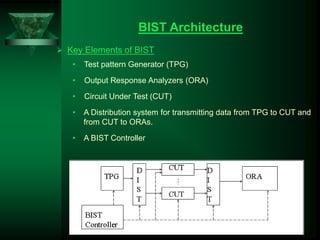
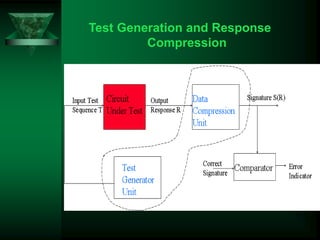
Built-in self-test (BIST) is a technique where circuits incorporate self-testing abilities. BIST architectures include a test pattern generator, output response analyzer, and circuit under test. BIST provides advantages like reduced testing costs and ability to test at operational speeds, but has disadvantages like increased silicon area. BIST is applied to systems like integrated circuits to allow for self-diagnosis and easier testing of components.