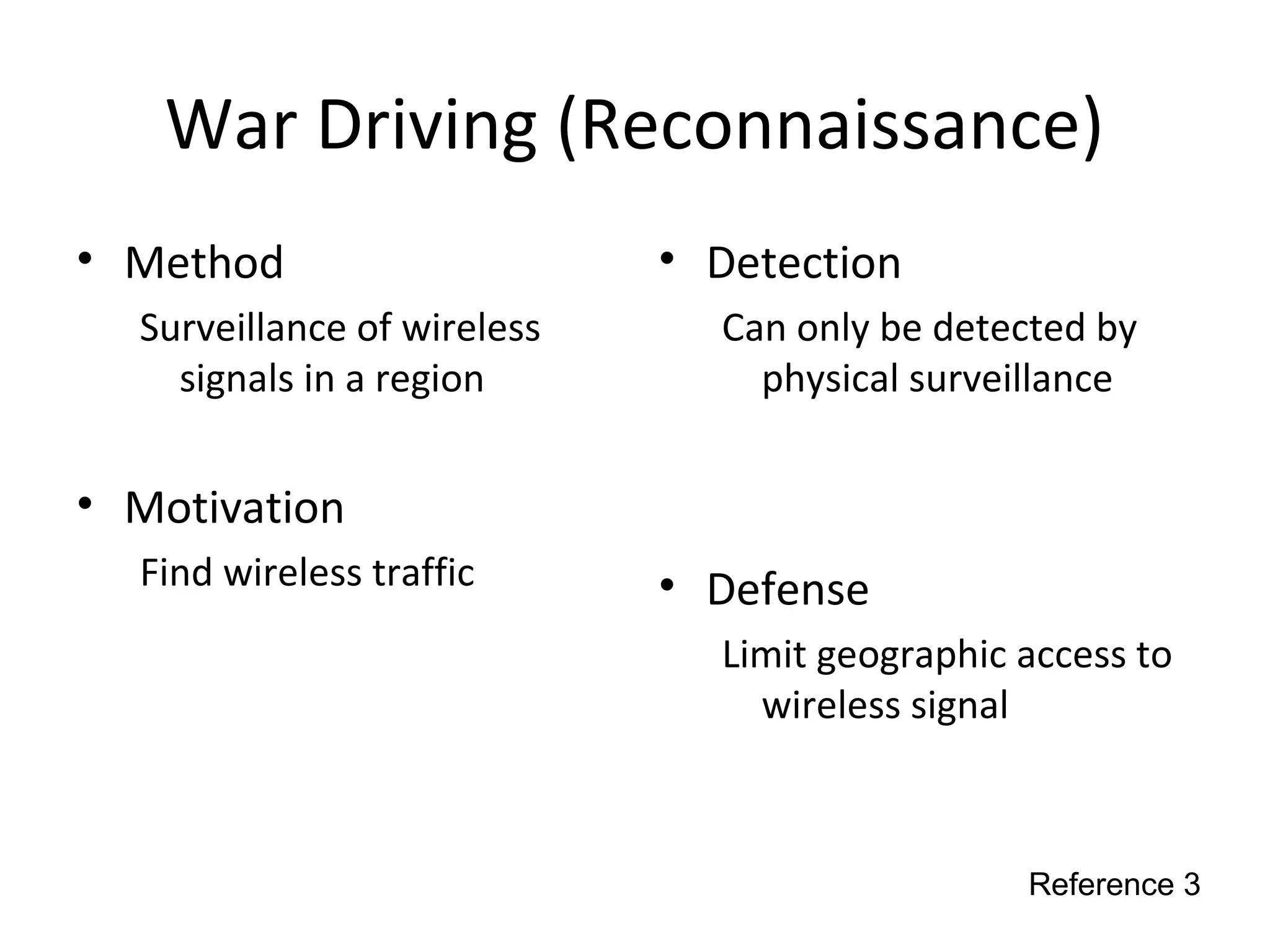
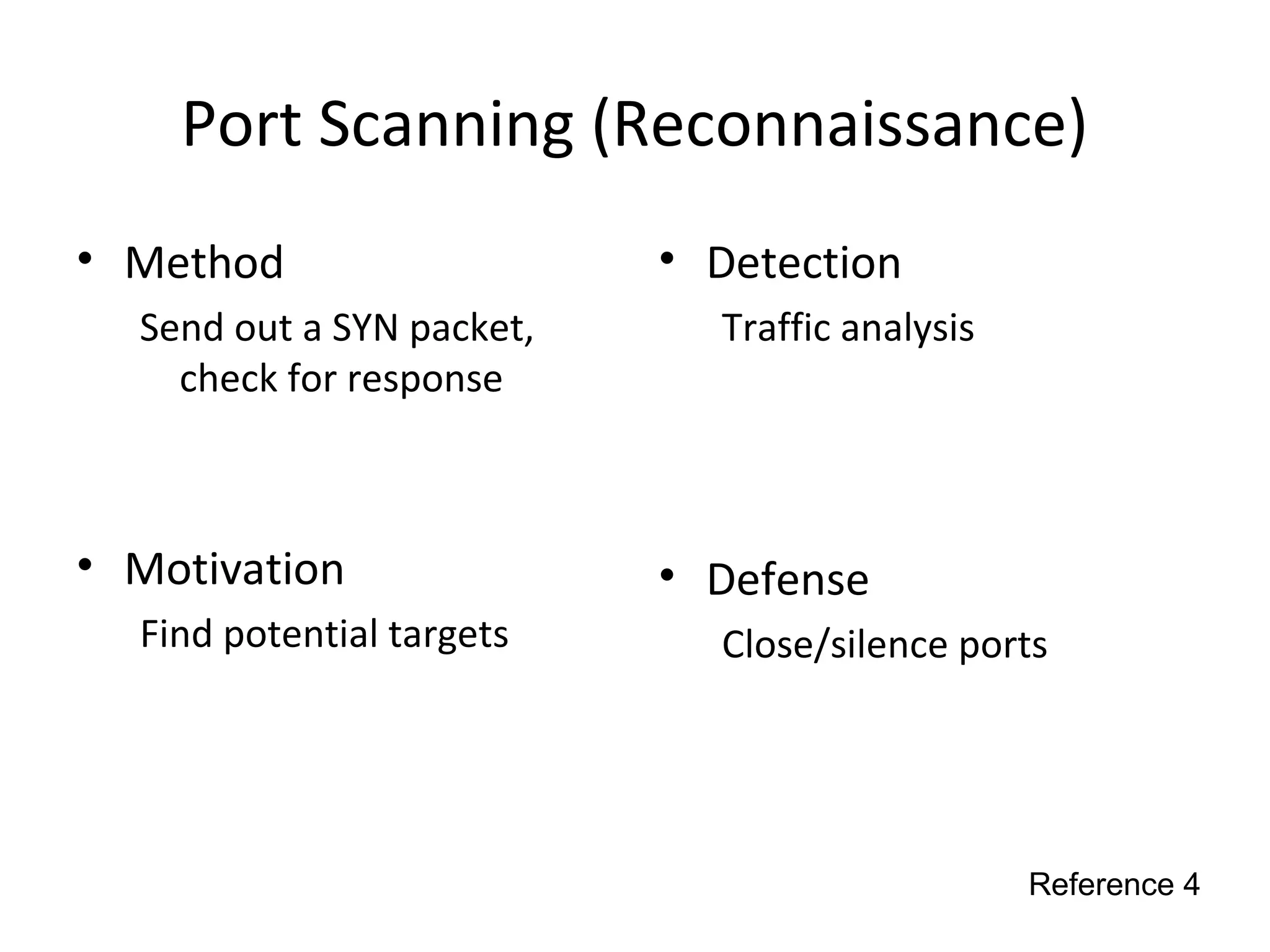
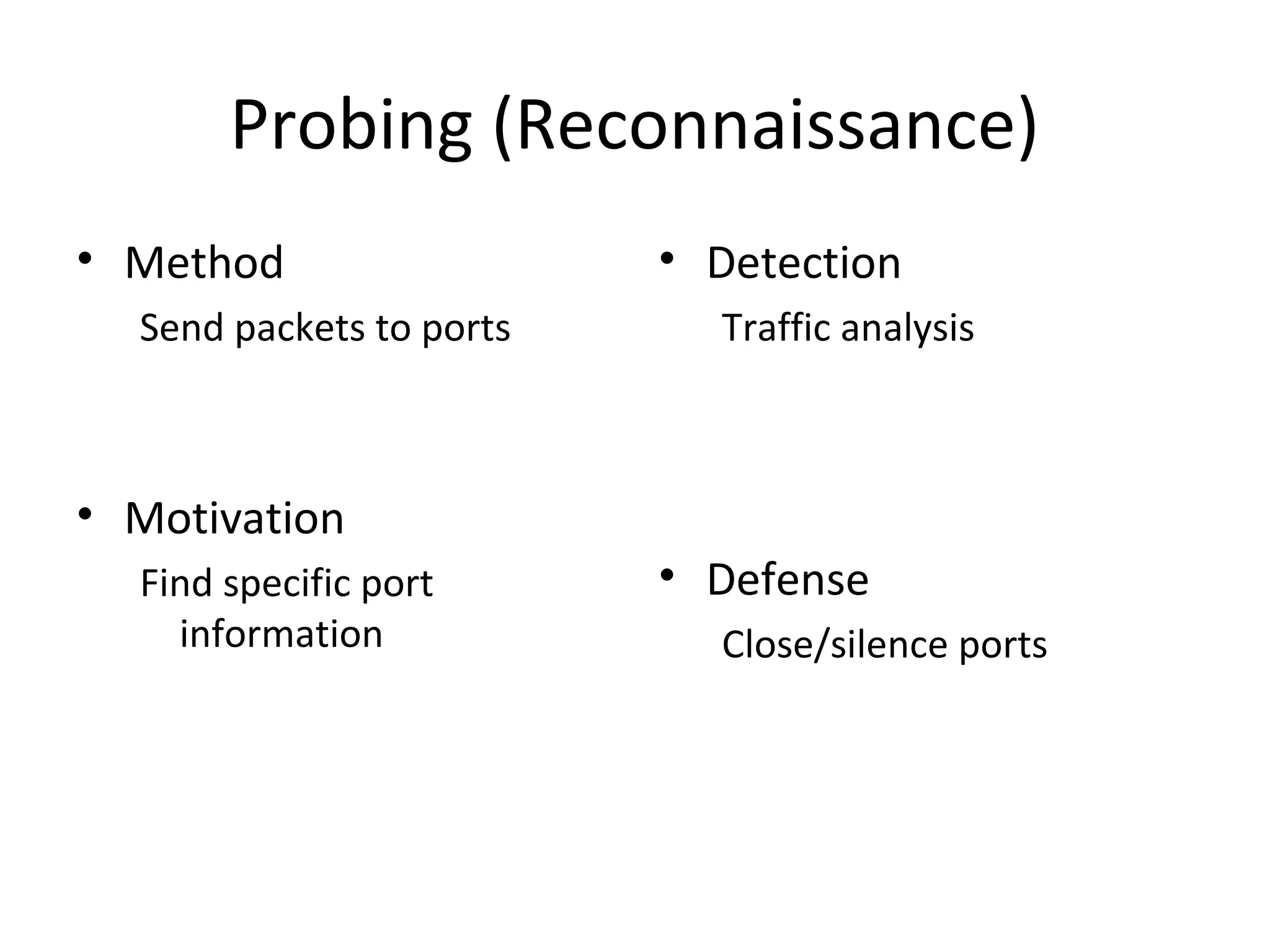
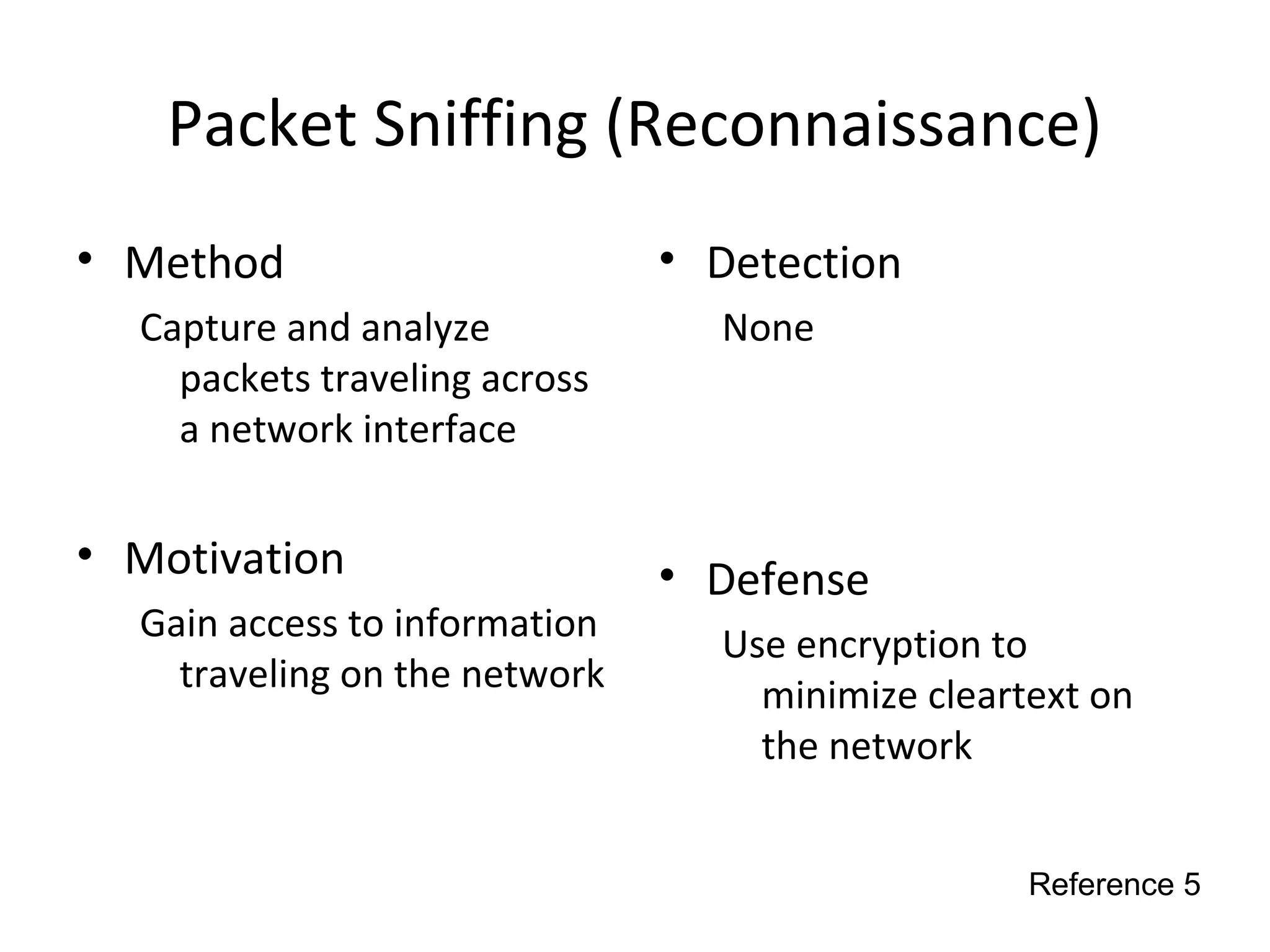
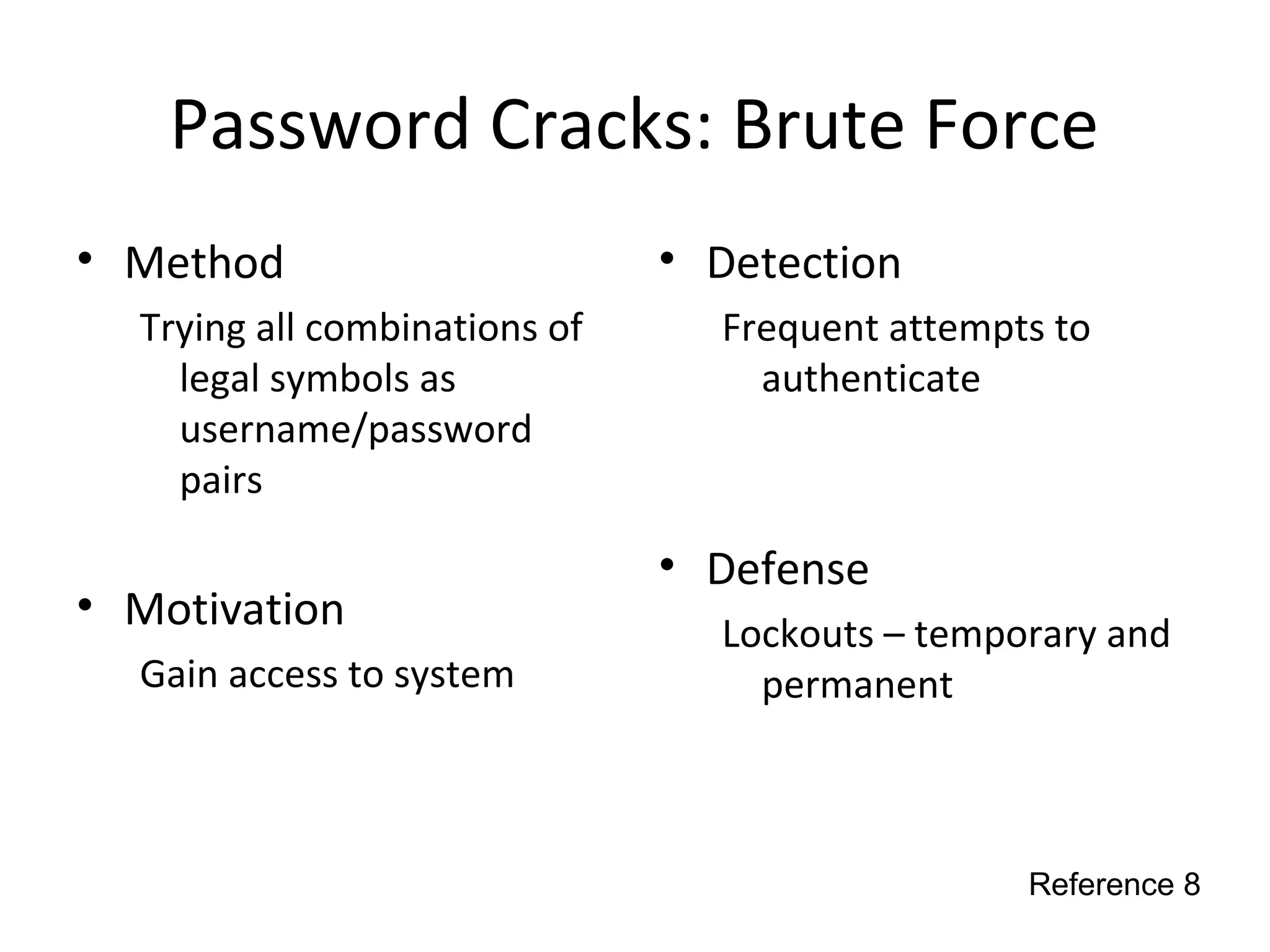
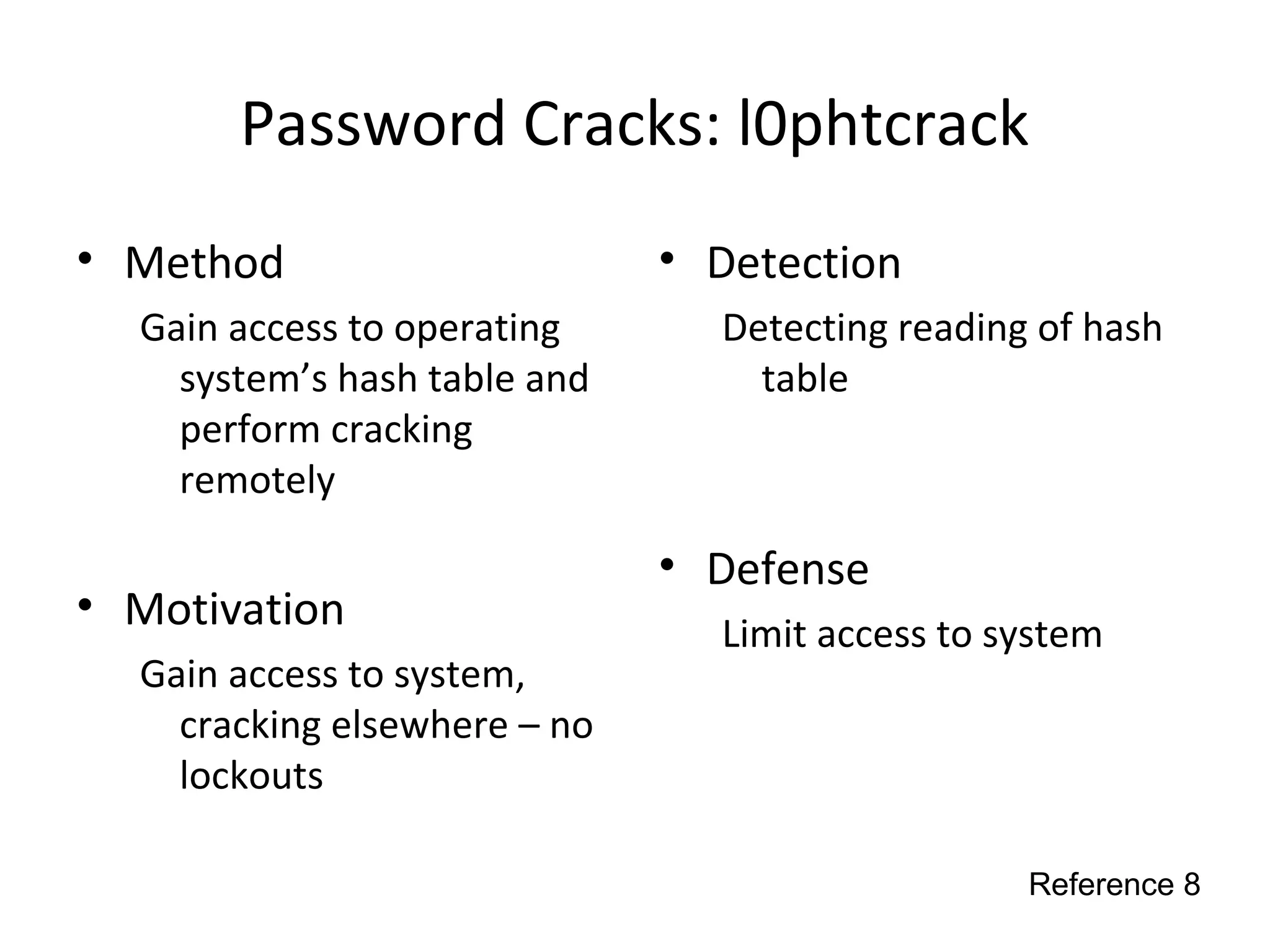
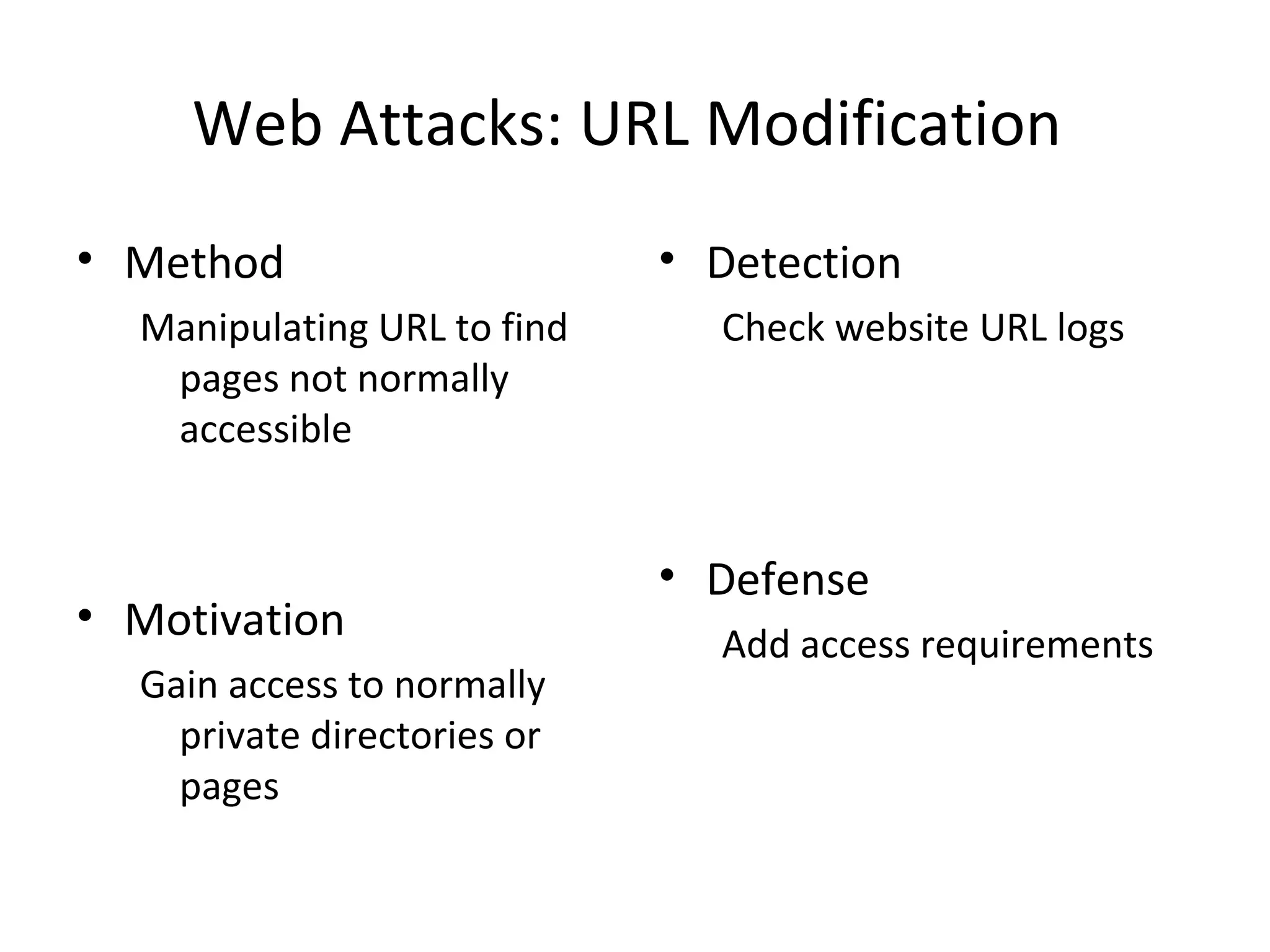
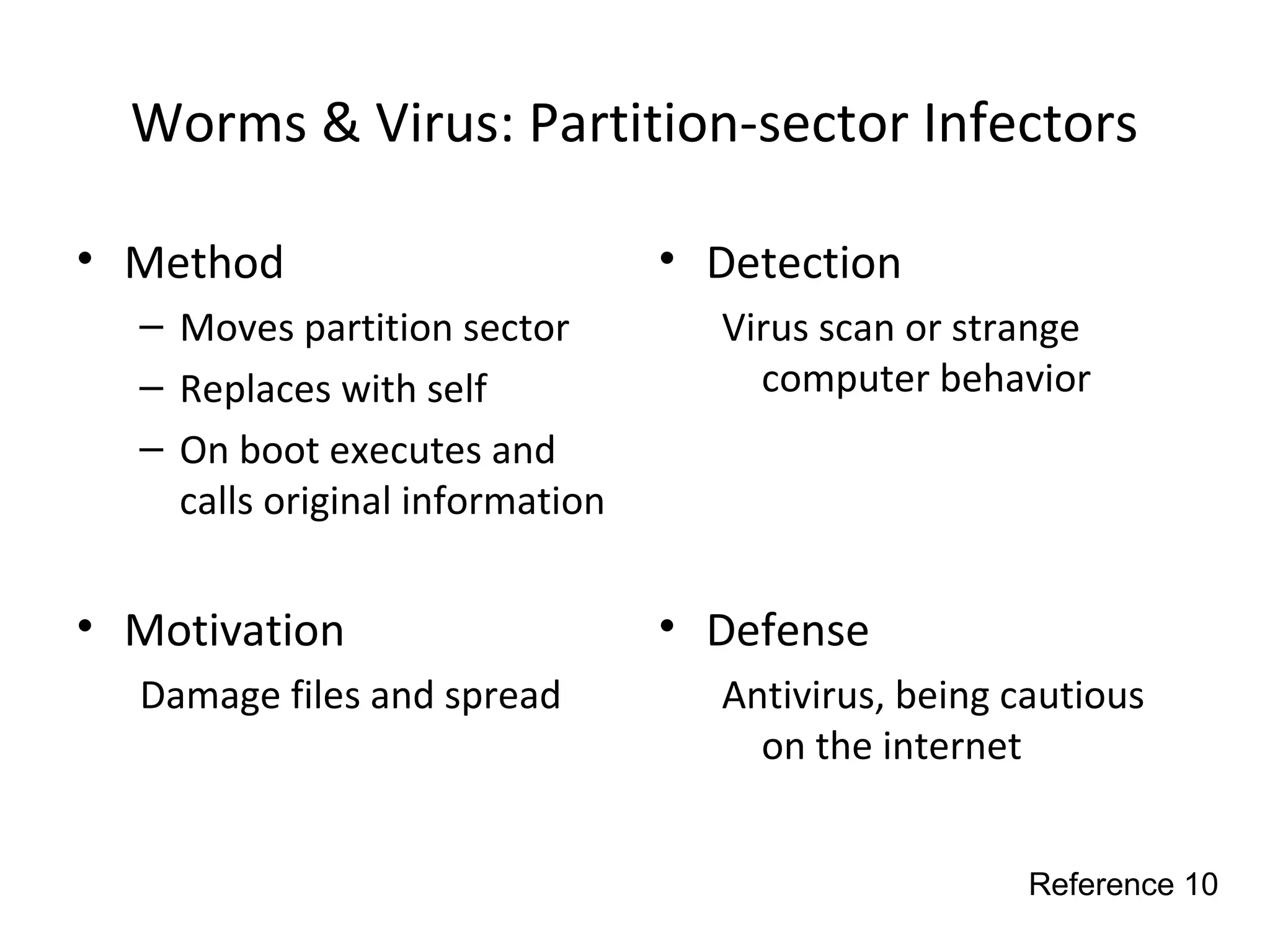
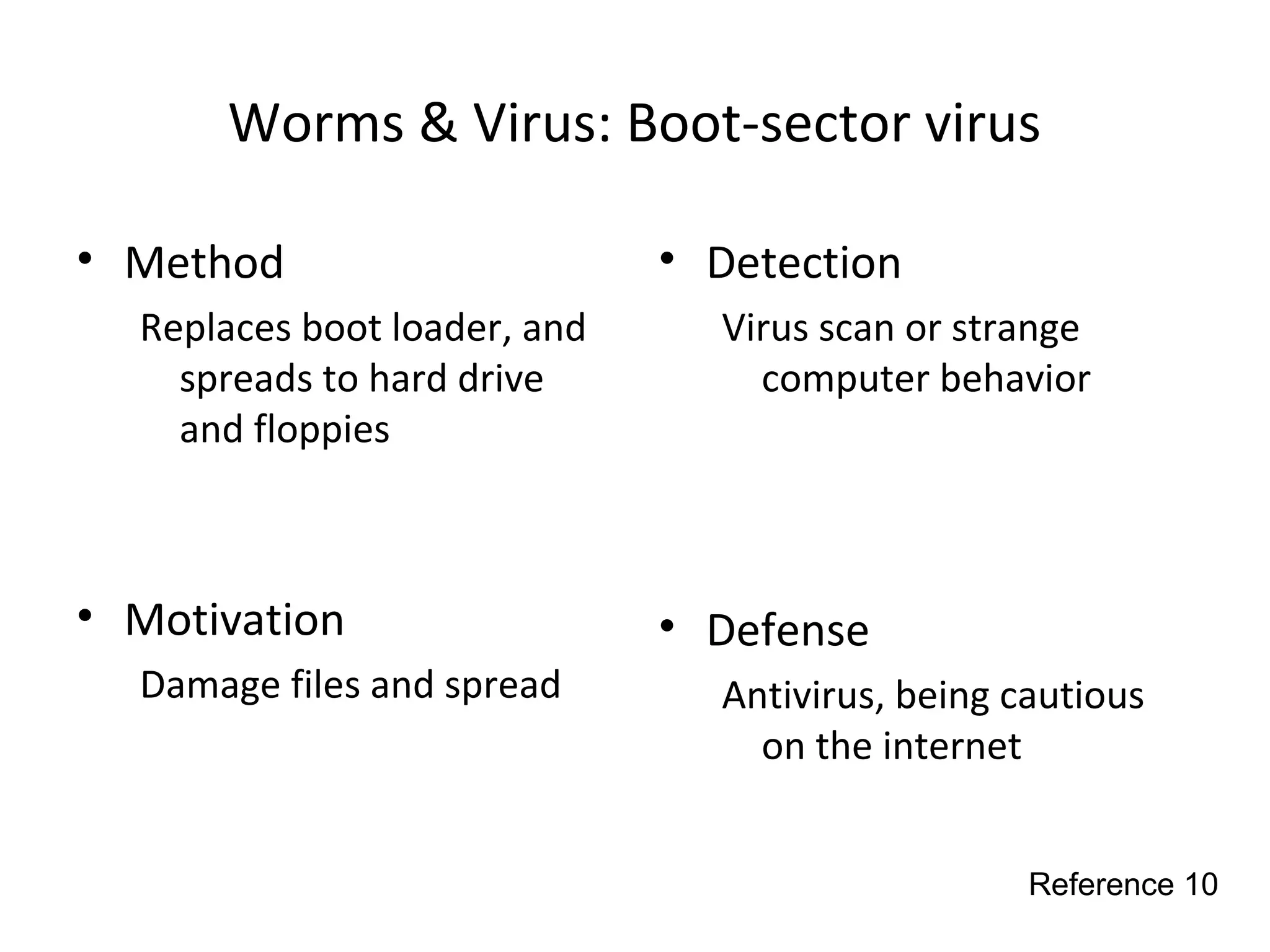
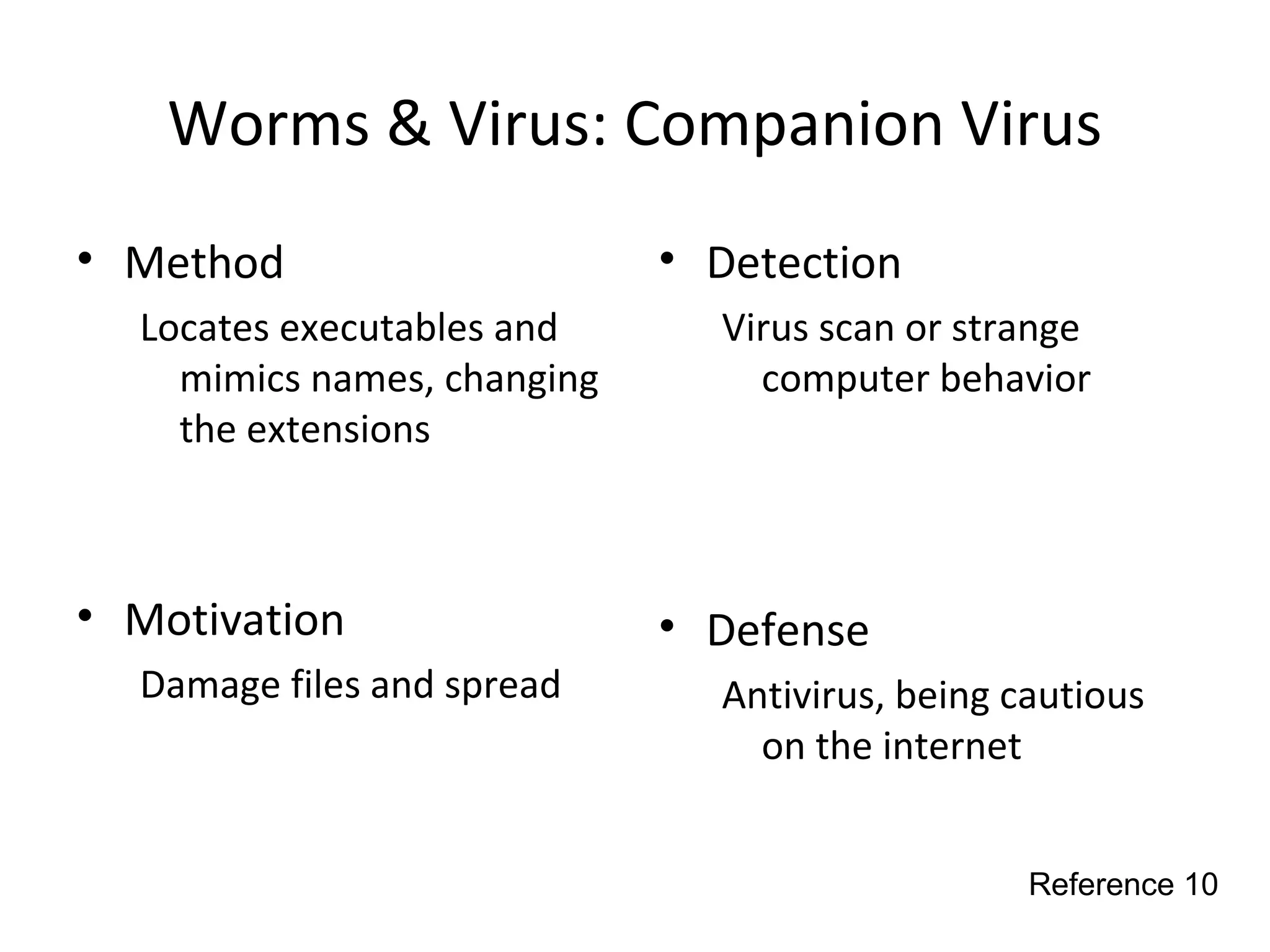
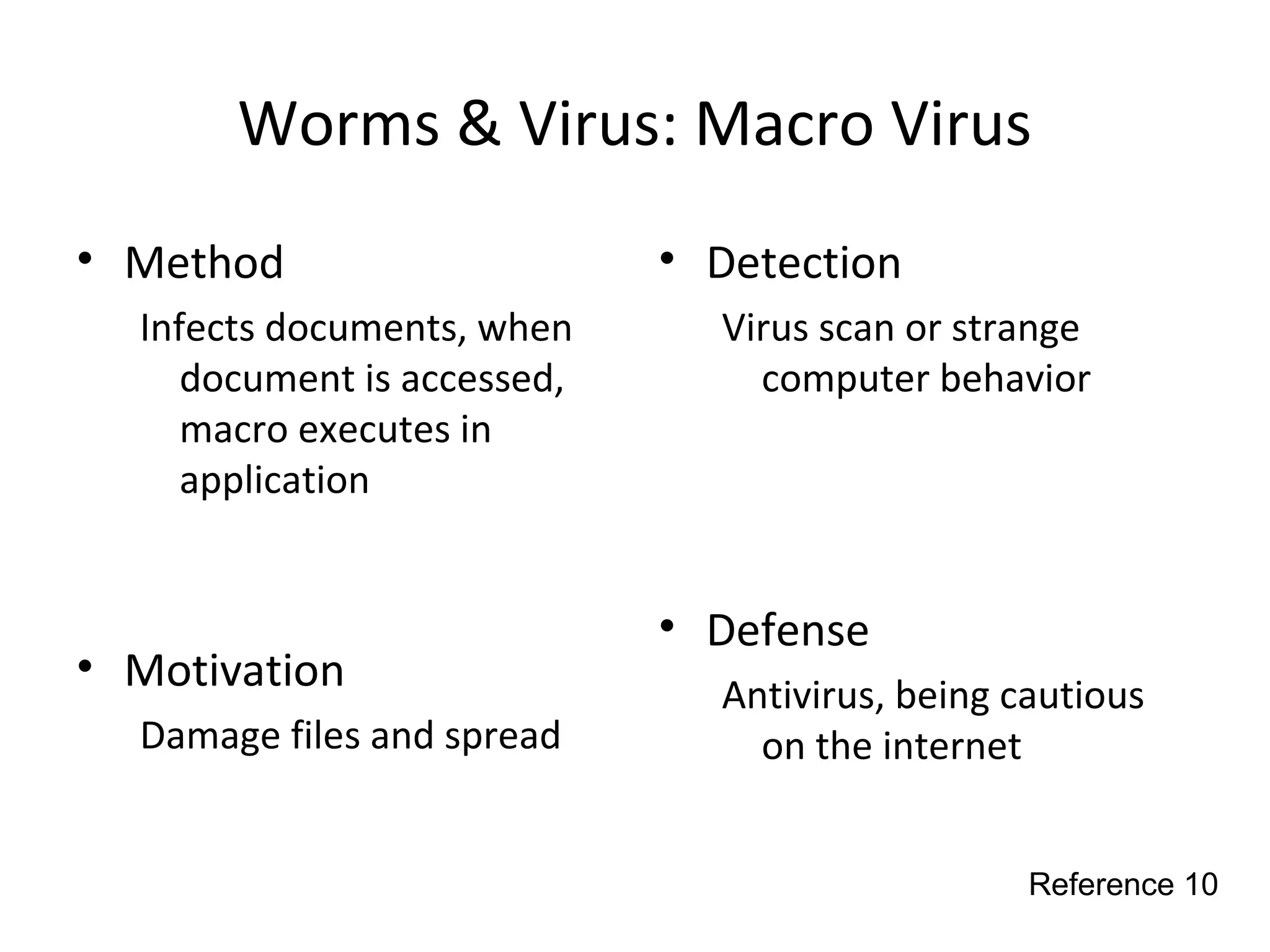
This document discusses techniques for reconnaissance, vulnerabilities, and attacks related to cybersecurity. Reconnaissance techniques covered include war dialing, war driving, port scanning, probing, and packet sniffing. Vulnerabilities explored are backdoors, code exploits, eavesdropping, indirect attacks, and social engineering. Attacks analyzed involve password cracking, web attacks, physical attacks, worms/viruses, logic bombs, buffer overflows, phishing, bots/zombies, spyware/malware, hardware keyloggers, eavesdropping/playback, and DDoS. Each topic provides details on method, motivation, detection, and defense.