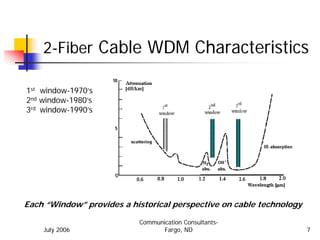
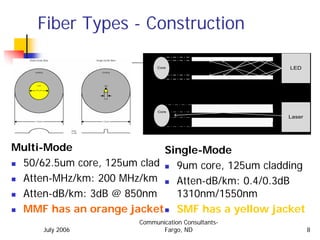
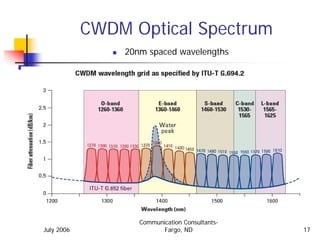
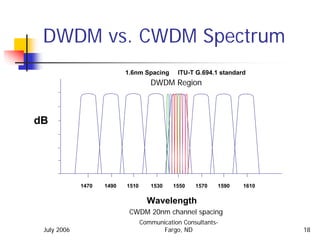
This document provides an overview of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technologies, specifically comparing coarse WDM (CWDM) and dense WDM (DWDM). It discusses the characteristics of fiber cables and dispersion effects. CWDM uses lower density 20nm channel spacing, while DWDM uses denser 1.6nm spacing. CWDM is better for shorter distances and lower costs, while DWDM enables maximum capacity and long distances using erbium-doped fiber amplifiers. The document examines applications of each technology and potential future developments in increasing capacities.