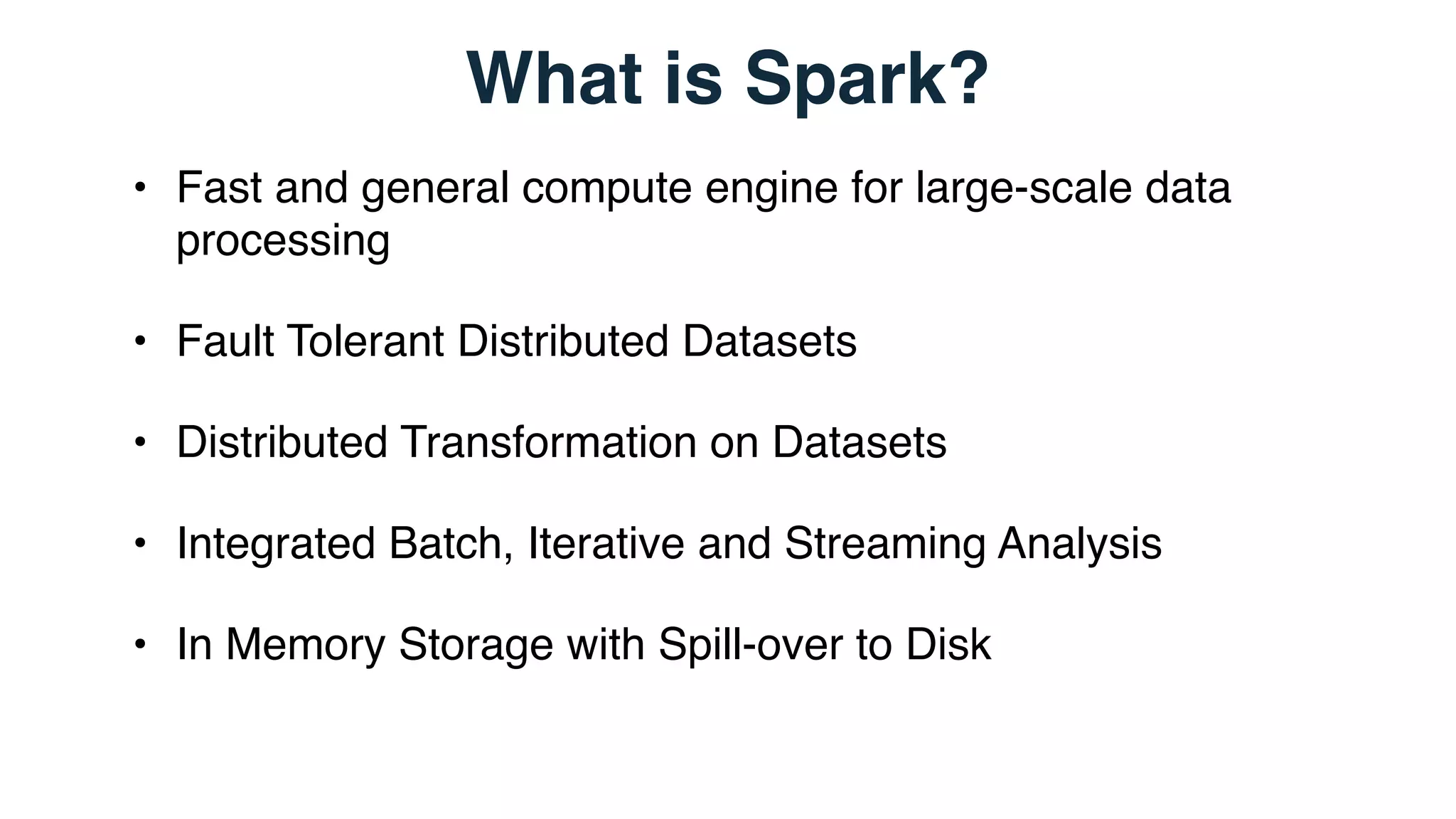
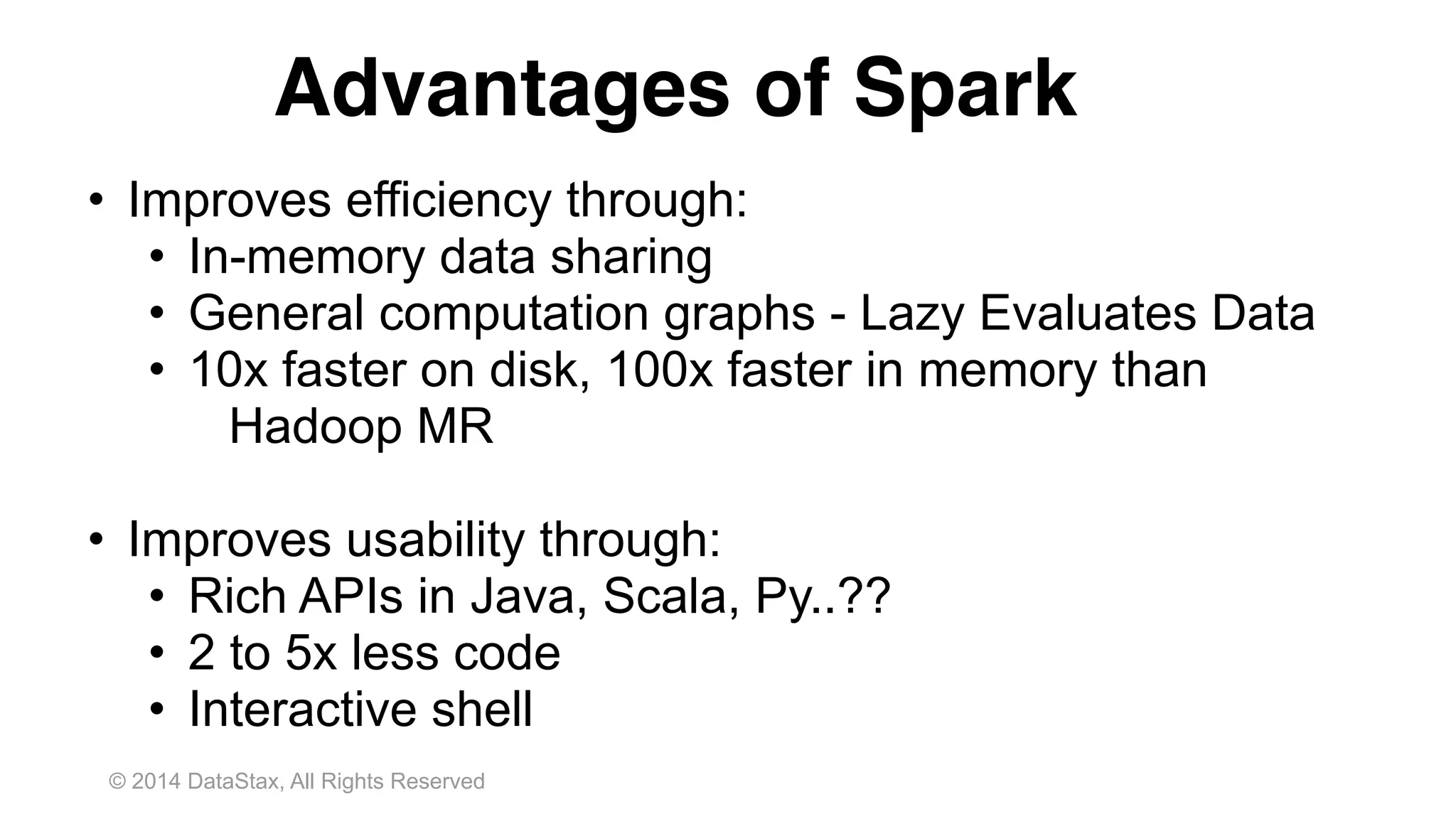
This document discusses real time analytics using Spark and Spark Streaming. It provides an introduction to Spark and highlights limitations of Hadoop for real-time analytics. It then describes Spark's advantages like in-memory processing and rich APIs. The document discusses Spark Streaming and the Spark Cassandra Connector. It also introduces DataStax Enterprise which integrates Spark, Cassandra and Solr to allow real-time analytics without separate clusters. Examples of streaming use cases and demos are provided.



























![Populating Kafka Topics
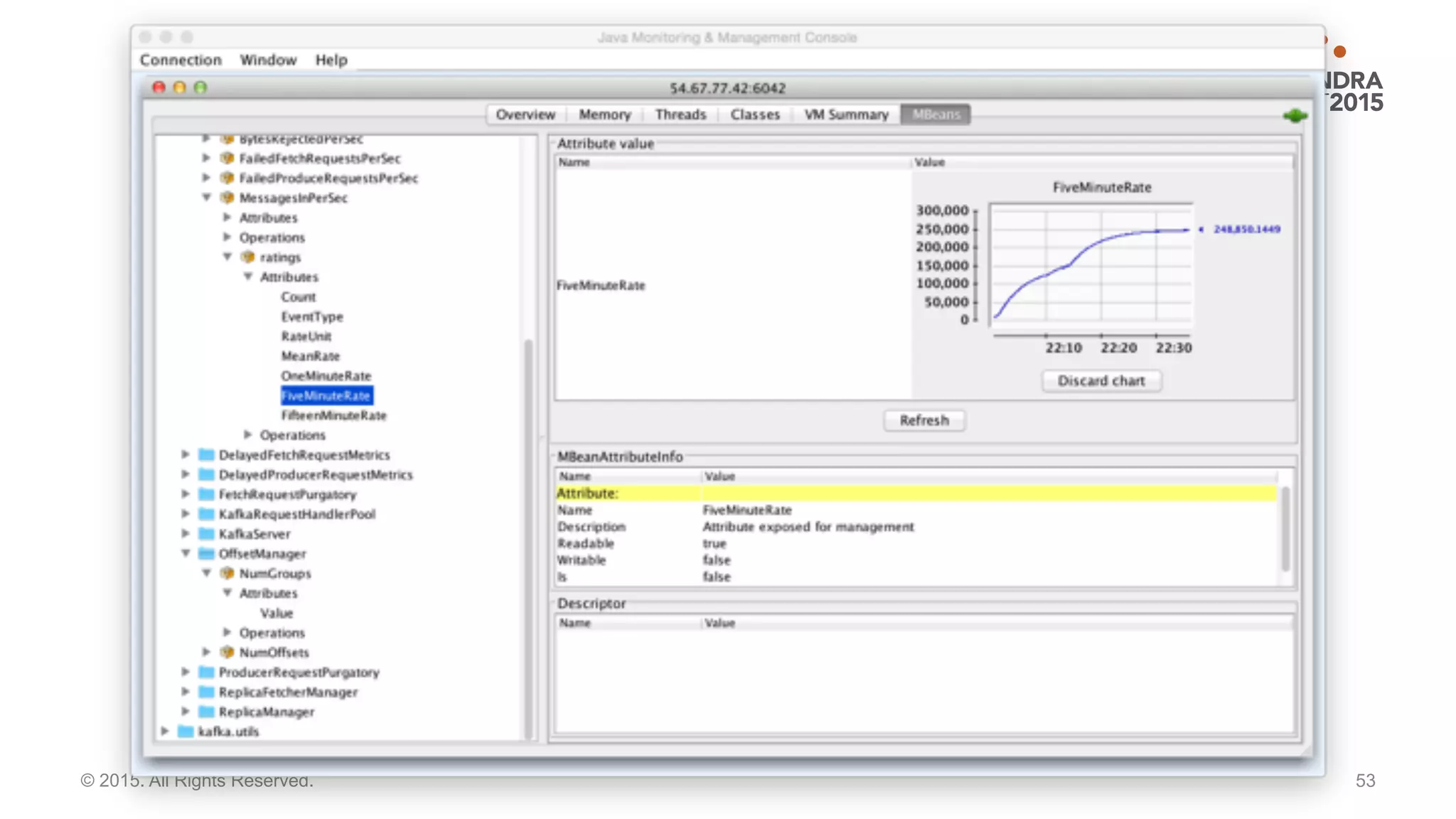
52© 2015. All Rights Reserved.
val record = new ProducerRecord[String, String]
(feederExtension.kafkaTopic, partNum, key,
nxtRating.toString)
val future = feederExtension.producer.send(record, new
Callback {](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-time-analytics-with-dse-160219184212/75/Real-Time-Analytics-with-Dse-52-2048.jpg)
![1. extract
text from
the tweet
https://
twitter.com/
andy_bf/status/
"Ceci n'est pas
un tweet"
2.
sequence
text as
tweet.sliding(2).t
oSeq
("Ce", "ec",
"ci", …, )
3. convert
bigrams
into
seq.map(_.hashCode
())
(2178, 3230,
3174, …, )
4. index
into
sparse tf
seq.map(_.hashCode
() % 1000)
(178, 230, 174,
…, )
5.
increment
feature
Vector.sparse(1000
, …)
(1000, [102,
104, …],
[0.0455, 0.0455,
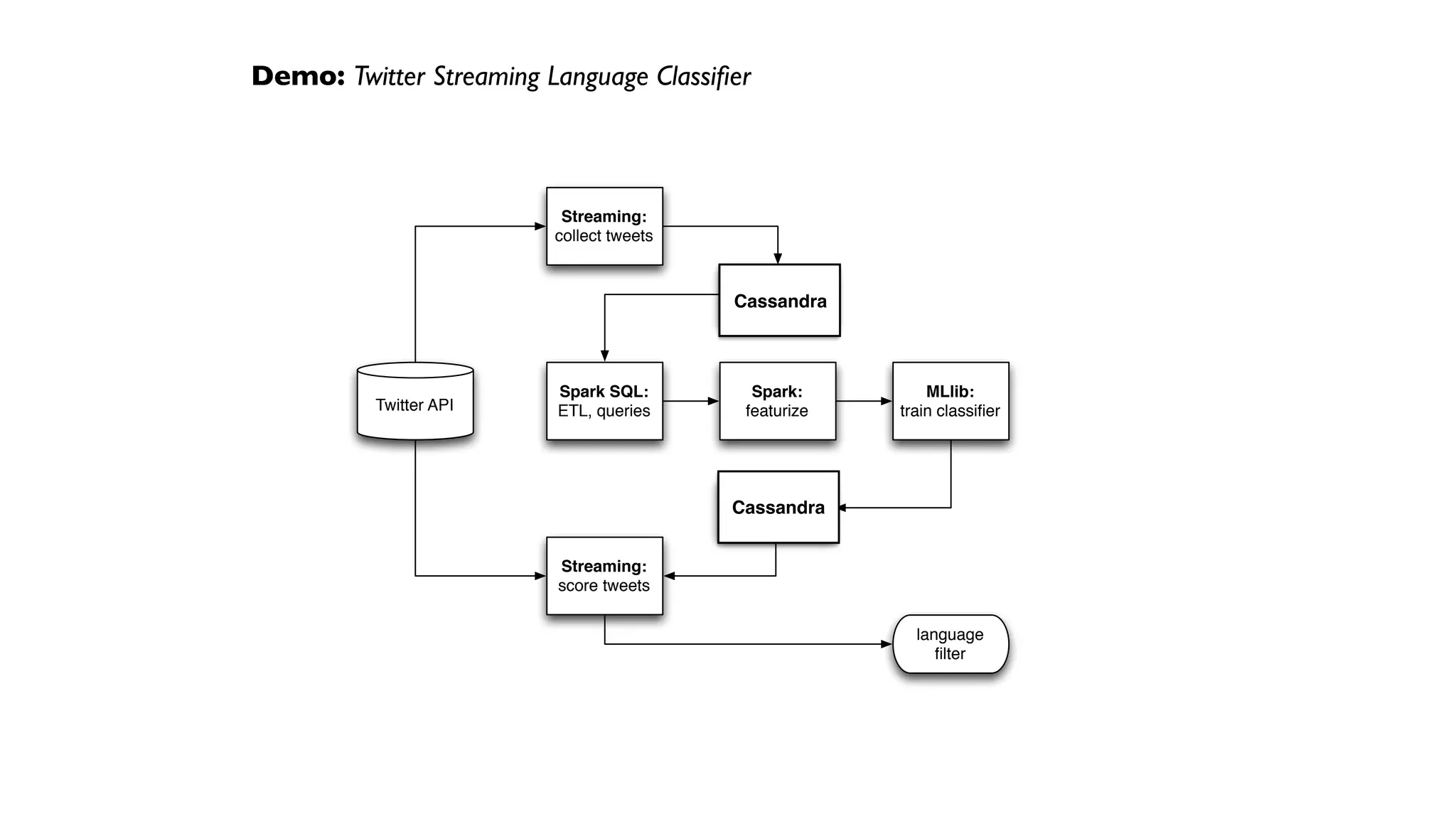
Demo: Twitter Streaming Language Classifier
From tweets to ML features,
approximated as sparse
vectors:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-time-analytics-with-dse-160219184212/75/Real-Time-Analytics-with-Dse-55-2048.jpg)

![Demo: Twitter Streaming Language Classifier
Sample Code + Output:
gist.github.com/ceteri/835565935da932cb59a2
val sc = new SparkContext(new SparkConf())
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(5))
val tweets = TwitterUtils.createStream(ssc, Utils.getAuth)
val statuses = tweets.map(_.getText)
val model = new KMeansModel(ssc.sparkContext.objectFile[Vector]
(modelFile.toString).collect())
val filteredTweets = statuses
.filter(t =>
model.predict(Utils.featurize(t)) == clust)
filteredTweets.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
CLUSTER 1:
TLあんまり⾒見ないけど
@くれたっら
いつでもくっるよ٩(δωδ)۶
そういえばディスガイアも今⽇日か
CLUSTER 4:
صدام بعد روحت العروبه قالوا
العروبه تحيى سلمان مع واقول
RT @vip588: √ مي فولو √ متابعني زيادة √ االن للمتواجدين vip588
√ ما يلتزم ما اللي √ رتويت عمل للي فولو √ للتغريدة رتويت √ باك فولو
بيستفيد …
سورة ن](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-time-analytics-with-dse-160219184212/75/Real-Time-Analytics-with-Dse-59-2048.jpg)
