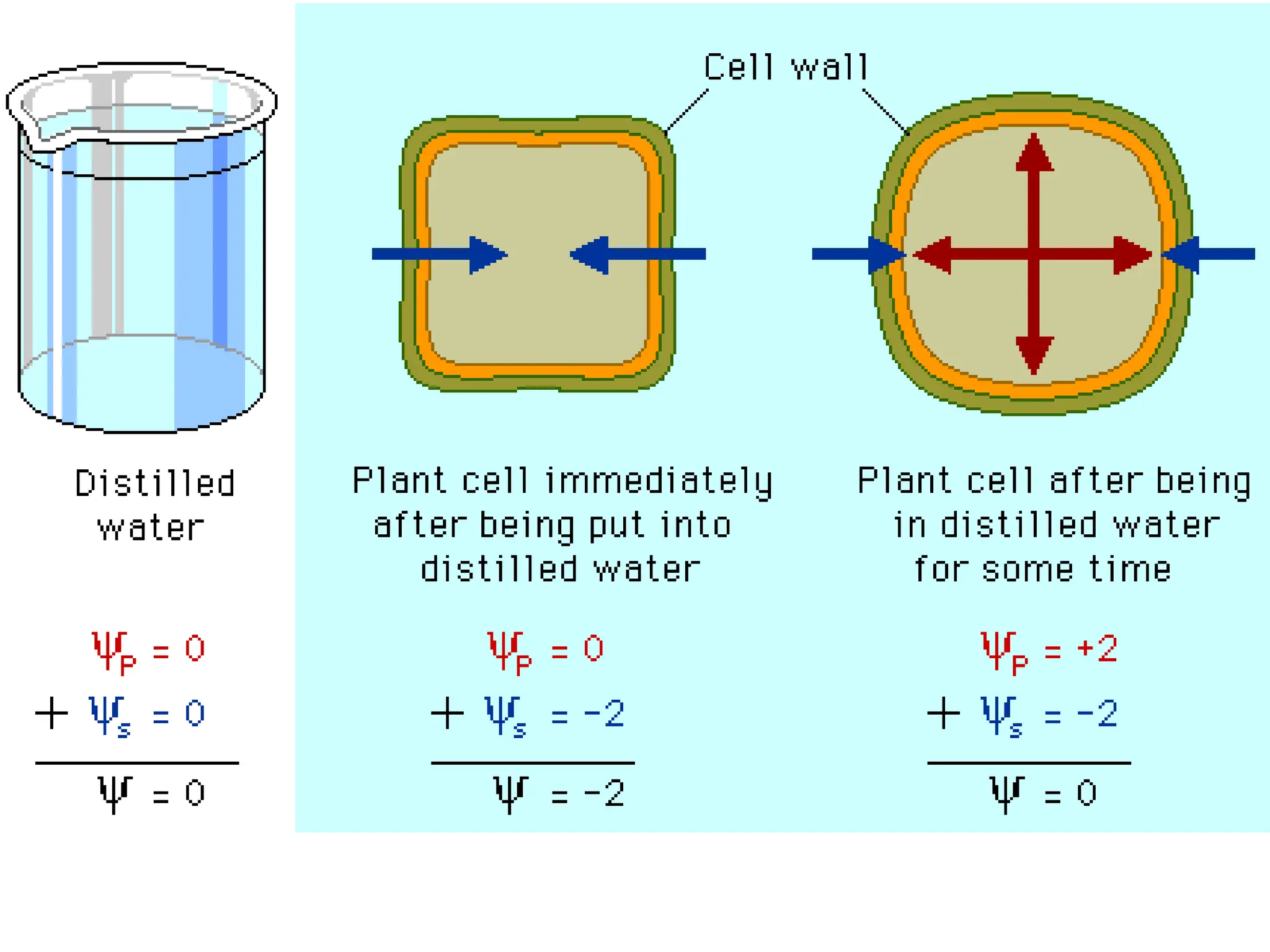
Water potential is a measure of the tendency of water to move from one area to another. It is determined by two factors: solute concentration and pressure. Pure water has a water potential of zero, while solutions have negative water potentials due to the lower concentration of water molecules. Water potential can be calculated from the sum of solute (osmotic) potential, due to solute concentration, and pressure potential, such as the pressure in plant cells from the rigid cell wall. Water will move from areas of high water potential to low water potential.