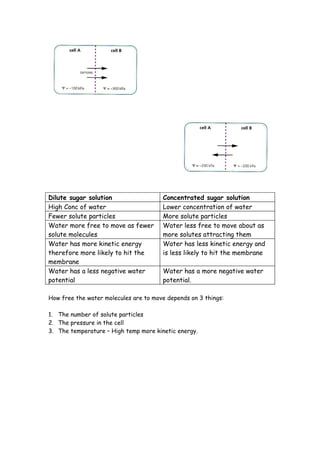
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to low water concentration until equilibrium is reached. Water potential is a measure of the kinetic energy of water molecules - pure water has a potential of 0 kPa while solutions have negative potentials as water molecules are less free to move. The concentration of solutes and number of solute particles restricts water movement by attracting and binding water molecules. Osmosis will occur if two solutions separated by a membrane have different water potentials.