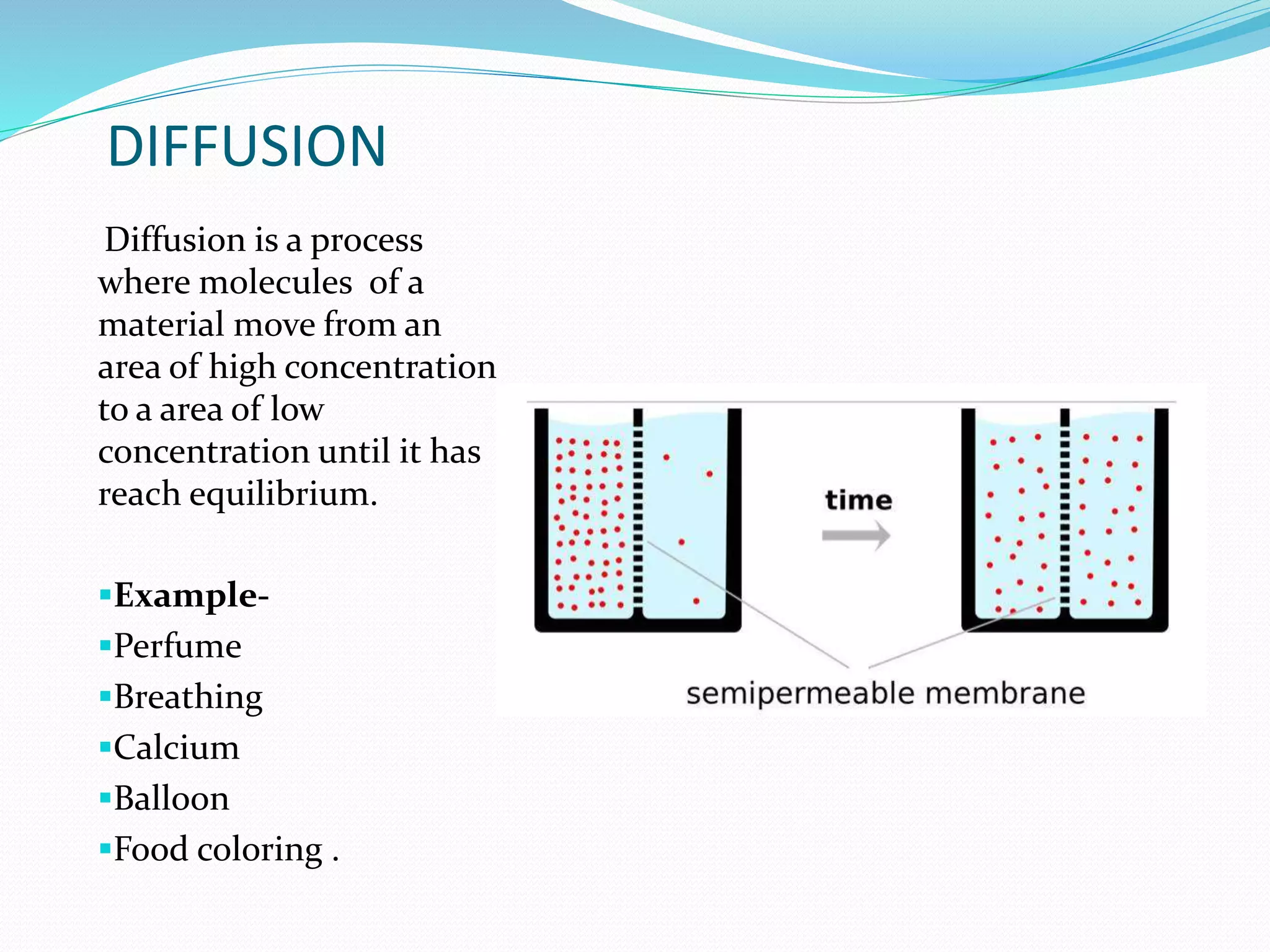
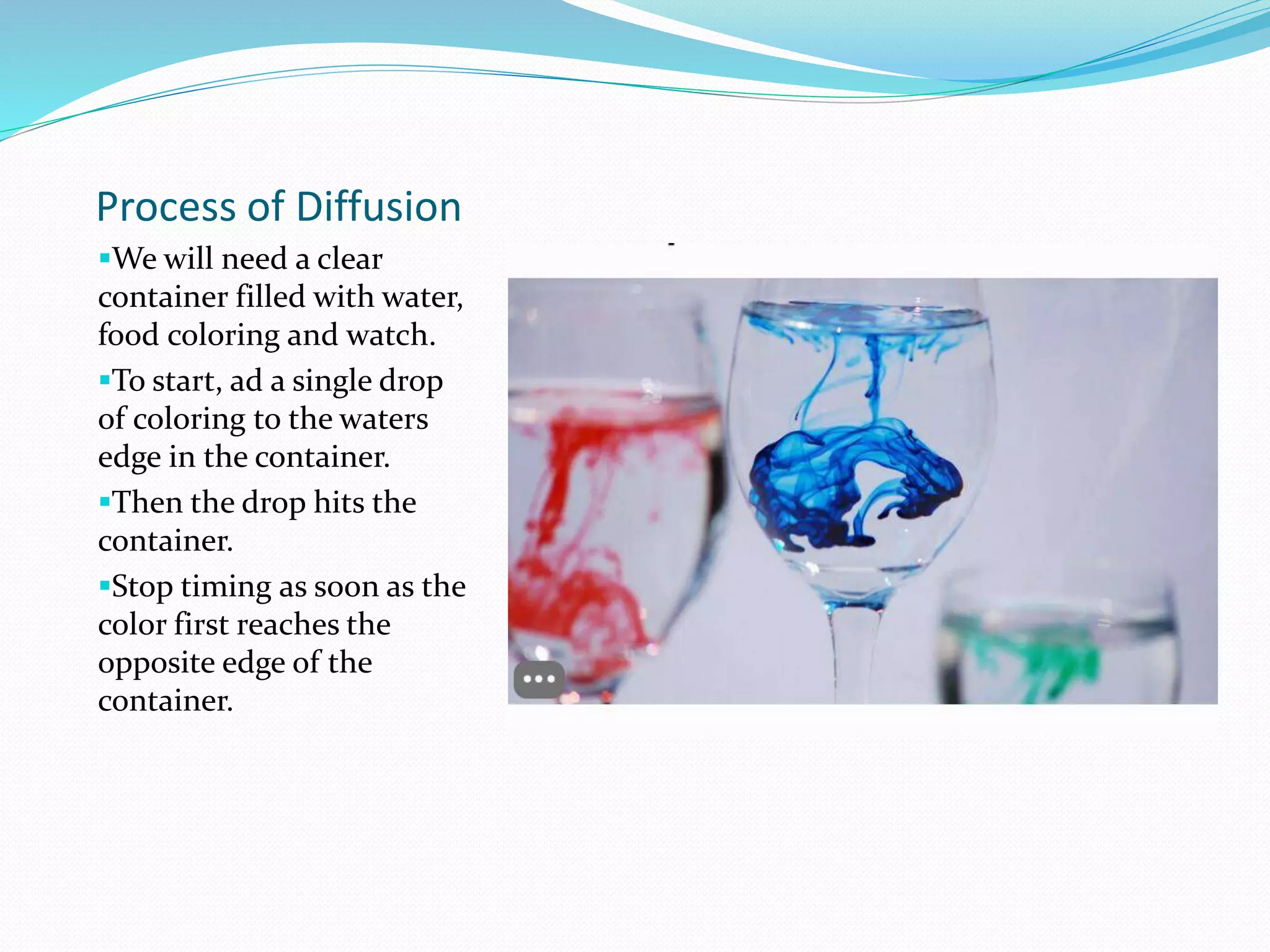
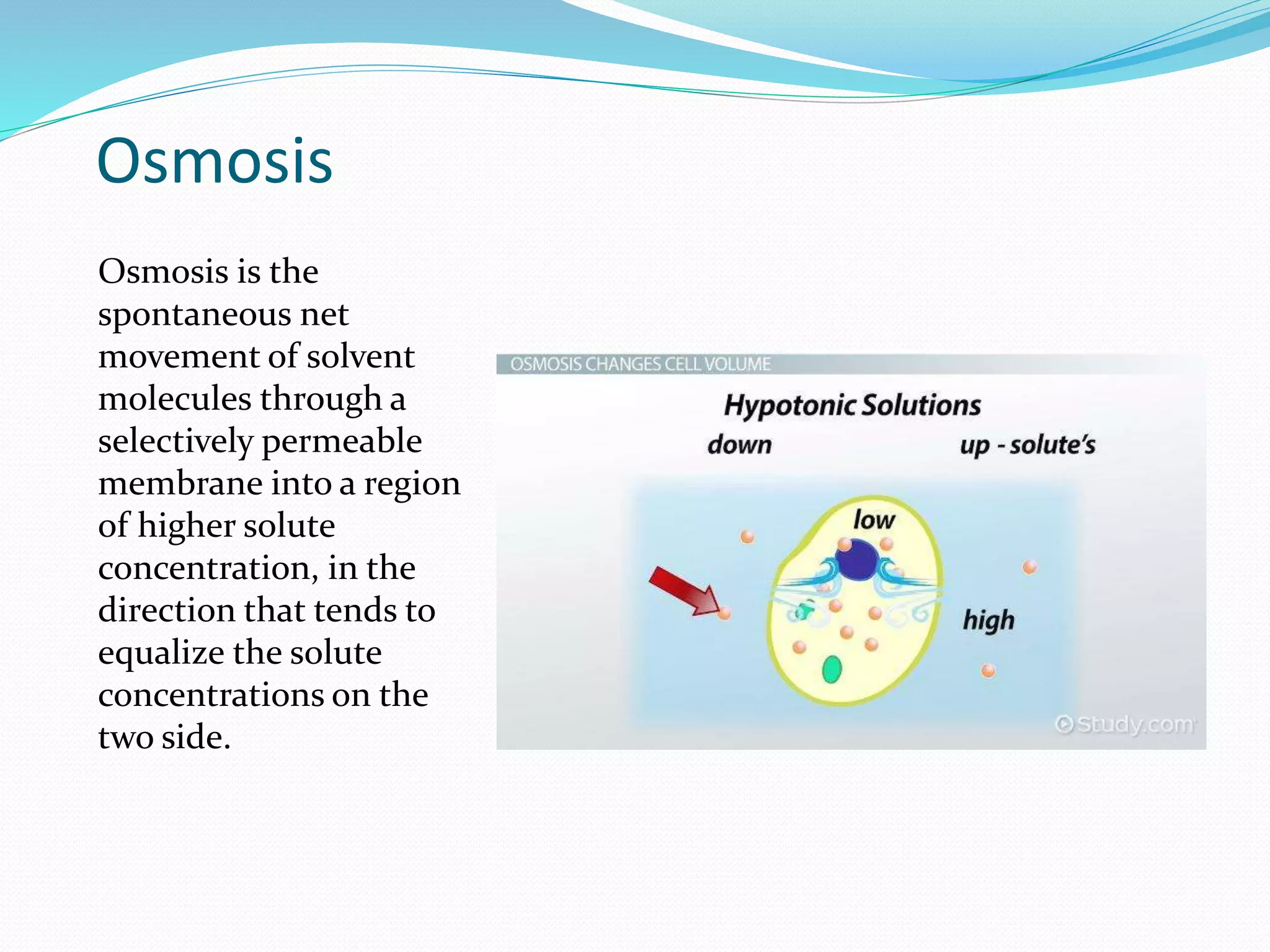
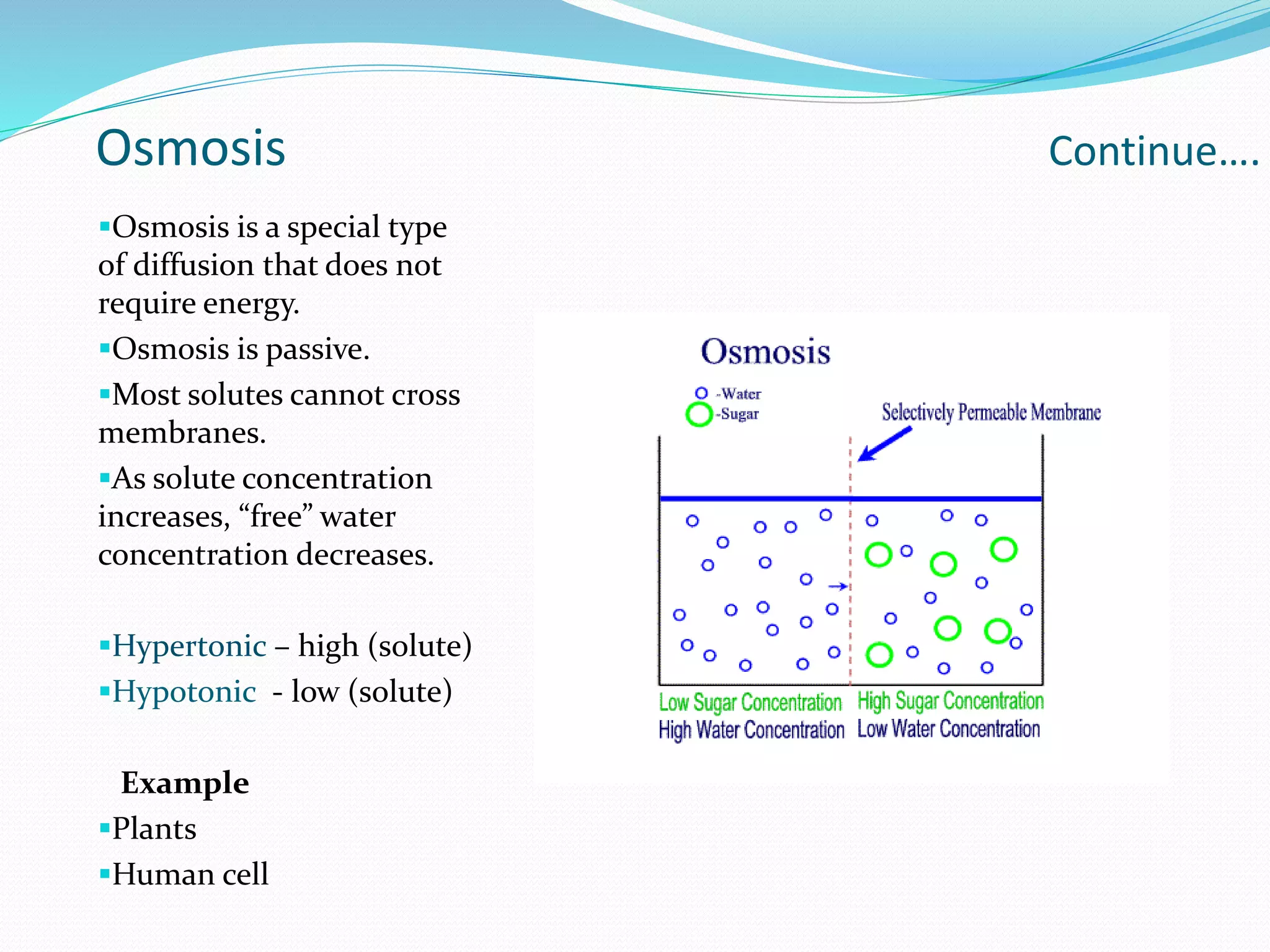
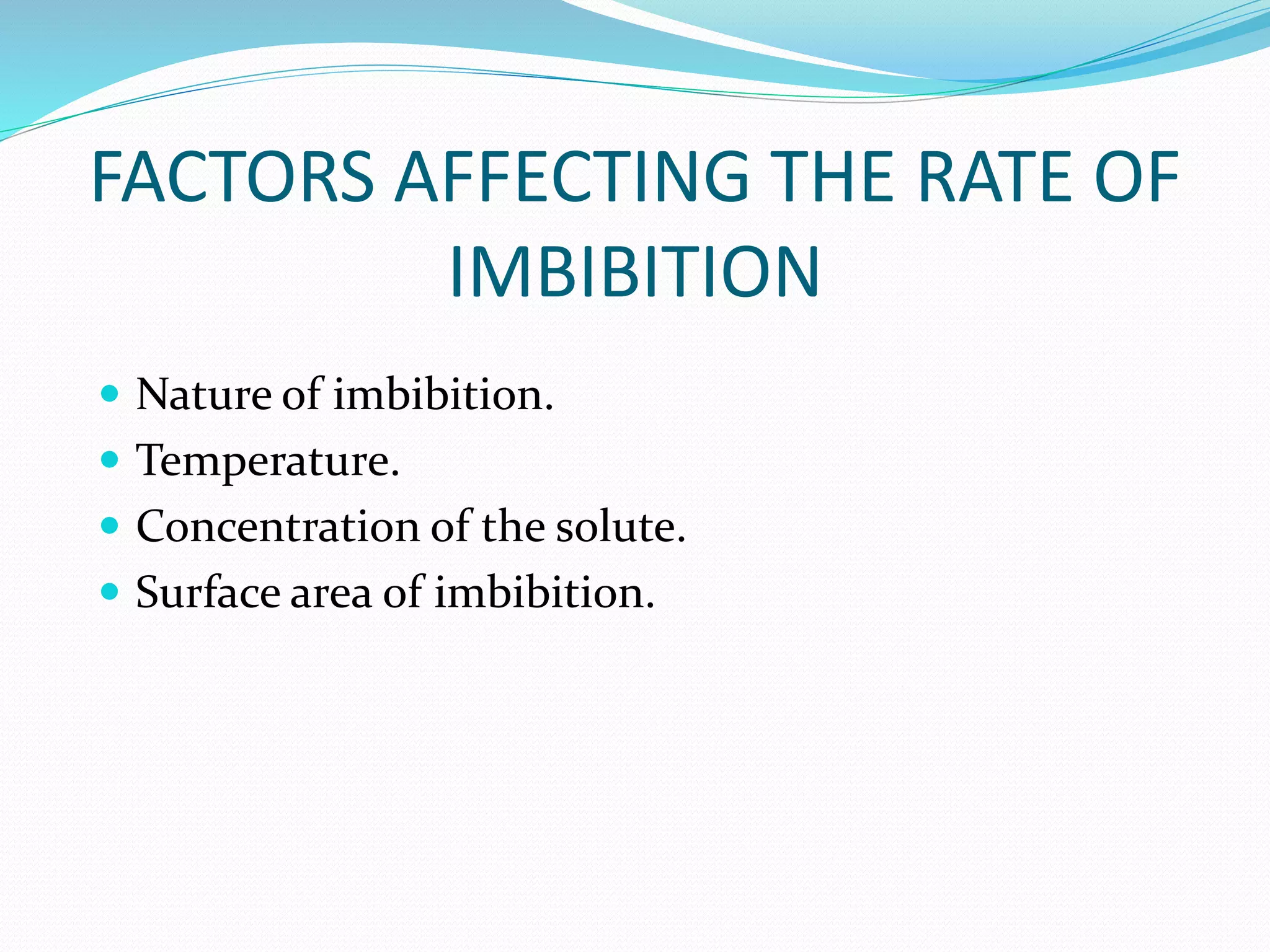
Diffusion, osmosis, and imbibition are processes of molecule movement. Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration. Osmosis is diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane, moving from higher to lower solute concentration. Imbibition is the absorption of water by hydrophilic colloids, such as when seeds swell as they take in water. These processes are important for various biological functions including plant water absorption and photosynthesis.