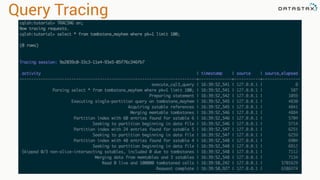
This document provides guidance on setting up server monitoring, application metrics, log aggregation, time synchronization, replication strategies, and garbage collection for a Cassandra cluster. Key recommendations include:
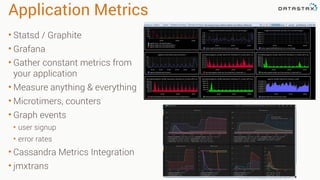
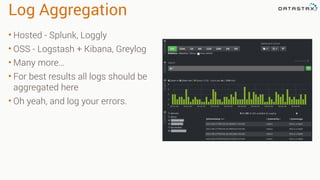
1. Use monitoring tools like Monit, Munin, Nagios, or OpsCenter to monitor processes, disk usage, and system performance. Aggregate all logs centrally with tools like Splunk, Logstash, or Greylog.
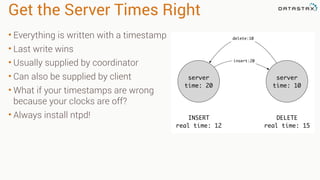
2. Install NTP to synchronize server times which are critical for consistency.
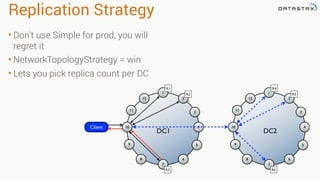
3. Use the NetworkTopologyStrategy replication strategy and avoid SimpleStrategy for production.
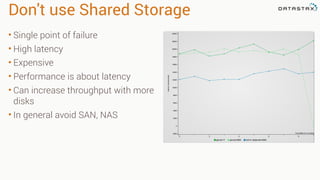
4. Avoid shared storage and focus on low latency and high throughput using multiple local disks.
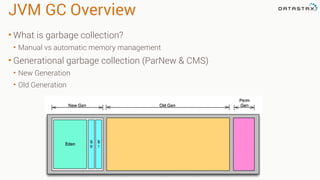
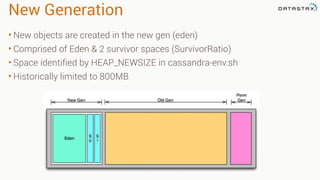
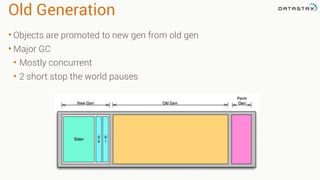
5. Understand