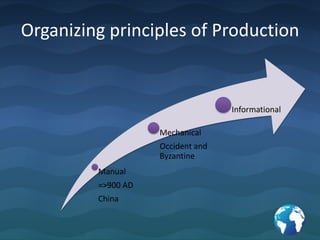
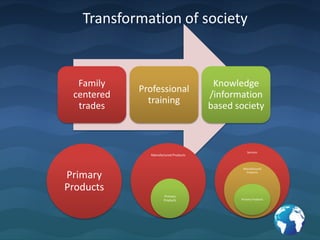
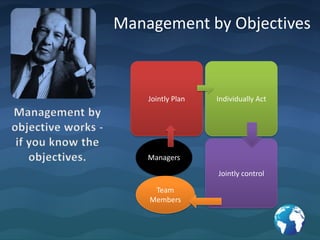
The document summarizes key insights from Peter Drucker's book "The Essential Drucker". It discusses Drucker's views on the purpose of business being to satisfy customer needs, the role of management being responsible for organizational performance, and the importance of marketing and understanding customers. It also provides lessons on effective decision making, treating an organization as a human community, management by objectives, and the differences between efficiency and effectiveness.