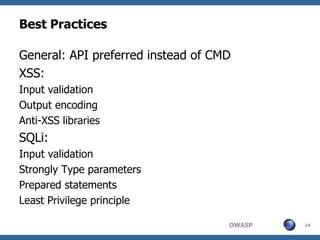
Good Secure Development Practices Presented By: Bil Corry lasso.pro Education Project. It recommends validating all user input, distrusting even your own requests, and taking a layered approach to validation, enforcement of business rules, and authentication. Some specific best practices include implementing positive authentication, principle of least privilege, centralized authorization routines, separating admin and user access, and ensuring error handling fails safely.