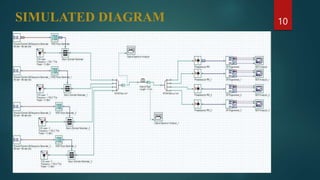
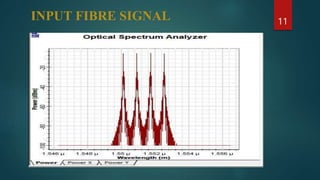
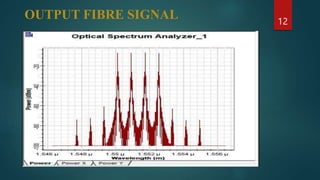
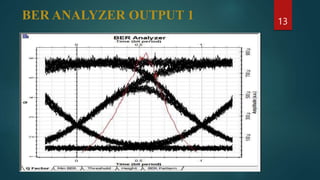
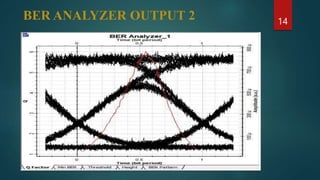
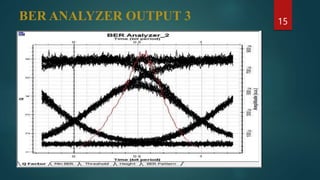
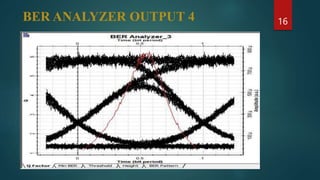
The document provides an overview of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology used in fiber optic communications, detailing its working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. It categorizes WDM into normal, coarse, and dense types, explaining their operational differences and suitability for various networking needs. Simulations and diagrams demonstrate the multiplexing process, and software tools used in analysis are also mentioned.
![DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
PONDICHERRY UNIVERSITY,KALAPET,
PUDUCHERRY-605014
SIMULATION
ON
“WDM SYSTEMS”
SUBMITTED BY
FAIZAN SHAFI [21304012]
ECENG-636 [FSON]
M.Tech (ECE) – II year
SUBMITTED TO
Dr. R. Nakkeeran
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR
Dept. Of Electronics Engineering](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fsonfilemodified-221020171522-7024b559/85/WDM-SYSTEMS-1-320.jpg)