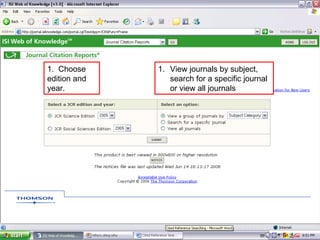
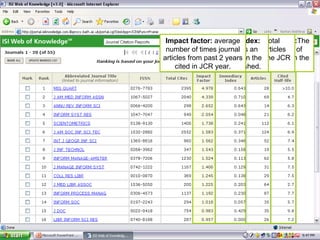
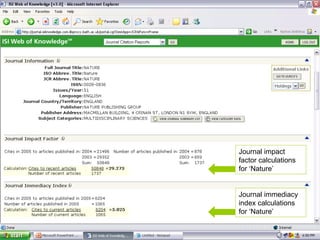
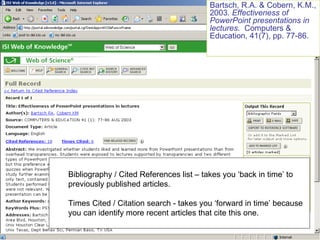
This document provides an introduction to citation searching and journal citation reports. It outlines how to use citation searching to find highly cited articles and authors, as well as those who have cited your own work. It also explains how journal citation reports can be used to find the most influential journals in a given field and compare the impact factors of different journals. The document gives guidance on using tools like Web of Science and Journal Citation Reports to conduct citation searching and analyze journal metrics.

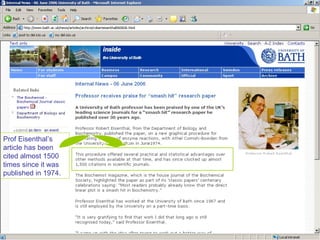











![The best measure? Professor Frank Jackson from the Australian National University was chosen as a ‘citation laureate’ by Thomson ISI (publisher of Web of Science). He wrote two much discussed papers setting out an argument in the philosophy of mind – an argument he has since repudiated. “ These later papers get cited a fair bit but not as much as those that presented the views I no longer accept… but that’s life,” Professor Jackson said.* Lane, Bernard. 2006 ‘Over-citation puts integrity under cloud’. The Australian [online]. Available: http://www.theaustralian.news.com.au/story/0,20867,20063447-12332,00.html. [Accessed: 9 Aug 2006]. Can you foresee any other difficulties with this method?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whos-citing-whom-13508/85/Who-s-citing-whom-24-320.jpg)