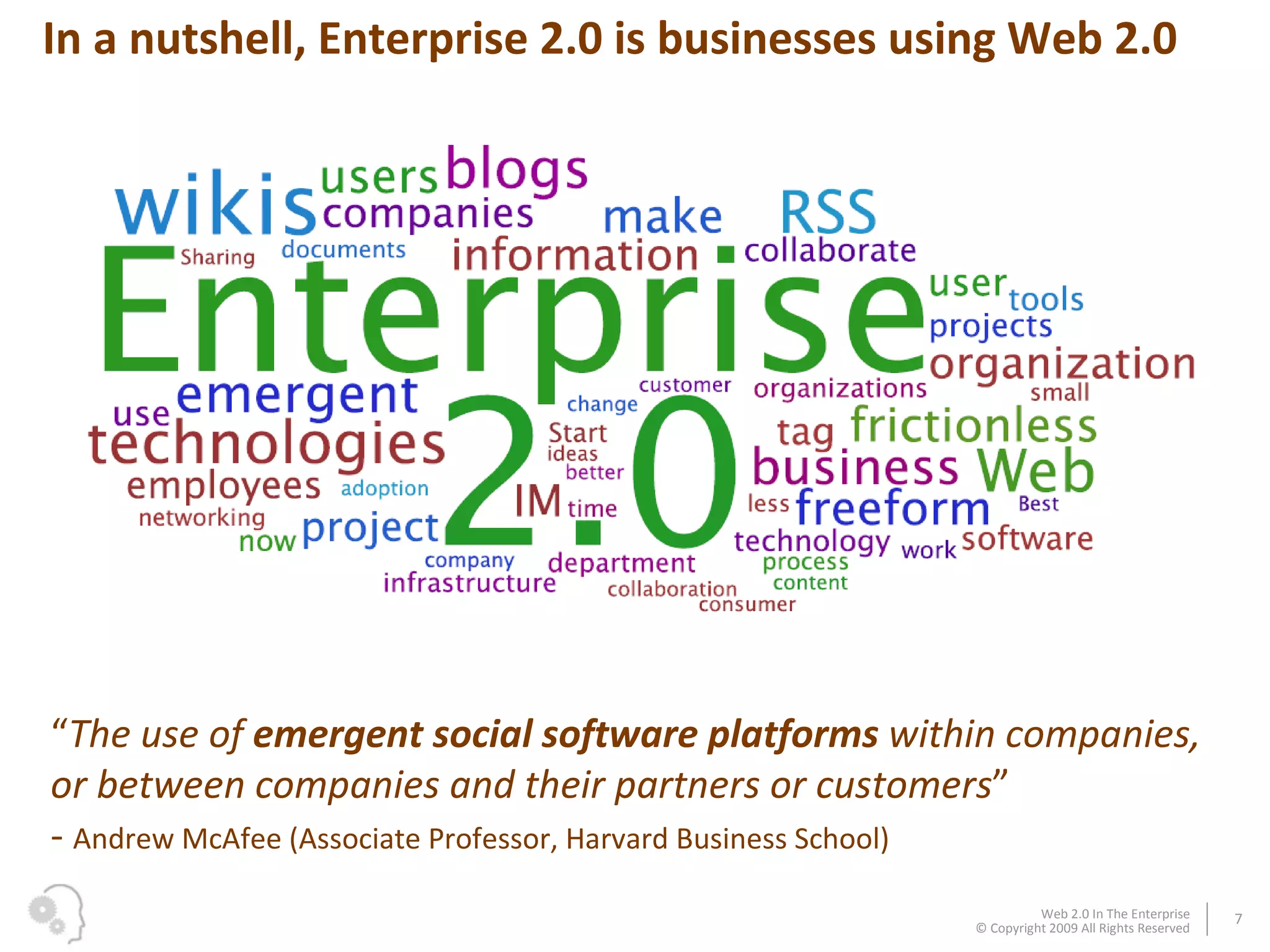
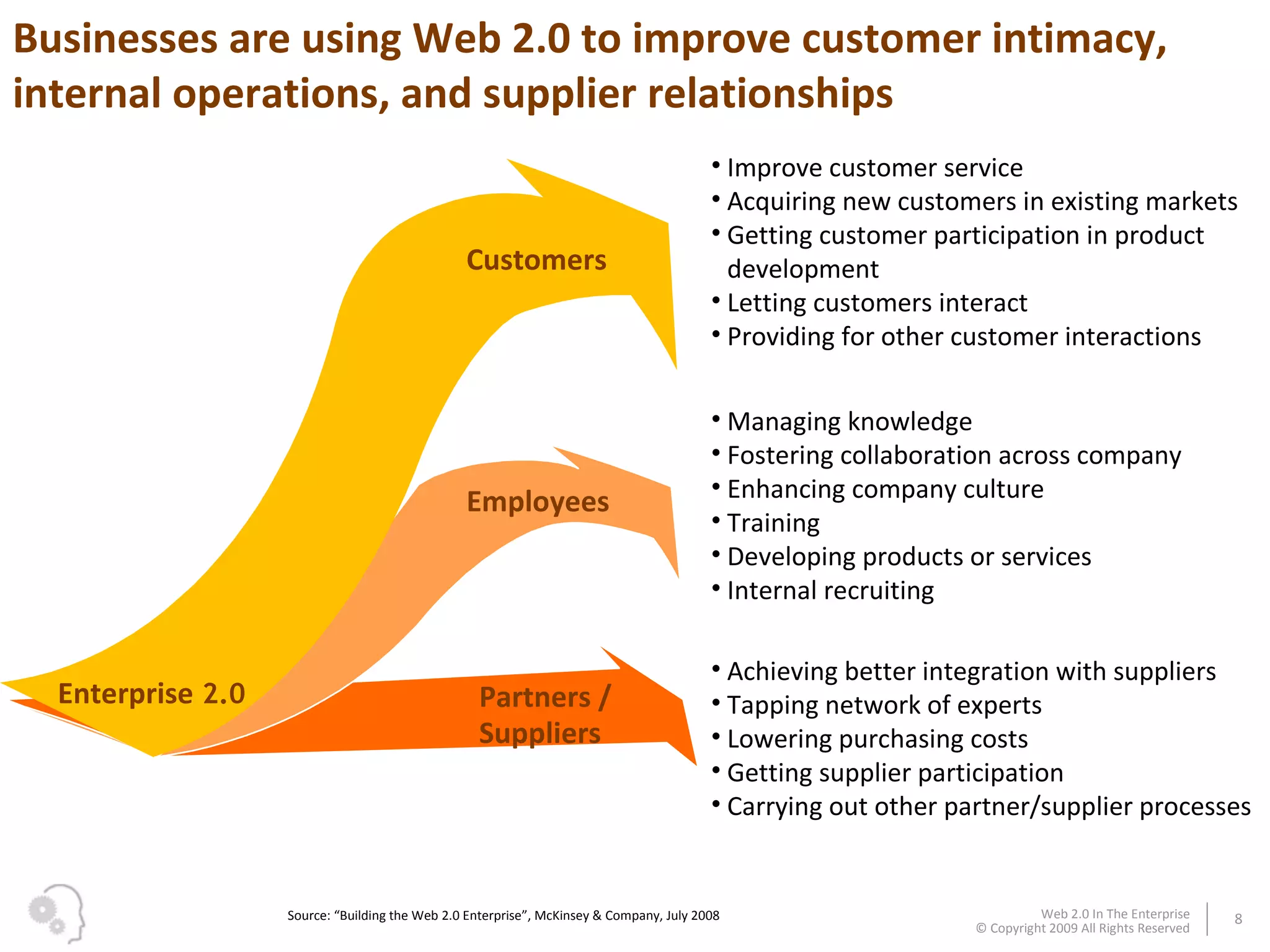
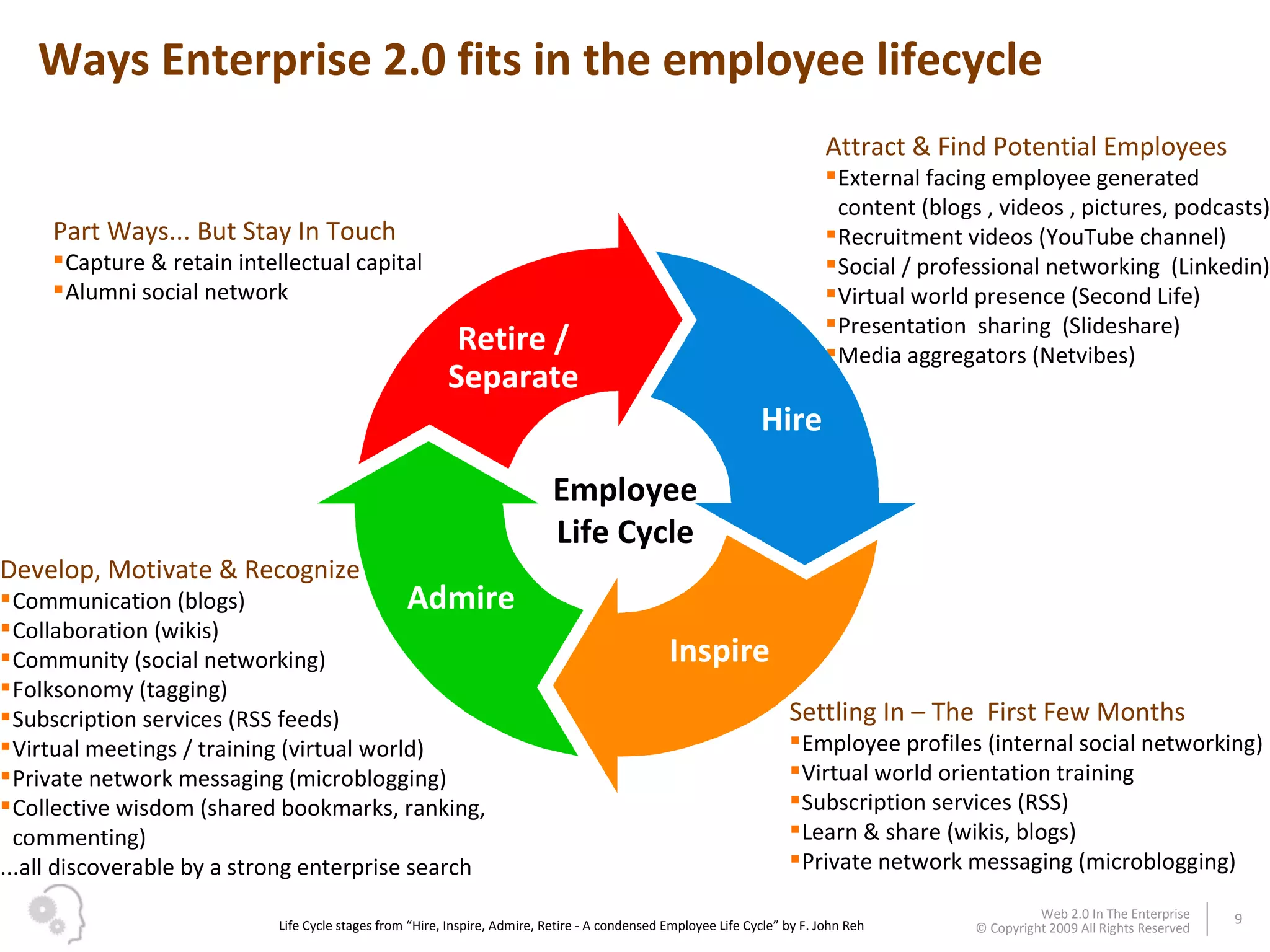
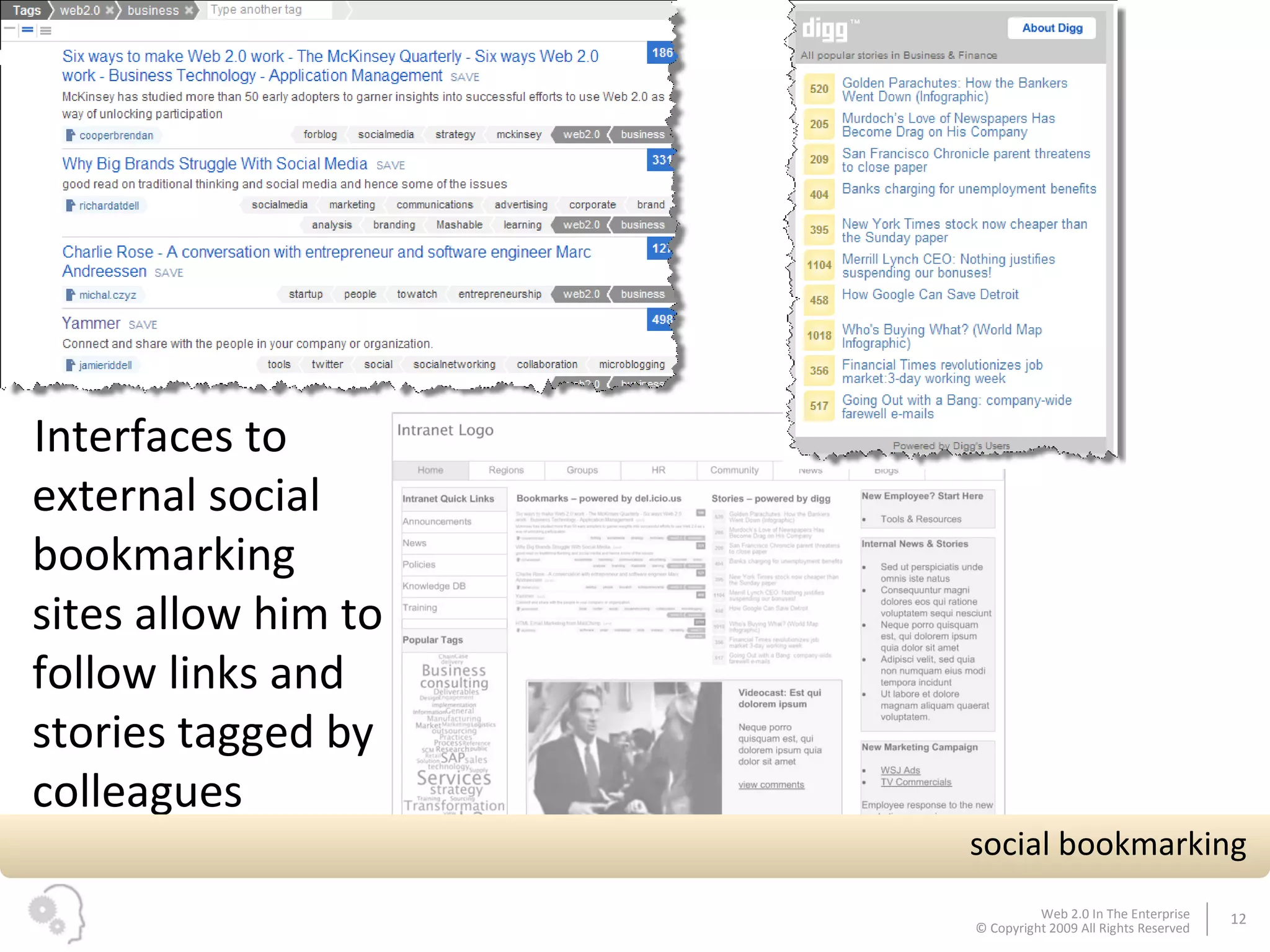
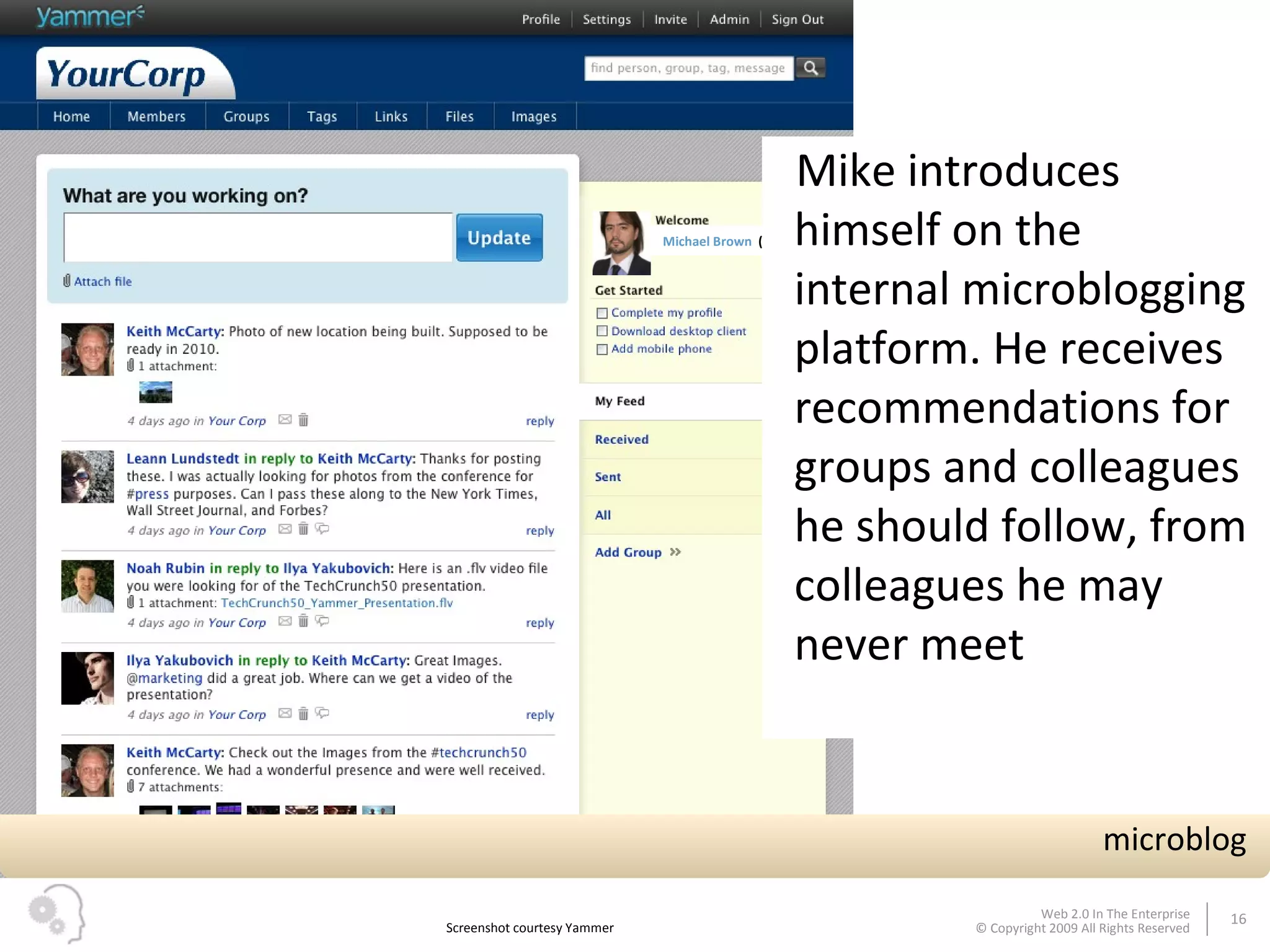
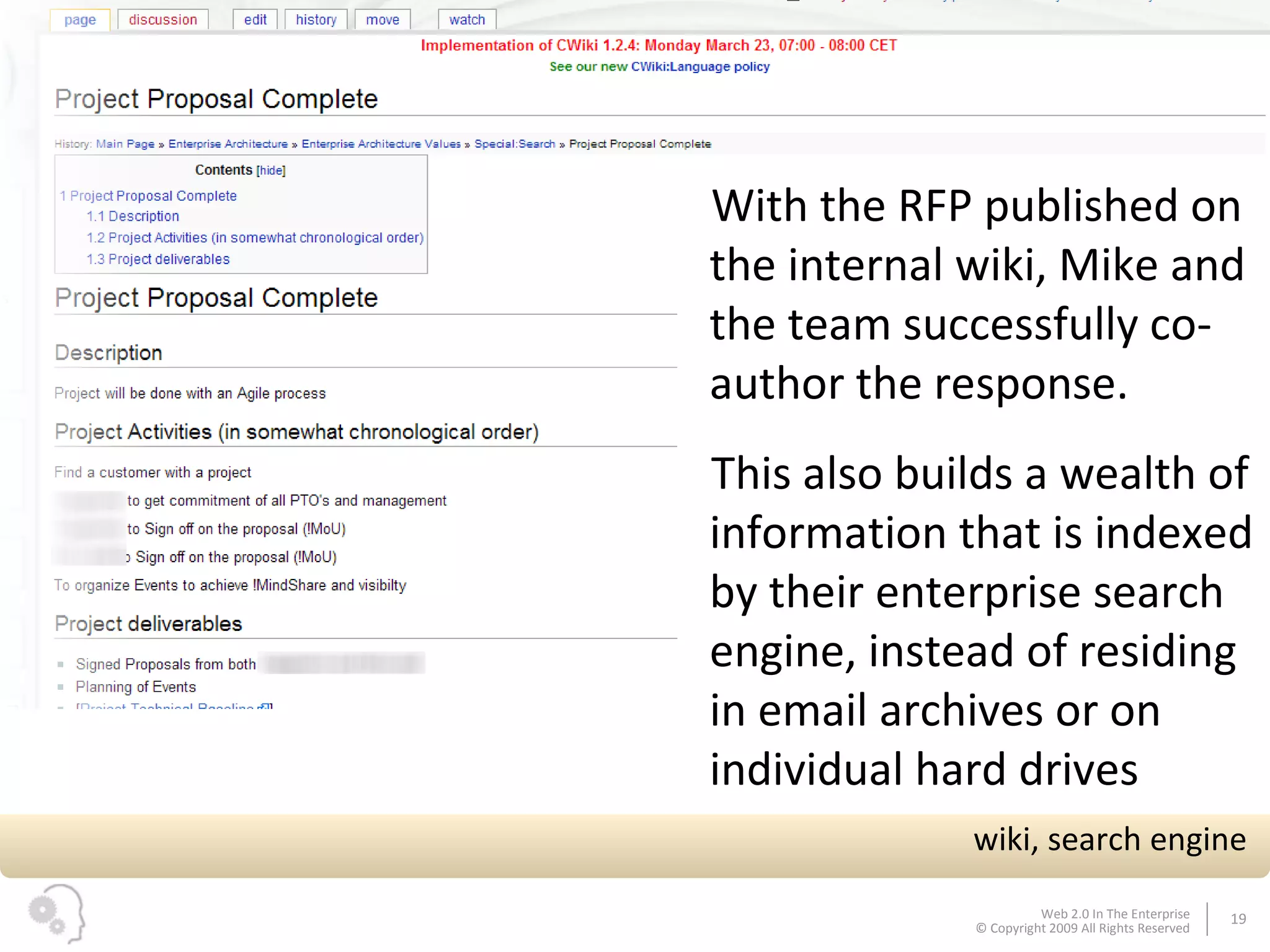
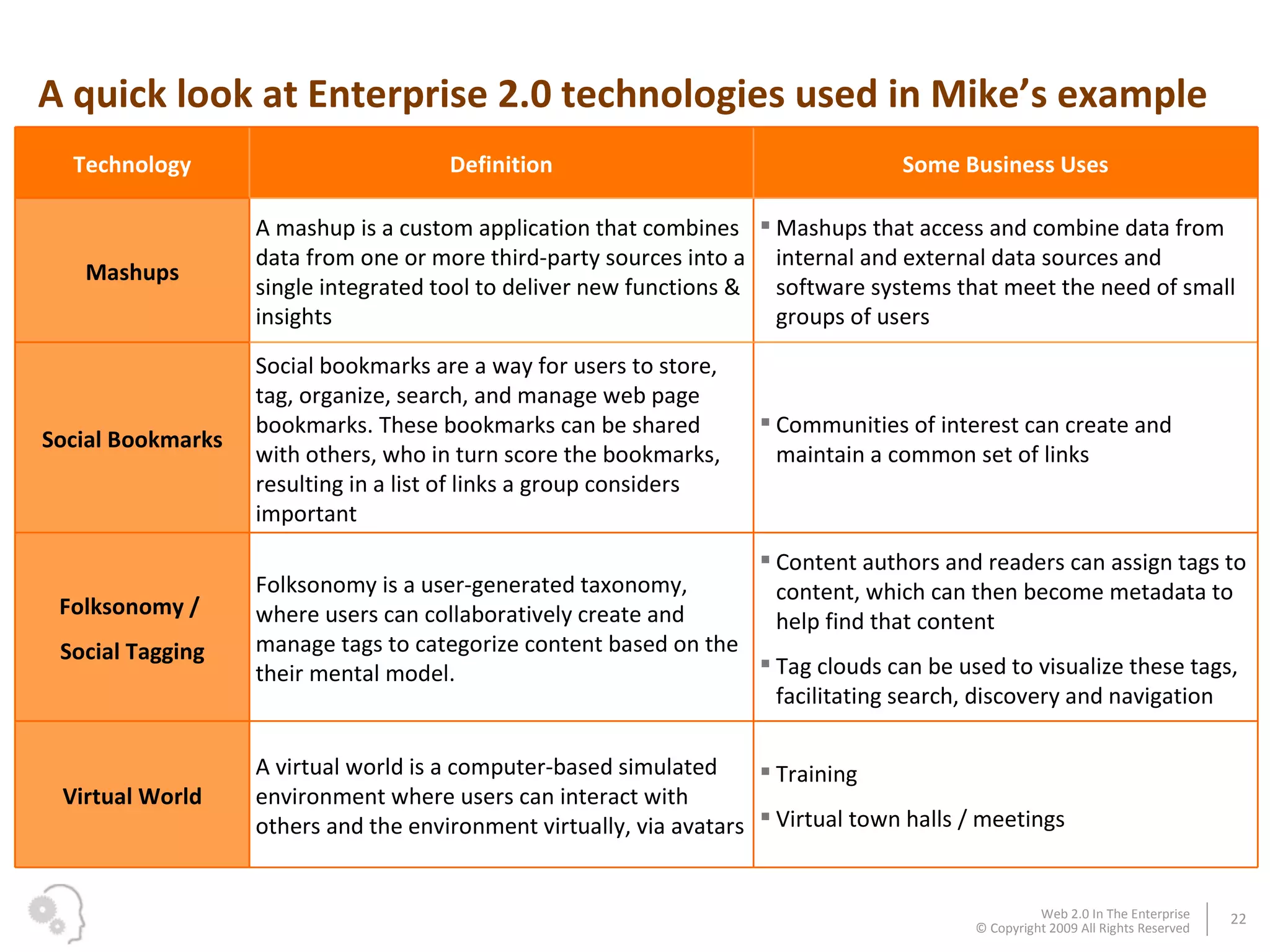
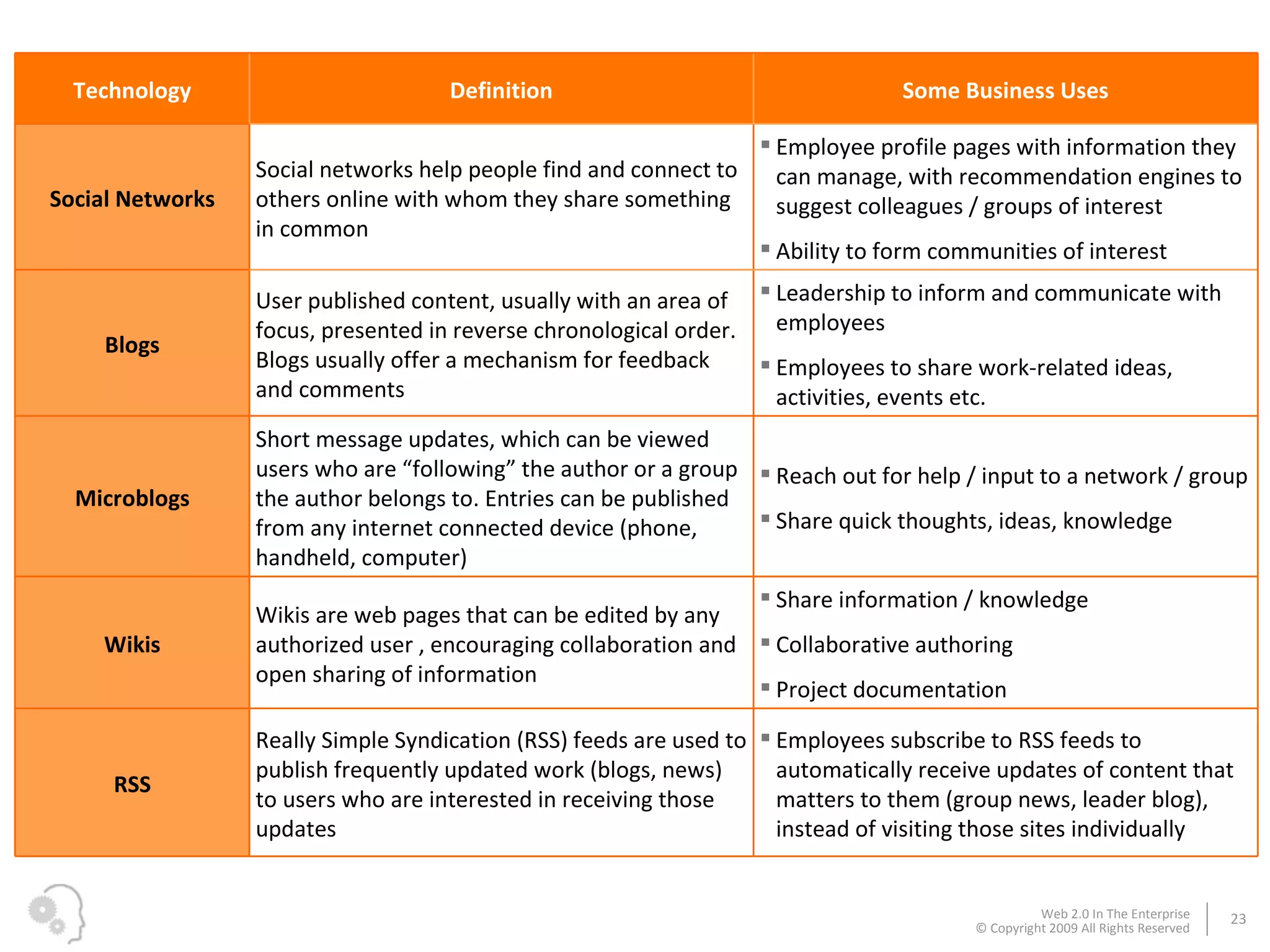
The document discusses how businesses utilize Web 2.0 technologies, referred to as Enterprise 2.0, to enhance customer engagement, internal operations, and supplier relationships. It outlines various tools and platforms, such as wikis, social networks, and mashups, that facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing among employees. A case study illustrates how these technologies assist an employee, Michael, in onboarding and collaborating effectively within his new organization.