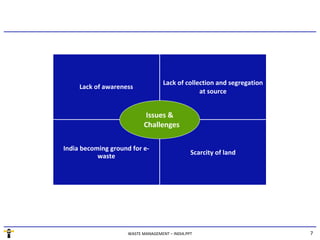
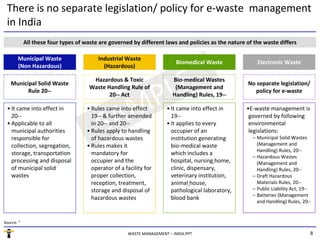
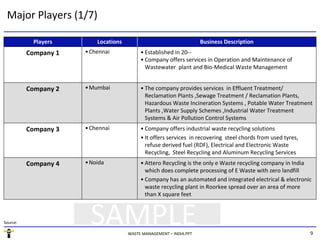
The document summarizes the waste management market in India. It discusses the key segments of the market - municipal waste, industrial waste, e-waste, and biomedical waste. It outlines some of the major issues facing waste management in India like lack of proper collection and segregation, scarcity of land, and lack of awareness. It also provides an overview of the regulatory framework for different types of waste and some of the major players in the industry.