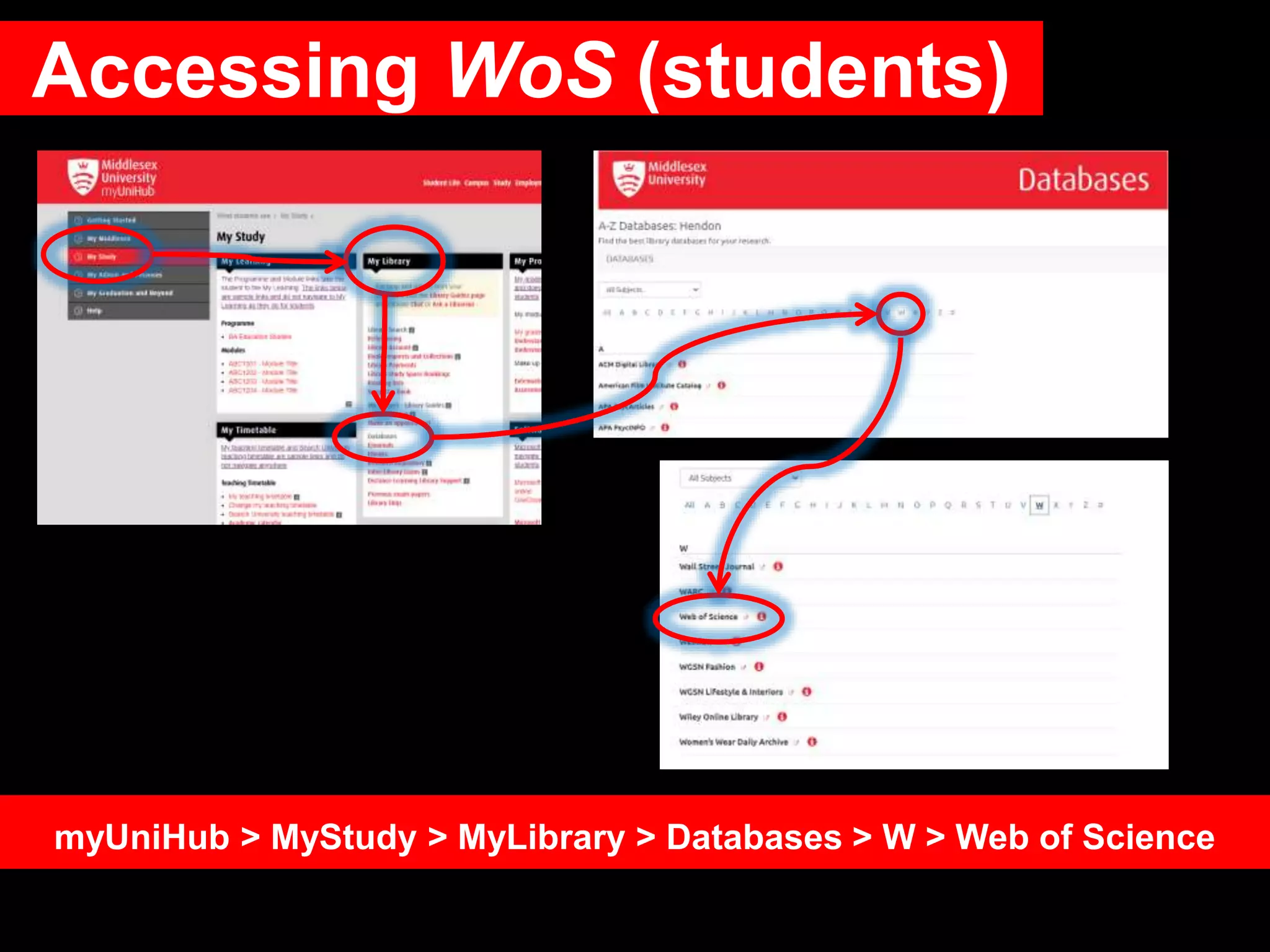
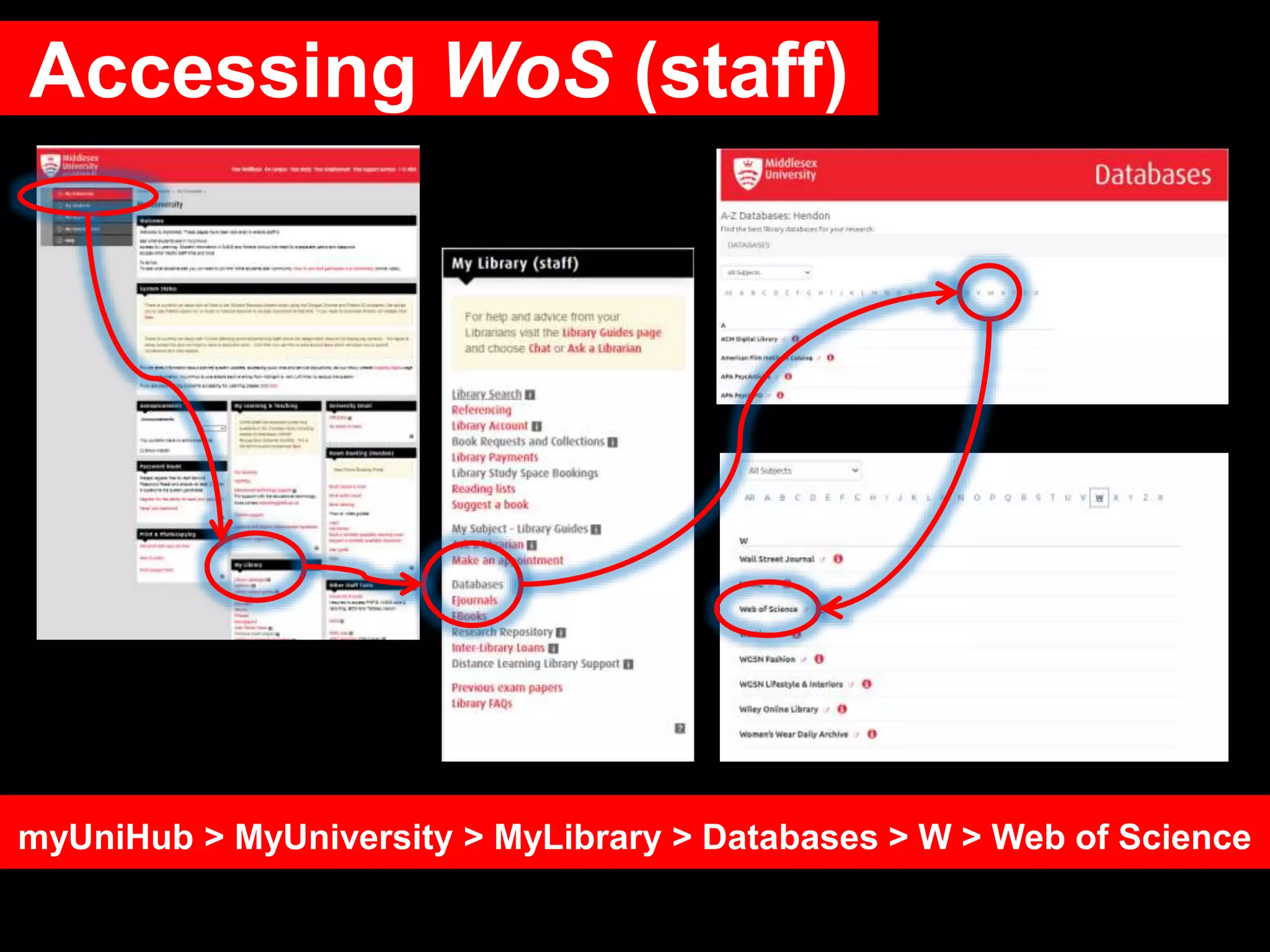
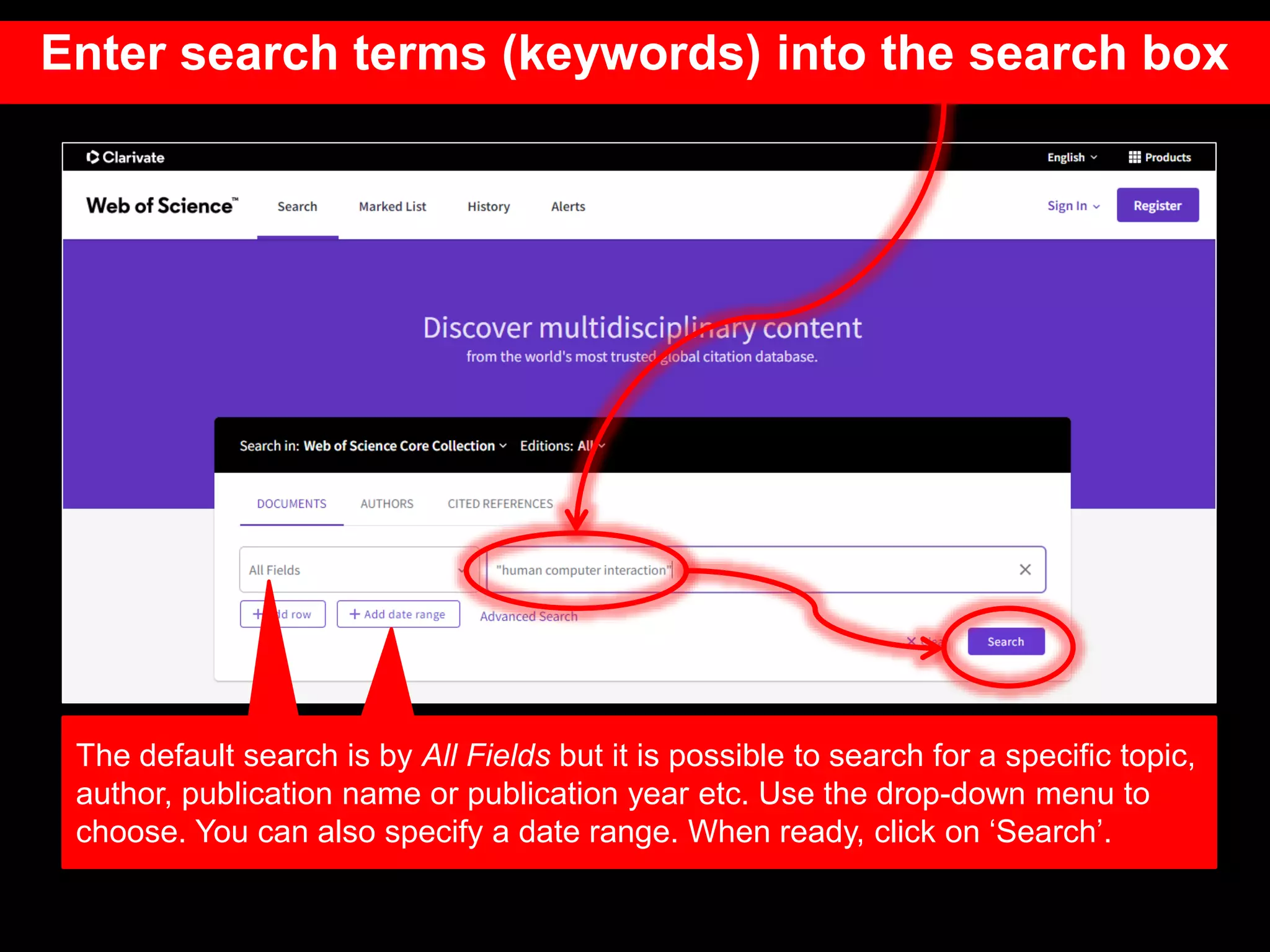
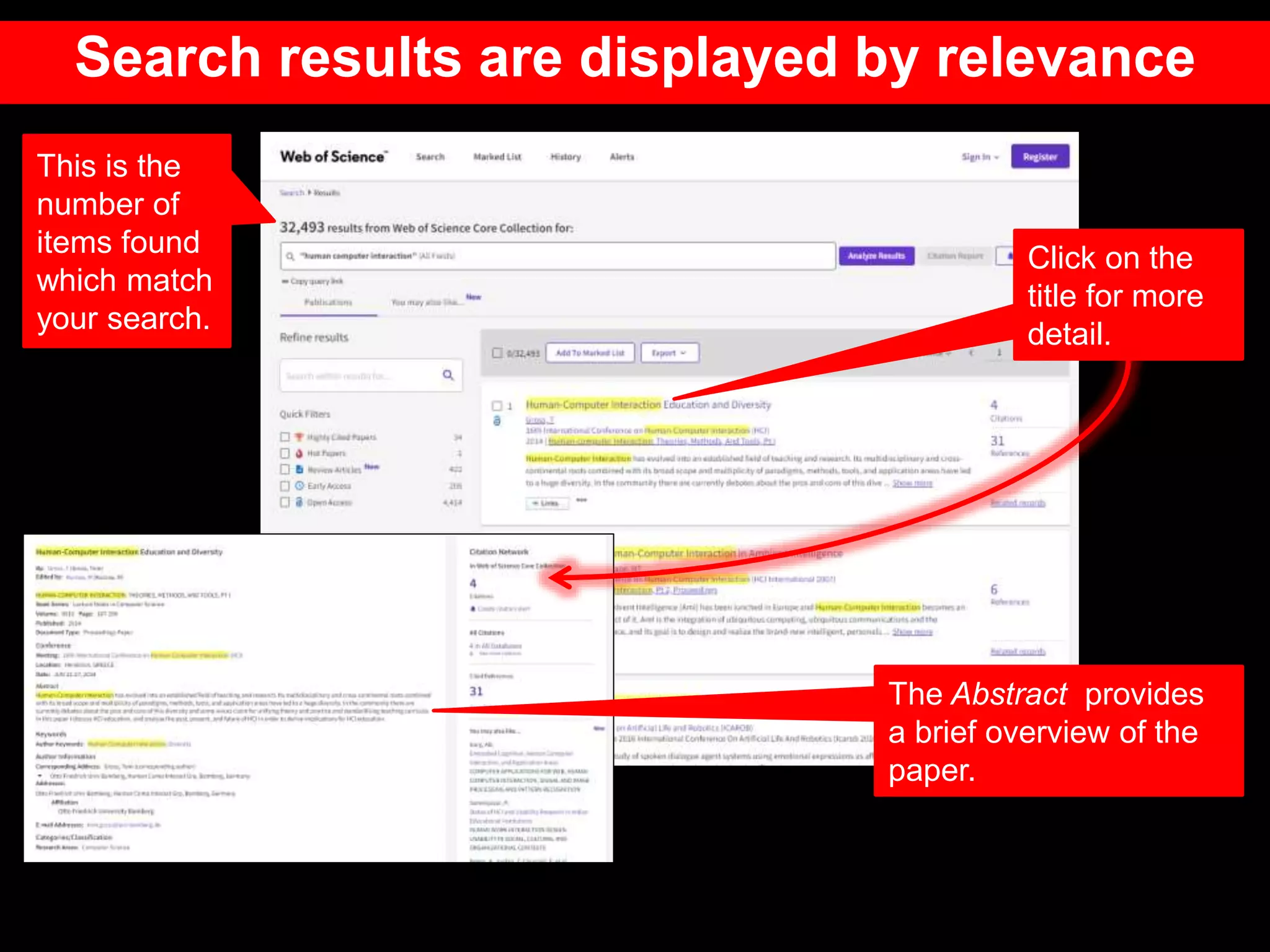
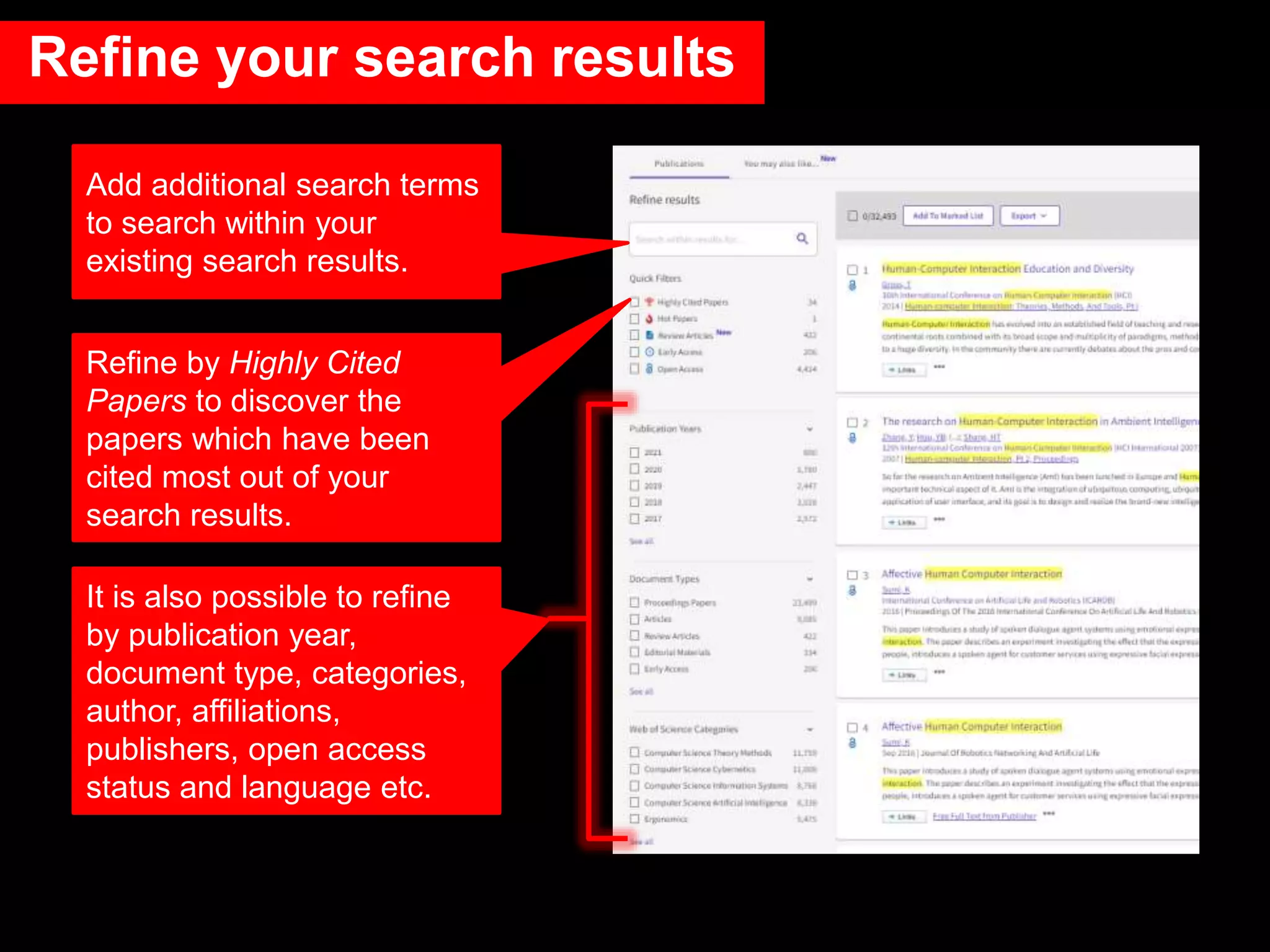
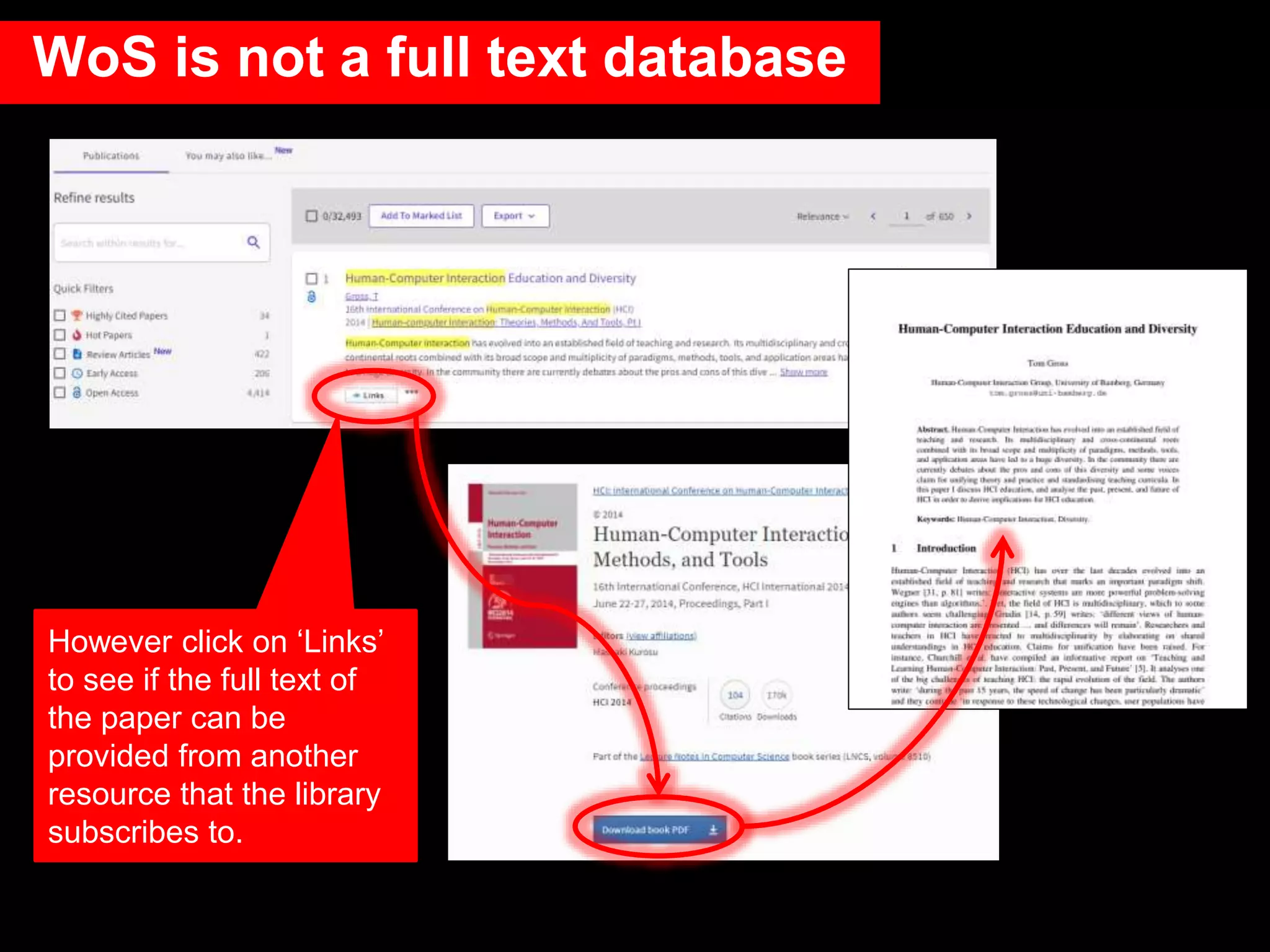
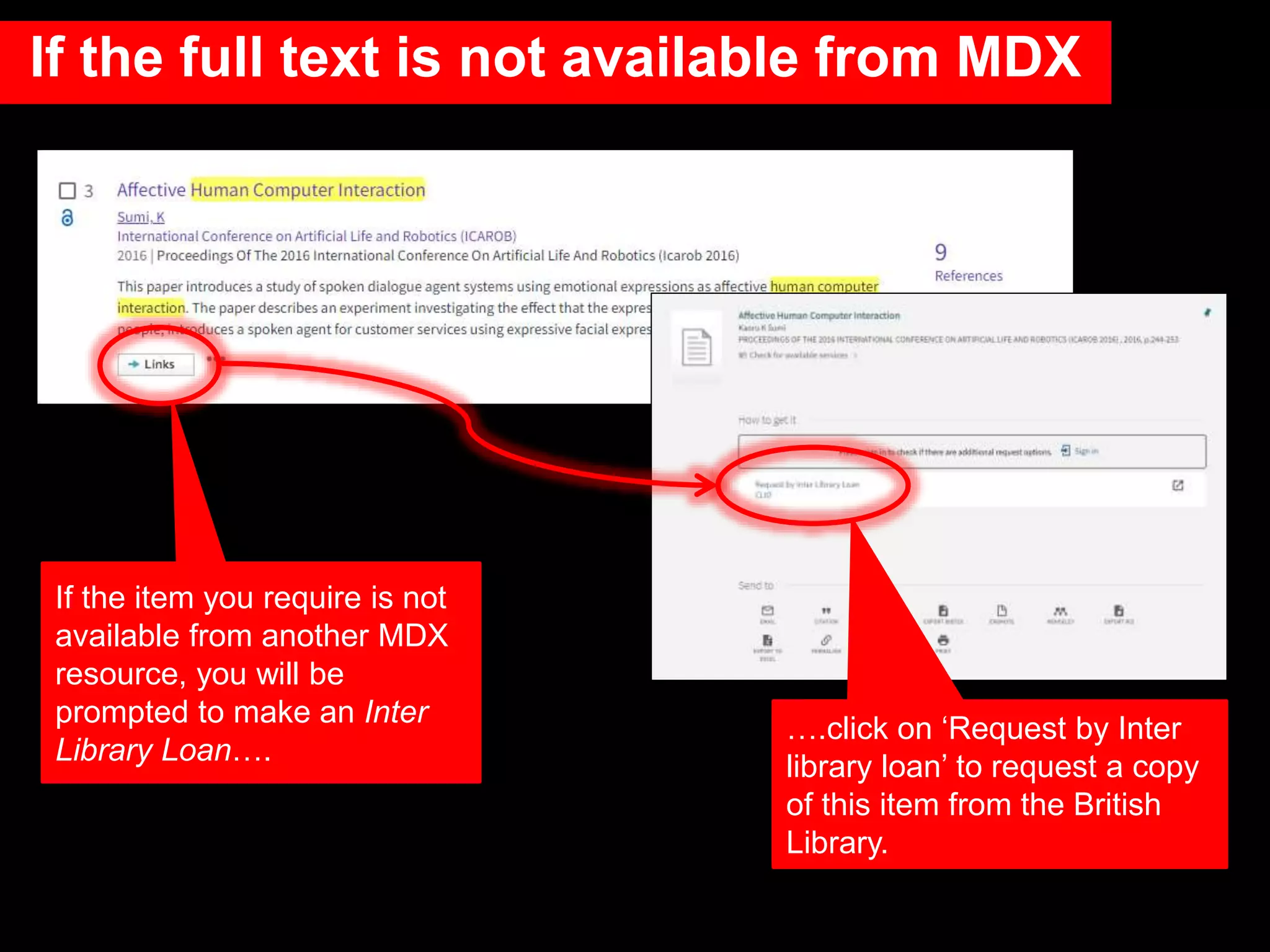
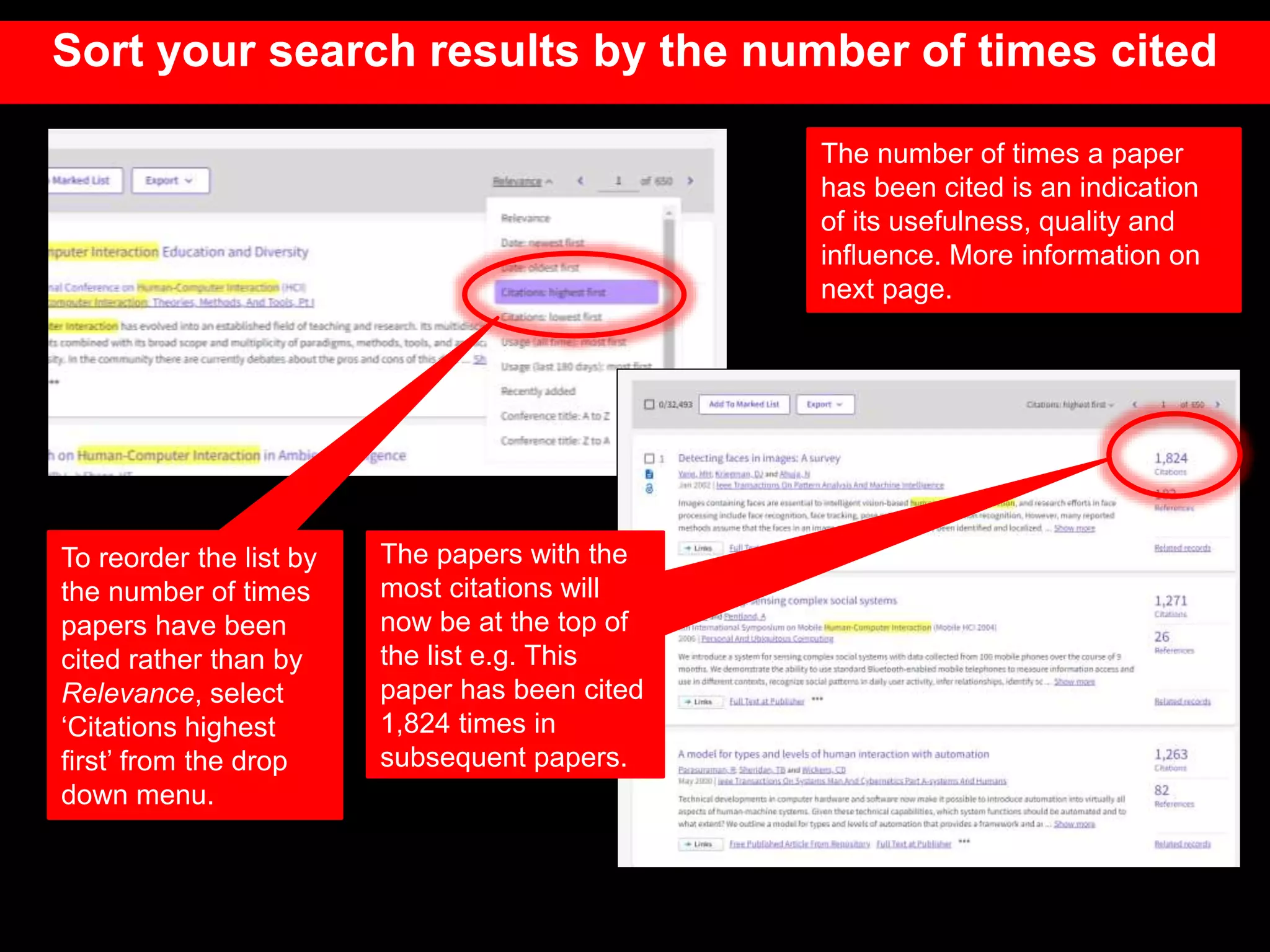
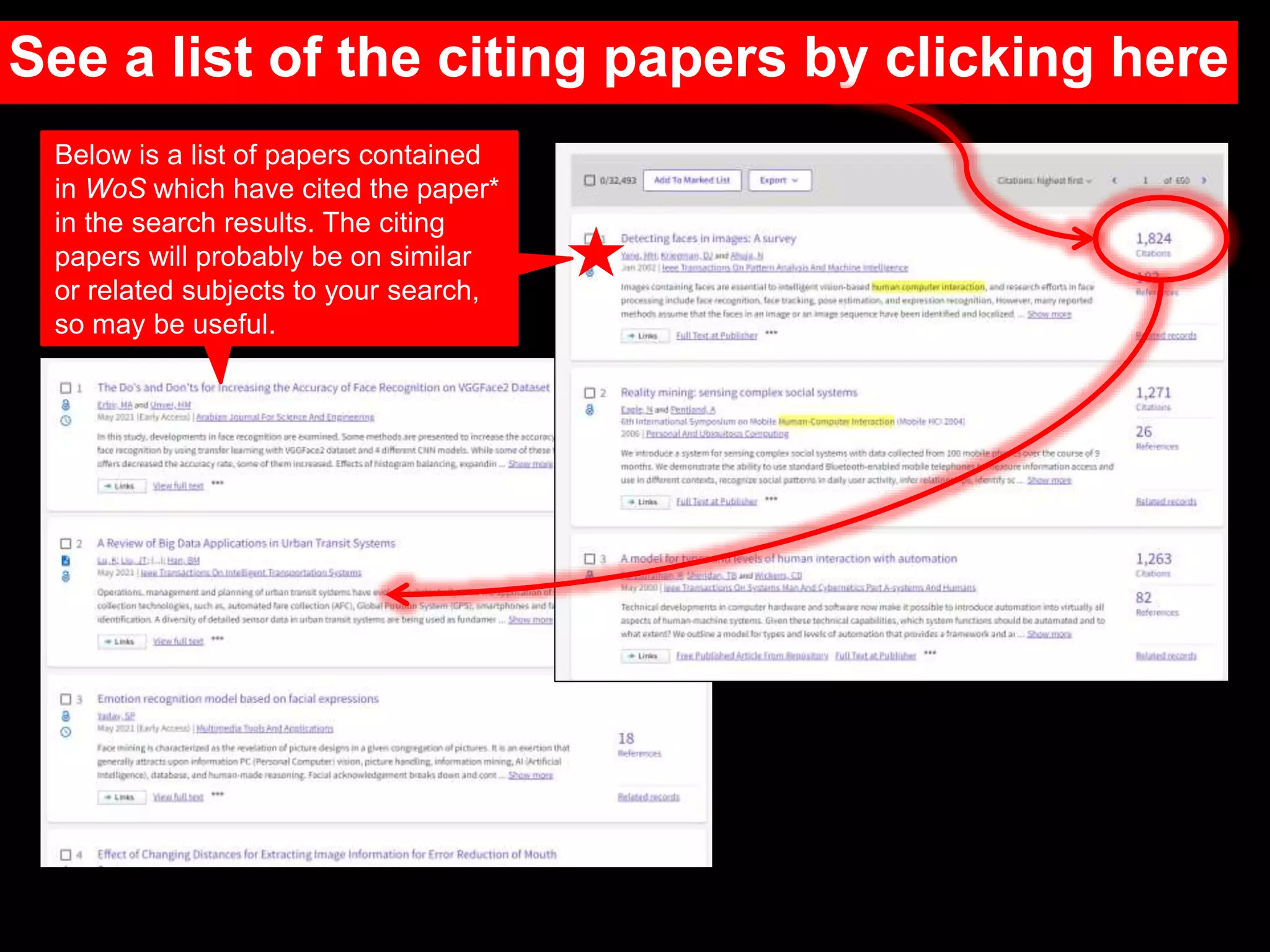
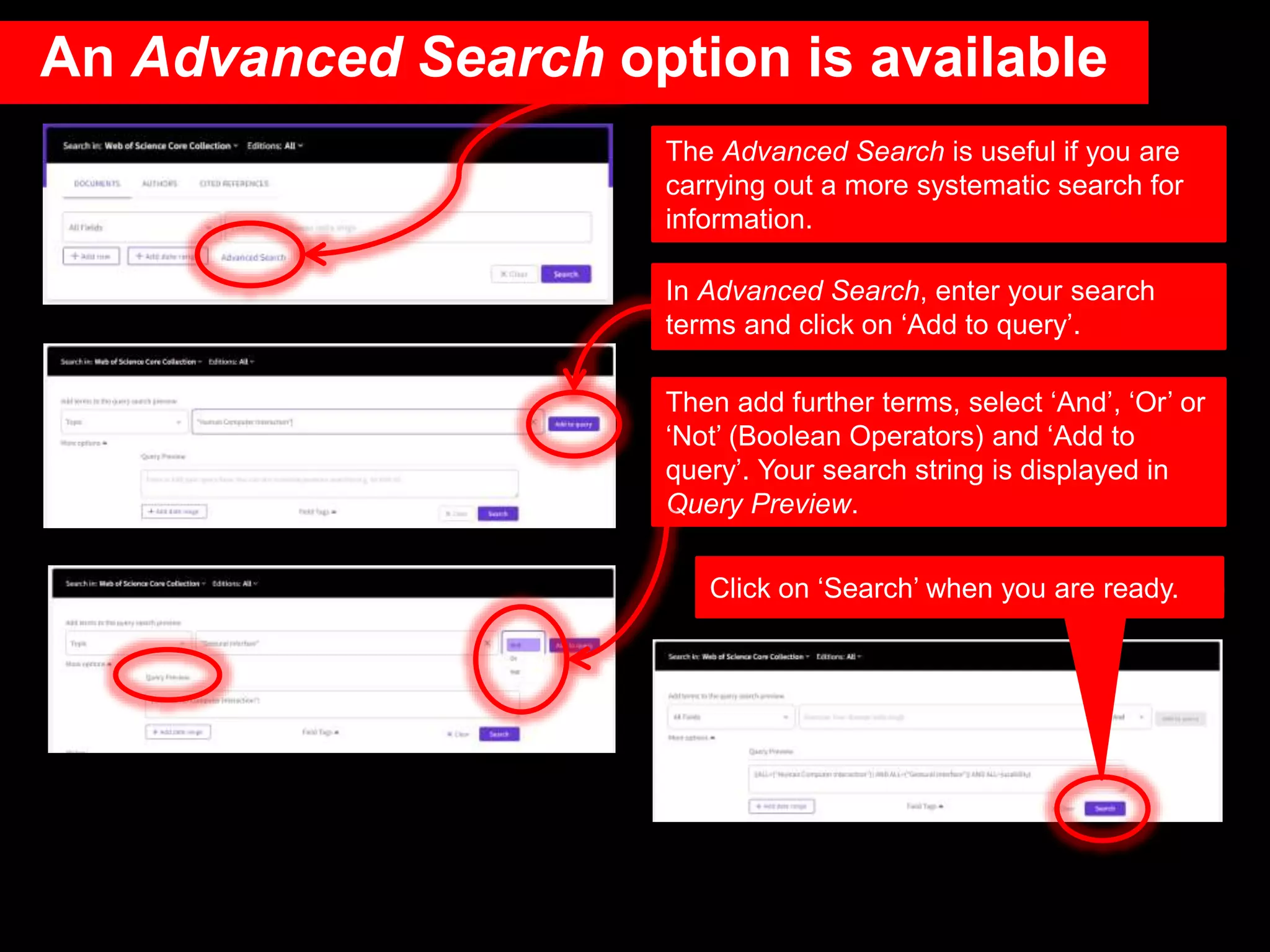
This document provides an introduction to using Web of Science (WoS), a citation index database. It describes how WoS can be used to search for journal articles and conference papers, find citation information to gauge a paper's impact and influence, and discover related works. It also explains how WoS provides access to bibliographic records and citations from scientific journals, social sciences, arts and humanities. Basic searching, filtering, and accessing full text is demonstrated.